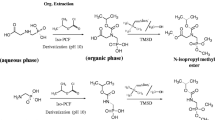
Abstract
Glyphosate [N-(phosphonomethyl) glycine] is a widely used herbicide and a molecule of interest in the environmental sciences, due to its global use in agriculture and its potential impact on ecosystems. This study presents the first position-specific carbon isotope (13C/12C) analyses of glyphosates from multiple sources. In contrast to traditional isotope ratio mass spectrometry (IRMS), position-specific analysis provides 13C/12C ratios at individual carbon atom positions within a molecule, rather than an average carbon isotope ratio across a mixture or a specific compound. In this work, glyphosate in commercial herbicides was analyzed with only minimal purification, using a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy method that detects 1H nuclei with bonds to either 13C or 12C, and isolates the signals of interest from other signals in the mixture. Results demonstrate that glyphosate from different sources can have significantly different intramolecular 13C/12C distributions, which were found to be spread over a wide range, with δ13C Vienna Peedee Belemnite (VPDB) values of −28.7 to −57.9‰. In each glyphosate, the carbon with a bond to the phosphorus atom was found to be depleted in 13C compared to the carbon at the C2 position, by 4 to 10‰. Aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) was analyzed for method validation; AMPA contains only a single carbon position, so the 13C/12C results provided by the NMR method could be directly compared with traditional isotope ratio mass spectrometry. The glyphosate mixtures were also analyzed by IRMS to obtain their average 13C/12C ratios, for comparison with our position-specific results. This comparison revealed that the IRMS results significantly disguise the intramolecular isotope distribution. Finally, we introduce a 31P NMR method that can provide a position-specific 13C/12C ratio for carbon positions with a C-P chemical bond, and the results obtained by 1H and 31P for C3 carbon agree with one another within their analytical uncertainty. These analytical tools for position-specific carbon isotope analysis permit the isotopic fingerprinting of target molecules within a mixture, with potential applications in a range of fields, including the environmental sciences and chemical forensics.
Graphical Abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
In addition, raw NMR data and R-scripts for processing the data are available at the Texas Data Repository at: https://doi.org/10.18738/T8/HLYCSP.
References
Slater GF. Stable isotope forensics - when isotopes work. Env Forensics. 2003;4:13–23.
Schmidt TC, Jochmann MA. Origin and fate of organic compounds in water: characterization by compound-specific stable isotope analysis. Annual Rev Anal Chem. 2012;5:133–55.
Braeckevelt M, Fischer A, Kästner M. Field applicability of compound-specific isotope analysis (CSIA) for characterization and quantification of in situ contaminant degradation in aquifers. Appl Microbiol Biotech. 2012;94:1401–21.
Cerling TE. The stable isotopic composition of modern soil carbonate and its relationship to climate. Earth Plan Sci Lett. 1984;71:229–40.
Schidlowski M. Carbon isotopes as biogeochemical recorders of life over 3.8 Ga of Earth history: evolution of a concept. Precam Res. 2001;106:117–34.
Penger J, Conrad R, Blaser M. Stable carbon isotope fractionation by methylotrophic methanogenic Archaea. Appl Envir Microbio. 2012;78:7596–602.
Gentile N, Siegwolf RT, Esseiva P, Doyle S, Zollinger K, Delemont O. Isotope ratio mass spectrometry as a tool for source inference in forensic science: a critical review. Forensic Sci Int. 2015;251:139–58.
Aguilera R, Chapman TE, Starcevic B, Hatton CK, Catlin DH. Performance characteristics of a carbon isotope ratio method for detecting doping with testosterone based on urine diols: controls and athletes with elevated testosterone/epitestosterone ratios. Clin Chem. 2001;47:292–300.
Lamprecht G, Pichlmayer F, Schmid ER. Determination of the authenticity of vanilla extracts by stable isotope ratio analysis and component analysis by HPLC. J Agricu Food Chem. 1994;42:1722–7.
Le PM, Martineau E, Akoka S, Remaud G, Chartrand MM, Meija J, Mester Z. Site-specific carbon isotope measurements of vanillin reference materials by nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022;414:7153–65.
Kennett DJ, Prufer KM, Culleton BJ, George RJ, Robinson M, Trask WR, Buckley GM, Moes E, Kate EJ, Harper TK, O’Donnell L. Early isotopic evidence for maize as a staple grain in the Americas. Sci Advances. 2020;6:eaba3245.
Matthews DE, Hayes JM. Isotope-ratio-monitoring gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 1978;50:1465–73.
Brenna JT. Natural intramolecular isotope measurements in physiology: elements of the case for an effort toward high-precision position-specific isotope analysis. Rapid Com Mass Spec. 2001;15:1252–62.
Sacks GL, Brenna JT. High-precision position-specific isotope analysis of 13C/12C in leucine and methionine analogues. Anal Chem. 2003;75:5495–503.
Savidge WB, Blair NE. Seasonal and within-plant gradients in the intramolecular carbon isotopic composition of amino acids of Spartina alterniflora. J Exp Marine Biol Ecol. 2004;308:151–67.
Dunn PJ, Honch NV, Evershed RP. Comparison of liquid chromatography - isotope ratio mass spectrometry (LC/IRMS) and gas chromatography–combustion–isotope ratio mass spectrometry (GC/C/IRMS) for the determination of collagen amino acid δ13C values for palaeodietary and palaeoecological reconstruction. Rapid Com Mass Spec. 2011;25:2995–3011.
Tea I, Tcherkez G. Natural isotope abundance in metabolites: techniques and kinetic isotope effect measurement in plant, animal, and human tissues. In Meth Enzym. 2017;596:113–47.
Gauchotte-Lindsay C, Turnbull SM. On-line high-precision carbon position-specific stable isotope analysis: a review. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2016;76:115–25.
Neubauer C, Sweredoski MJ, Moradian A, Newman DK, Robins RJ, Eiler JM. Scanning the isotopic structure of molecules by tandem mass spectrometry. Int J Mass Spec. 2018;434:276–86.
Wilkes EB, Sessions AL, Zeichner SS, Dallas B, Schubert B, Jahren AH, Eiler JM. Position-specific carbon isotope analysis of serine by gas chromatography/Orbitrap mass spectrometry, and an application to plant metabolism. Rapid Com Mass Spec. 2022;36: e9347.
Chimiak L, Elsila JE, Dallas B, Dworkin JP, Aponte JC, Sessions AL, Eiler JM. Carbon isotope evidence for the substrates and mechanisms of prebiotic synthesis in the early solar system. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 2021;292:188–202.
Fry B, Carter JF, Yamada K, Yoshida N. Position specific 13C/12C analysis of amino acid carboxyl groups - automated flow injection analysis based on reaction with ninhydrin. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2018;32:992–1000.
Gilbert A, Silvestre V, Robins RJ, Remaud GS. Accurate quantitative isotopic 13C NMR spectroscopy for the determination of the intramolecular distribution of 13C in glucose at natural abundance. Anal Chem. 2009;81:8978–85.
Romek KM, Krzemińska A, Remaud GS, Julien M, Paneth P, Robins RJ. Insights into the role of methionine synthase in the universal 13C depletion in O-and N-methyl groups of natural products. Arch Biochem Biophy. 2017;635:60–5.
Fox AC, Martineau E, Remaud GS, Freeman KH. Position-specific isotope fractionation in amino acids sorbed to ice: Implications for the preservation of isotopologue biosignatures. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 2021;309:45–56.
Rasmussen C, Hoffman DW. Intramolecular distribution of 13C/12C isotopes in amino acids of diverse origins. Amino Acids. 2020;52:955–64.
Rasmussen C, Hoffman DW. Novel nuclear magnetic resonance method for position-specific carbon isotope analysis of organic molecules with significant impurities. Anal Chem. 2022;94:15124–31.
Hoffman DW, Rasmussen C. Position-specific carbon stable isotope ratios by proton NMR spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 2019;91:15661–9.
Hoffman DW, Rasmussen C. Absolute carbon stable isotope ratio in the Vienna Peedee Belemnite isotope reference determined by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 2022;94:5240–7.
Kujawinski DM, Wolbert JB, Zhang L, Jochmann MA, Widory D, Baran N, Schmidt TC. Carbon isotope ratio measurements of glyphosate and AMPA by liquid chromatography coupled to isotope ratio mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013;405:2869–78.
Mogusu EO, Wolbert JB, Kujawinski DM, Jochmann MA, Elsner M. Dual element (15N/14N, 13C/12C) isotope analysis of glyphosate and AMPA by derivatization-gas chromatography isotope ratio mass spectrometry (GC/IRMS) combined with LC/IRMS. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015;407:5249–60.
Shaka AJ, Keeler J, Frenkiel T, Freeman RAY. An improved sequence for broadband decoupling: WALTZ-16. J Magn Reason. 1983;52:335–8.
Willcott MR. MestReNova. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:13180–13180.
Tiainen M, Maaheimo H, Soininen P, Laatikainen R. 13C isotope effects on 1H chemical shifts: NMR spectral analysis of 13C-labelled d-glucose and some 13C-labelled amino acids. Magn Reson Chem. 2010;48:117–22.
Malinovsky D, Dunn PJH, Holcombe G, Cowen S, Goenaga-Infante H. Development and characterisation of new glycine certified reference materials for SI-traceable 13C/12C isotope amount ratio measurements. J Anal At Spectrom. 2019;34:147–59.
Revesz K, Qi H, Coplan TB. Determination of the δ15N and δ13C of total nitrogen and carbon in solids. In: Stable-Isotope Ratio Methods, Methods of the Reston Stable Isotope Laboratory: US Geological Survey, Revesz and Coplen eds., book 10, chap. 5. 2006.
Coplen TB, Brand WA, Gehre M, Gröning M, Meijer HAJ, Toman B, Verkouteren RM. New guidelines for delta 13C measurements: Anal. Chem. 2006;78:2439–41.
Abelson PH, Hoering T. Carbon isotope fractionation in formation of amino acids by photosynthetic organisms. Proceed Nat Ac Sci. 1961;47:623–32.
Holtvoeth J, Whiteside JH, Engels S, Freitas FS, Grice K, Greenwood P, Johnson S, Kendall I, Lengger SK, Lücke A, Mayr C. The paleolimnologist’s guide to compound-specific stable isotope analysis - an introduction to principles and applications of CSIA for Quaternary lake sediments. Quat Sci Rev. 2019;207:101–33.
Yushchenkoa DY, Khlebnikovaa TB, Paia ZP, Bukhtiyarov VI. Glyphosate: methods of synthesis. Kin Catal. 2021;62:331–41.
Bernard BB, Brooks JM, Sackett WM. Natural gas seepage in the Gulf of Mexico. Earth Plan Sci Lett. 1976;31:48–54.
Yang S, Lan X, Talbot R, Liu L. Characterizing anthropogenic methane sources in the Houston and Barnett Shale areas of Texas using the isotopic signature δ13C in CH4. Sci Total Env. 2019;2019(696):133856.
Schwietzke S, Sherwood OA, Bruhwiler LM, Miller JB, Etiope G, Dlugokencky EJ, Michel SE, Arling VA, Vaughn BH, White JW, Tans PP. Upward revision of global fossil fuel methane emissions based on isotope database. Nature. 2016;538:88–91.
Ogbesejana AB, Liu B, Ostadhassan M. Stable isotope geochemistry of the organic elements within shales and crude oils: a comprehensive review. Molecules. 2021;27:34.
Milkov AV, Schwietzke S, Allen G, Sherwood OA, Etiope G. Using global isotopic data to constrain the role of shale gas production in recent increases in atmospheric methane. Sci Rep. 2020;10:4199.
Limon AW, Moingt M, Widory D. The carbon stable isotope compositions of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA): improved analytical sensitivity and first application to environmental water matrices. Rapid Com Mass Spec. 2021;35:e9017.
Kudzin MH, Żyłła R, Mrozińska Z, Urbaniak P. 31P NMR investigations on roundup degradation by AOP procedures. Water. 2019;11:331–47.
Cartigny B, Azaroual N, Imbenotte M, Mathieu D, Vermeersch G, Goullé JP, Lhermitte M. Determination of glyphosate in biological fluids by 1H and 31P NMR spectroscopy. Forensic Sci Int. 2004;143:141–5.
Funding
This research was supported by a Department of Energy Basic Energy Sciences research grant DE-SC0022524.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.H. and C.R. performed experiments, developed protocols, acquired and analyzed NMR spectra, and contributed to manuscript preparation. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hoffman, D.W., Rasmussen, C. Position-specific carbon stable isotope analysis of glyphosate: isotope fingerprinting of molecules within a mixture. Anal Bioanal Chem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05326-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05326-5