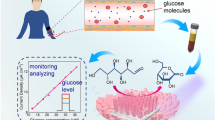
Abstract
Nanozymes are nanomaterials with mimetic enzyme properties and the related research has attracted much attention. It is of great value to develop methods to construct nanozymes and to study their application in bioanalysis. Herein, the metal–ligand cross-linking strategy was developed to fabricate superstructure nanozymes. This strategy takes advantage of being easy to operate, adjustable, cheap, and universal. The fabricated superstructure nanozymes possess efficient peroxidase-like catalytic activity. The enzyme reaction kinetic tests demonstrated that for TMB and H2O2, the Km is 0.229 and 1.308 mM, respectively. Furthermore, these superstructure nanozymes are applied to highly efficient and sensitive detection of glucose. The linear range for detecting glucose is 20–2000 μM, and the limit of detection is 17.5 μM. Furthermore, mechanistic research illustrated that this integrated system oxidizes glucose to produce hydrogen peroxide and further catalyzes the production of ·OH and O2·–, which results in a chromogenic reaction of oxidized TMB for the detection of glucose. This work could not only contribute to the development of efficient nanozymes but also inspire research in the highly sensitive detection of other biomarkers.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liang M, Yan X. Nanozymes: from new concepts, mechanisms, and standards to applications. Acc Chem Res. 2019;52(8):2190–200.
Zhang X, Yang C, An P, Cui C, Ma Y, Liu H, et al. Creating enzyme-mimicking nanopockets in metal-organic frameworks for catalysis. Sci Adv. 2022;8(40):eadd5678.
Gao L, Zhuang J, Nie L, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Gu N, et al. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007;2(9):577–83.
He M-Q, Ai Y, Hu W, Guan L, Ding M, Liang Q. Recent advances of seed-mediated growth of metal nanoparticles: from growth to applications. Adv Mater. 2023;35(46):2211915.
Ai Y, He M-Q, Sun H, Jia X, Wu L, Zhang X, et al. Ultra-small high-entropy alloy nanoparticles: efficient nanozyme for enhancing tumor photothermal therapy. Adv Mater. 2023;35(23):2302335.
Ai Y, Hu Z-N, Liang X, Sun H, Xin H, Liang Q. Recent advances in nanozymes: from matters to bioapplications. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;32(14):2110432.
Abdelhamid HN, Mahmoud GA-E, Sharmouk W. A cerium-based MOFzyme with multi-enzyme-like activity for the disruption and inhibition of fungal recolonization. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(33):7548–56.
Abdelhamid HN, Sharmoukh W. Intrinsic catalase-mimicking MOFzyme for sensitive detection of hydrogen peroxide and ferric ions. Microchem J. 2021;163:105873.
Najmi P, Keshmiri N, Ramezanzadeh M, Ramezanzadeh B, Arjmand M. Design of nacre-inspired 2D-MoS2 nanosheets assembled with mesoporous covalent organic frameworks (COFs) for smart coatings. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(48):54141–56.
Ai Y, Sun H, Gao Z, Wang C, Guan L, Wang Y, et al. Dual enzyme mimics based on metal–ligand cross-linking strategy for accelerating ascorbate oxidation and enhancing tumor therapy. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31(40):2103581.
Jin G, Wang C, Ran G, Hao S, Song Q. Protein-stabilized Ir nanoparticles with usual charge-selective peroxidase properties. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(40):8464–71.
Ai Y, You J, Gao J, Wang J, Sun H, Ding M, et al. Multi-shell nanocomposites based multienzyme mimetics for efficient intracellular antioxidation. Nano Res. 2021;14(8):2644–53.
Zeng Y, Li Y, Tan X, Gong J, Wang Z, An Y, et al. B, N-doped PdRu aerogels as high-performance peroxidase mimics for sensitive detection of glucose. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(31):36816–23.
An M, He M-Q, Lin C, Wu Y, Ai Y, Xin H, et al. Recent progress of nanozymes with different spatial dimensions for bioanalysis. Mater Today Nano. 2023;22:100330.
Liu M, Zhu Y, Jin D, Li L, Cheng J, Liu Y. Hemin-caged ferritin acting as a peroxidase-like nanozyme for the selective detection of tumor cells. Inorg Chem. 2021;60(19):14515–9.
Teng L, Han X, Liu Y, Lu C, Yin B, Huan S, et al. Smart nanozyme platform with activity-correlated ratiometric molecular imaging for predicting therapeutic effects. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2021;60(50):26142–50.
Zhao C, Chen J, Ye J, Li Z, Su L, Wang J, et al. Structural transformative antioxidants for dual-responsive anti-inflammatory delivery and photoacoustic inflammation imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2021;60(26):14458–66.
Li F, Sun H, Ren J, Zhang B, Hu X, Fang C, et al. A nuclease-mimetic platinum nanozyme induces concurrent DNA platination and oxidative cleavage to overcome cancer drug resistance. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):7361.
Zhang J, Zhao B, Chen S, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, et al. Near-infrared light irradiation induced mild hyperthermia enhances glutathione depletion and DNA interstrand cross-link formation for efficient chemotherapy. ACS Nano. 2020;14(11):14831–45.
Sun H, Ai Y, Qi H, Guan L, Hu W, Huang H, et al. Pt/Ag-PEG-Ce6 nanosystem with enhanced near-infrared absorption and peroxidase-like activity for synergistic photodynamic/photothermal therapy. Adv Ther. 2022;5(11):2200089.
Ai Y, He M-Q, Wan C, Luo H, Xin H, Wang Y, et al. Nanoplatform-based reactive oxygen species scavengers for therapy of ischemia-reperfusion injury. Adv Ther. 2022;5(11):2200066.
Fu R, Ma Z, Zhao H, Jin H, Tang Y, He T, et al. Research progress in iron-based nanozymes: catalytic mechanisms, classification, and biomedical applications. Anal Chem. 2023;95(29):10844–58.
Li Y, Wang L, Liu H, Pan Y, Li C, Xie Z, et al. Ionic covalent-organic framework nanozyme as effective cascade catalyst against bacterial wound infection. Small. 2021;17(32):e2100756.
Li S, Shang L, Xu B, Wang S, Gu K, Wu Q, et al. A nanozyme with photo-enhanced dual enzyme-like activities for deep pancreatic cancer therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2019;58(36):12624–31.
Xu J, Wang J, Ye J, Jiao J, Liu Z, Zhao C, et al. Metal-coordinated supramolecular self-assemblies for cancer theranostics. Adv Sci. 2021;8(16):e2101101.
Song E, Li Y, Chen L, Lan X, Hou C, Liu C, et al. An amino acid-based supramolecular nanozyme by coordination self-assembly for cascade catalysis and enhanced chemodynamic therapy towards biomedical applications. Nanoscale Adv. 2021;3(22):6482–9.
Liu Q, Tian J, Liu J, Zhu M, Gao Z, Hu X, et al. Modular assembly of tumor-penetrating and oligomeric nanozyme based on intrinsically self-assembling protein nanocages. Adv Mater. 2021;33(39):e2103128.
Zhao L, Liu Y, Chang R, Xing R, Yan X. Supramolecular photothermal nanomaterials as an emerging paradigm toward precision cancer therapy. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29(4):1806877.
Zhang J, Zheng Y, Lee J, Hoover A, King SA, Chen L, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring enabled by fluorescent nanodiamond boronic hydrogel. Adv Sci. 2023;10(7):2203943.
Liu K, Liu R, Wang D, Pan R, Chen H-Y, Jiang D. Real-time and spatial electroanalysis of biomolecules in one living cell using liquid-phase modified nanopipette. CCS Chem. 2023;5(6):1285–92.
Adeel M, Asif K, Rahman MM, Daniele S, Canzonieri V, Rizzolio F. Glucose detection devices and methods based on metal–organic frameworks and related materials. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31(52):2106023.
Nguyen PT, Lee J, Cho A, Kim MS, Choi D, Han JW, et al. Rational development of co-doped mesoporous ceria with high peroxidase-mimicking activity at neutral pH for paper-based colorimetric detection of multiple biomarkers. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;32(21):2112428.
Nguyen QH, Lee DH, Nguyen PT, Le PG, Kim MI. Foldable paper microfluidic device based on single iron site-containing hydrogel nanozyme for efficient glucose biosensing. Chem Eng J. 2023;454:140541.
Ahn HT, An H-R, Hong YC, Lee SC, Le TN, Le XA, et al. Ultrarapid, size-controlled, high-crystalline plasma-mediated synthesis of ceria nanoparticles for reagent-free colorimetric glucose test strips. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2020;320:128404.
Ai Y, Sun H, Wang C, Zheng W, Han Q, Liang Q. Tunable assembly of organic-inorganic molecules into hierarchical superstructures as ligase mimics for enhancing tumor photothermal therapy. Small. 2022;18(10):e2105304.
Ai Y, Sun H, Gao Z, Wang C, Guan L, Wang Y, et al. Dual enzyme mimics based on metal–ligand cross-linking strategy for accelerating ascorbate oxidation and enhancing tumor therapy. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31(40):2103581.
Duan Y, Liu X, Han L, Asahina S, Xu D, Cao Y, et al. Optically active chiral CuO “nanoflowers.” J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136(20):7193–6.
Jiang W, Qu Z, Kumar P, Vecchio D, Wang Y, Ma Y, et al. Emergence of complexity in hierarchically organized chiral particles. Science. 2020;368(6491):642–8.
Tang L, Vo T, Fan X, Vecchio D, Ma T, Lu J, et al. Self-assembly mechanism of complex corrugated particles. J Am Chem Soc. 2021;143(47):19655–67.
Liu M, Chen G, Qin Y, Li J, Hu L, Gu W, et al. Proton-regulated catalytic activity of nanozymes for dual-modal bioassay of urease activity. Anal Chem. 2021;93(28):9897–903.
Zhao J, Bao X, Meng T, Wang S, Lu S, Liu G, et al. Fe(II)-driven self-assembly of enzyme-like coordination polymer nanoparticles for cascade catalysis and wound disinfection applications. Chem Eng J. 2021;420(1):129674.
Gilbertson LM, Albalghiti EM, Fishman ZS, Perreault F, Corredor C, Posner JD, et al. Shape-dependent surface reactivity and antimicrobial activity of nano-cupric oxide. Environ Sci Technol. 2016;50(7):3975–84.
Chang S, Liu C, Sun Y, Yan Z, Zhang X, Hu X, et al. Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated with Ag-nanoparticle-embedded metal–organic framework MIL-100(Fe) for the catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2020;3(3):2302–9.
Ye N, Huang S, Yang H, Wu T, Tong L, Zhu F, et al. Hydrogen-bonded biohybrid framework-derived highly specific nanozymes for biomarker sensing. Anal Chem. 2021;93(41):13981–9.
Wang J, Zhang J, Hu Y, Jiang H, Li C. Activating multisite high-entropy alloy nanocrystals via enriching M-pyridinic N-C bonds for superior electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Sci Bull. 2022;67(18):1890–7.
Chavalala R, Mashazi P. Pd nanocatalysts adsorbed onto silica nanoparticle coated indium tin oxide: a reusable nanozyme for glucose detection. J Mater Chem B. 2023;11(33):7961–71.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82304442, 22304099, 82270302), National Key R&D Program of China (2023YFC3504401, 2022YFA1103403), Postdoctoral Innovative Talent Support Program (BX20220160), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project (2023T160372, 2022M711779), and Young Elite Scientist Sponsorship Program of the Beijing Association for Science and Technology (BYESS2023166).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mengying An, Meng-Qi He, Yongjian Ai, and Hongbo Xin designed the experiments and wrote the manuscript with inputs from all authors. Mengying An, Meng-Qi He, Caishi Lin, Keyu Deng, and Yongjian Ai carried out the material synthesis, characterization, and catalytic performance and analysed the data. Hongbo Xin provided technical guidance and financial support.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Published in the topical collection featuring Nanozymes with guest editors Vipul Bansal, Sudipta Seal, and Hui Wei.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
An, M., He, MQ., Lin, C. et al. Metal–ligand cross-link strategy engineered iron-doped dopamine-based superstructure as peroxidase-like nanozymes for detection of glucose. Anal Bioanal Chem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05317-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05317-6