Abstract
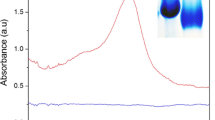
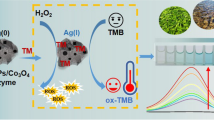
Nanozyme technology has gained significant regard and been successfully implemented in various applications including chemical sensing, bio-medicine, and environmental monitoring. Fe-CDs were synthesized and characterized well in this study. As compared to HRP (3.7 mM), the Fe-CDs exhibited a higher affinity towards H2O2 (0.2 mM) using the steady-state kinetic assay and stronger catalytic capability by changing the color of TMB to the blue color of the oxidized state, oxTMB. Additionally, an efficient peroxidase mimic, Fe-CDs/GOx, based on the hybrid cascade system to produce in situ H2O2 for the visual detection of glucose (color change: colorless to blue, and then to green), has been developed in detail, with limits of detection (LODs) for H2O2 and glucose of 0.33 μM and 1.17 μM, respectively. The changes further demonstrate a linear relationship between absorbance and H2O2 concentration, ranging from 10 to 60 μM, and for glucose (1 to 60 μM). To assess the accuracy and detection capability of the Fe-CDs/GOx system, we evaluated a real human serum sample obtained from adult males in a local hospital. In conclusion, Fe-CDs serving as a peroxidase mimic have the potential for various applications in the fields of biomedicine and nanozymes.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao LZ, Zhuang J, Nie L, Zhang JB, Zhang Y, Gu N, Wang TH, Feng J, Yang DL, Perrett S, Yan X. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007;2(9):577–83.
Hou JJ, Xianyu YL. Tailoring the surface and composition of nanozymes for enhanced bacterial binding and antibacterial activity. Small. 2023;19:e2302640.
Jiang DW, Ni DL, Rosenkrans ZT, Huang P, Yan XY, Cai WB. Nanozyme: new horizons for responsive biomedical applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2019;48(14):3683–704.
Yang YY, Tan XL, Wang YR, Shen BX, Yang YQ, Huang H. Heteroatom-doped nanozyme progress and perspectives: from synthesis strategies to biomedical applications. Chem Eng J. 2023;468:143703.
Amin N, Afkhami A, Hosseinzadeh L, Madrakian T. Green and cost-effective synthesis of carbon dots from date kernel and their application as a novel switchable fluorescence probe for sensitive assay of zoledronic acid drug in human serum and cellular imaging. Anal Chim Acta. 2018;1030:183–93.
Lu WJ, Guo YJ, Zhang JH, Yue YF, Fan L, Li F, Dong C, Shuang SM. A high catalytic activity nanozyme based on cobalt-doped carbon dots for biosensor and anticancer cell effect. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2022;14(51):57206–14.
Fan KL, Xi JQ, Fan L, Wang PX, Zhu CH, Tang Y, Xu XD, Liang MM, Jiang B, Yan XY, Gao LZ. In vivo guiding nitrogen-doped carbon nanozyme for tumor catalytic therapy. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1440.
Zhang XL, Li GL, Chen G, Wu D, Zhou XX, Wu YN. Single-atom nanozymes: a rising star for biosensing and biomedicine. Coordin Chem Rev. 2020;418:213376.
Zhang FY, Li YM, Li XM, Liu RB, Sang YX, Wang XH, Wang S. Nanozyme-enabled sensing strategies for determining the total antioxidant capacity of food samples. Food Chem. 2022;384:132412.
Zhang XN, Huang XY, Wang ZL, Zhang Y, Huang XW, Li ZH, Daglia M, Xiao JB, Shi JY, Zou XB. Bioinspired nanozyme enabling glucometer readout for portable monitoring of pesticide under resource-scarce environments. Chem Eng J. 2022;429:132243.
Wang H, Wang Y, Lu LL, Ma Q, Feng RX, Xu SY, James TD, Wang LY. Reducing valence states of co active sites in a single-atom nanozyme for boosted tumor therapy. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;32(28):2200331.
Shen W, Zhu JM, Hu Y, Yin J, Zheng Y, Xi PX. Applications of rare earth promoted transition metal sulfides in electrocatalysis. Chinese J Chem. 2023;41(14):1740–52.
Han L, Liu P, Zhang HJ, Li F, Liu AH. Phage capsid protein-directed MnO2 nanosheets with peroxidase-like activity for spectrometric biosensing and evaluation of antioxidant behaviour. Chem Commun. 2017;53(37):5216–9.
Qiu ZW, Duan W, Cao SF, Zeng T, Zhao TY, Huang JK, Lu XQ, Zeng JB. Highly specific colorimetric probe for fluoride by triggering the intrinsic catalytic activity of a AgPt-Fe3O4 hybrid nanozyme encapsulated in SiO2 shells. Environ Sci Technol. 2022;56(3):1713–23.
Duan W, Qiu ZW, Cao SF, Guo Q, Huang JK, Xing JY, Lu XQ, Zeng JB. Pd-Fe3O4 Janus nanozyme with rational design for ultrasensitive colorimetric detection of biothiols. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022;196:113724.
Huang YY, Liu Z, Liu CQ, Ju EG, Zhang Y, Ren JS, Qu XG. Self-Assembly of multi-nanozymes to mimic an intracellular antioxidant defense system. Angew Chem Int Edit. 2016;55(23):6646–50.
Liu YF, Cheng Y, Zhang H, Zhou M, Yu YJ, Lin SC, Jiang B, Zhao XZ, Miao LY, Wei CW, Liu QY, Lin YW, Du Y, Butch CJ, Wei H. Integrated cascade nanozyme catalyzes in vivo ROS scavenging for anti-inflammatory therapy. Sci Adv. 2020;6(29):eabb2695.
Li W, Liu Z, Liu CQ, Guan YJ, Ren JS, Qu XG. Manganese dioxide nanozymes as responsive cytoprotective shells for individual living cell encapsulation. Angew Chem Int Edit. 2017;56(44):13661–5.
Sun HJ, Zhou Y, Ren JS, Qu XG. Carbon nanozymes: enzymatic properties, catalytic mechanism, and applications. Angew Chem Int Edit. 2018;57(30):9224–37.
Liu L, Jiang H, Wang XM. Functionalized gold nanomaterials as biomimetic nanozymes and biosensing actuators. Trac-Trend Anal Chem. 2021;143:116376.
Gao WH, He JY, Chen L, Meng XQ, Ma YN, Cheng LL, Tu KS, Gao XF, Liu C, Zhang MZ, Fan KL, Pang DW, Yan XY. Deciphering the catalytic mechanism of superoxide dismutase activity of carbon dot nanozyme. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):160.
Wu H, Xu HM, Shi YX, Yuan T, Meng T, Zhang Y, Xie WJ, Li XH, Li YC, Fan LZ. Recent advance in carbon dots: from properties to applications. Chinese J Chem. 2021;39(5):1364–88.
Shi WB, Wang QL, Long YJ, Cheng ZL, Chen SH, Zheng HZ, Huang YM. Carbon nanodots as peroxidase mimetics and their applications to glucose detection. Chem Commun. 2011;47(23):6695–7.
Liu ZX, Chen BB, Liu ML, Zou HY, Huang CZ. Cu(I)-Doped carbon quantum dots with zigzag edge structures for highly efficient catalysis of azide-alkyne cycloadditions. Green Chem. 2017;19(6):1494–8.
Li SQ, Liu XD, Chai HX, Huang YM. Recent advances in the construction and analytical applications of metal-organic frameworks-based nanozymes. Trac-Trend Anal Chem. 2018;105:391–403.
Zhang AM, Pan SJ, Zhang YH, Chang J, Cheng J, Huang ZC, Li TL, Zhang CL, de la Fuentea JM, Zhang Q, Cui DX. Carbon-gold hybrid nanoprobes for real-time imaging, photothermal/photodynamic and nanozyme oxidative therapy. Theranostics. 2019;9(12):3443–58.
Tripathi KM, Ahn HT, Chung M, Le XA, Saini D, Bhati A, Sonkar SK, Kim MI, Kim T. N, S, and P-co-doped carbon quantum dots: intrinsic peroxidase activity in a wide pH range and its antibacterial applications. Acs Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(10):5527–37.
Zhu JL, Luo G, Xi XX, Wang YJ, Selvaraj JN, Wen W, Zhang XH, Wang SF. Cu2+-modified hollow carbon nanospheres: an unusual nanozyme with enhanced peroxidase-like activity. Microchim Acta. 2021;188(1):8.
Wang XY, Wang H, Zhou SQ. Progress and perspective on carbon-based nanozymes for peroxidase-like applications. J Phys Chem Lett. 2021;12(48):11751–60.
Qin RX, Feng YS, Ding DD, Chen L, Li S, Deng HP, Chen SL, Han ZX, Sun WJ, Chen HM. Fe-coordinated carbon nanozyme dots as peroxidase-like nanozymes and magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021;4(7):5520–8.
Zhang RF, Chen L, Liang Q, Xi JQ, Zhao HQ, Jin YL, Gao XF, Yan XY, Gao LZ, Fan KL. Unveiling the active sites on ferrihydrite with apparent catalase-like activity for potentiating radiotherapy. Nano Today. 2021;41:101317.
Xi Z, Wei KC, Wang QX, Kim MJ, Sun SH, Fung V, Xia XH. Nickel-platinum nanoparticles as peroxidase mimics with a record high catalytic efficiency. J Am Chem Soc. 2021;143(7):2660–4.
Ouyang Y, Biniuri Y, Fadeev M, Zhang P, Carmieli R, Vazquez-Gonzalez M, Willner I. Aptamer-modified Cu2+-functionalized C-dots: versatile means to improve nanozyme activities-“aptananozymes.” J Am Chem Soc. 2021;143(30):11510–9.
Saengsrichan A, Khemthong P, Wanmolee W, Youngjan S, Phanthasri J, Arjfuk P, Pongchaikul P, Ratchahat S, Posoknistakul P, Laosiripojana N, Wu KCW, Sakdaronnarong C. Platinum/carbon dots nanocomposites from palm bunch hydrothermal synthesis as highly efficient peroxidase mimics for ultra-low H2O2 sensing platform through dual mode of colorimetric and fluorescent detection. Anal Chim Acta. 2022;1230:340368.
Li X, Ding SC, Lyu ZY, Tieu P, Wang MY, Feng ZX, Pan XQ, Zhou Y, Niu XH, Du D, Zhu WL, Lin YH. Single-atomic iron doped carbon dots with both photoluminescence and oxidase-like activity. Small. 2022;18(37):e2203001.
Geng BJ, Yan L, Zhu YP, Shi WJ, Wang HN, Mao JJ, Ren LJ, Zhang JQZ, Tian YJ, Gao FY, Zhang XF, Chen JK, Zhu JB. Carbon dot@MXene nanozymes with triple enzyme-mimic activities for mild NIR-II photothermal-amplified nanocatalytic therapy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(5):e2202154.
Li QL, Li H, Li KX, Gu Y, Wang YJ, Yang DZ, Yang YL, Gao L. Specific colorimetric detection of methylmercury based on peroxidase-like activity regulation of carbon dots/Au NPs nanozyme. J Hazard Mater. 2023;441:129919.
Mao GB, Cai Q, Wang FB, Luo CL, Ji XH, He ZK. One-step synthesis of Rox-DNA functionalized CdZnTeS quantum dots for the visual detection of hydrogen peroxide and blood glucose. Anal Chem. 2017;89(21):11628–35.
Wu YF, Gao YF, Du JX. Bifunctional gold nanoclusters enable ratiometric fluorescence nanosensing of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. Talanta. 2019;197:599–604.
Essick EE, Sam F. Oxidative stress and autophagy in cardiac disease, neurological disorders, aging and cancer. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2010;3(3):168–77.
Woo HA, Yim SH, Shin DH, Kang D, Yu DY, Rhee SG. Inactivation of peroxiredoxin I by phosphorylation allows localized H2O2 accumulation for cell signaling. Cell. 2010;140(4):517–28.
Hanaoka S, Lin JM, Yamada M. Chemiluminescent flow sensor for H2O2 based on the decomposition of H2O2 catalyzed by cobalt(II)-ethanolamine complex immobilized on resin. Anal Chim Acta. 2001;426(1):57–64.
Hai X, Li YF, Zhu CZ, Song WL, Cao JY, Bi S. DNA-based label-free electrochemical biosensors: from principles to applications. Trac-Trend Anal Chem. 2020;133:116098.
Lobnik A, Cajlakovic M. Sol-gel based optical sensor for continuous determination of dissolved hydrogen peroxide. Sensor Actuat B-Chem. 2001;74(1–3):194–9.
Komkova MA, Karyakin AA. Prussian blue: from advanced electrocatalyst to nanozymes defeating natural enzyme. Microchim Acta. 2022;189(8):290.
Wang B, Chen YF, Wu YY, Weng B, Liu YS, Li CM. Synthesis of nitrogen- and iron-containing carbon dots, and their application to colorimetric and fluorometric determination of dopamine. Microchim Acta. 2016;183(9):2491–500.
Lu J, Hu YH, Wang PX, Liu PQ, Chen ZG, Sun DP. Electrochemical biosensor based on gold nanoflowers-encapsulated magnetic metal-organic framework nanozymes for drug evaluation with in-situ monitoring of H2O2 released from H9C2 cardiac cells. Sensor Actuat B-Chem. 2020;311:127909.
Lu WJ, Guo YJ, Yue YF, Zhang JH, Fan L, Li F, Zhao Y, Dong C, Shuang SM. Smartphone-assisted colorimetric sensing platform based on molybdenum-doped carbon dots nanozyme for visual monitoring of ampicillin. Chem Eng J. 2023;468:143615.
Valekar AH, Batule BS, Kim MI, Cho KH, Hong DY, Lee UH, Chang JS, Park HG, Hwang YK. Novel amine-functionalized iron trimesates with enhanced peroxidase-like activity and their applications for the fluorescent assay of choline and acetylcholine. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;100:161–8.
Acknowledgements
Sijia Xie conducted all the experiments and Prof. Hai Xiong conceived the experiments. Sijia Xie and Hai Xiong wrote the manuscript. Yating Zeng helped discussion. All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Commission of Shenzhen, China (20231121191245001 and JCYJ20210324095607021 to HX) and the Special Project of Key Fields of Universities in Guangdong Province, China (2021ZDZX2047 to HX), and Top Young Talent of the Pearl River Talent Recruitment Program, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The use of the human serum samples used in this study was approved according to the guidelines of the China Ethical Committee by the Regional Ethic Board at Shenzhen University (ethical permissions PN-202400004). The participant provided written informed consent to participate in the detection of glucose.
Conflict of interest
The declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Published in the topical collection featuring Nanozymes with guest editors Vipul Bansal, Sudipta Seal, and Hui Wei.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, S., Zeng, Y., Li, J. et al. Fe-codoped carbon dots serving as a peroxidase mimic to generate in situ hydrogen peroxide for the visual detection of glucose. Anal Bioanal Chem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05196-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05196-x