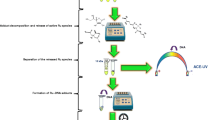
Abstract
The reactivity of thioredoxin (Trx1) with the Au(I) drug auranofin (AF) and two therapeutic N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC)2-Au(I) complexes (bis [1-methyl-3-acridineimidazolin-2-ylidene]gold(I) tetrafluoroborate (Au3BC) and [1,3-diethyl-4,5-bis(4methoxyphenyl)imidazol-2-ylidene]gold(I) (Au4BC)) was investigated. Direct infusion (DI) electrospray ionization (ESI) mass spectrometry (MS) allowed information on the structure, stoichiometry, and kinetics of formation of Trx-Au adducts. The fragmentation of the formed adducts in the gas phase gave insights into the exact Au binding site within the protein, demonstrating the preference for Trx1 Cys32 or Cys35 of AF or the (NHC)2-Au(I) complex Au3BC, respectively. Reversed-phase HPLC suffered from the difficulty of elution of gold compounds, did not preserve the formed metal-protein adducts, and favored the loss of ligands (phosphine or NHC) from Au(I). These limitations were eliminated by capillary electrophoresis (CE) which enabled the separation of the gold compounds, Trx1, and the formed adducts. The ICP-MS/MS detection allowed the simultaneous quantitative monitoring of the gold and sulfur isotopes and the determination of the metallation extent of the protein. The hyphenation of the mentioned techniques was used for the analysis of Trx1-Au adducts for the first time.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang J, Li X, Han X, Liu R, Fang J. Targeting the thioredoxin system for cancer therapy. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2017;38(9):794–808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2017.06.001.
Ghareeb H, Metanis N. The thioredoxin system: a promising target for cancer drug development. Chemistry. 2020;26(45):10175–84. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201905792.
Arnér ES, Holmgren A. Physiological functions of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. Eur J Biochem. 2000;267(20):6102–9. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01701.x.
Pearson RG. Hard and soft acids and bases—the evolution of a chemical concept. Coord Chem Rev. 1990;100:403–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-8545(90)85016-L.
Bhabak KP, Bhuyan BJ, Mugesh G. Bioinorganic and medicinal chemistry: aspects of gold(i)-protein complexes. Dalton Trans. 2011;40(10):2099. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0dt01057j.
Zhang X, Selvaraju K, Saei AA, et al. Repurposing of auranofin: thioredoxin reductase remains a primary target of the drug. Biochimie. 2019;162:46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2019.03.015.
Pratesi A, Gabbiani C, Ginanneschi M, Messori L. Reactions of medicinally relevant gold compounds with the C-terminal motif of thioredoxin reductase elucidated by MS analysis. Chem Commun. 2010;46(37):7001–3. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC01465F.
Pratesi A, Gabbiani C, Michelucci E, et al. Insights on the mechanism of thioredoxin reductase inhibition by gold N-heterocyclic carbene compounds using the synthetic linear selenocysteine containing C-terminal peptide hTrxR(488–499): an ESI-MS investigation. J Inorg Biochem. 2014;136:161–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2014.01.009.
Lamarche J, Alcoceba Álvarez E, Cordeau E, et al. Comparative reactivity of medicinal gold(i) compounds with the cyclic peptide vasopressin and its diselenide analogue. Dalton Trans. 2021;50(47):17487–90. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1DT03470G.
Ronga L, Tolbatov I, Giorgi E, et al. Mechanistic evaluations of the effects of auranofin triethylphosphine replacement with a trimethylphosphite moiety. Inorg Chem. 2023;62(26):10389–96. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.3c01280.
Mora M, Gimeno MC, Visbal R. Recent advances in gold–NHC complexes with biological properties. Chem Soc Rev. 2019;48(2):447–62. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CS00570B.
Geri A, Massai L, Messori L. Protein metalation by medicinal gold compounds: identification of the main features of the metalation process through ESI MS experiments. Molecules. 2023;28(13). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135196.
Zoppi C, Massai L, Cirri D, Gabbiani C, Pratesi A, Messori L. Protein metalation by two structurally related gold(I) carbene complexes: an ESI MS study. Inorg Chim Acta. 2021;520: 120297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2021.120297.
Augello G, Azzolina A, Rossi F, et al. New insights into the behavior of NHC-gold complexes in cancer cells. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(2):466. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020466.
Bernabeu de Maria M, Lamarche J, Ronga L, Messori L, Szpunar J, Lobinski R. Selenol (-SeH) as a target for mercury and gold in biological systems: contributions of mass spectrometry and atomic spectroscopy. Coord Chem Rev. 2023;474:214836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2022.214836.
Holmgren A. Thioredoxin structure and mechanism: conformational changes on oxidation of the active-site sulfhydryls to a disulfide. Structure. 1995;3(3):239–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-2126(01)00153-8.
Gimeno MC, Laguna A, Visbal R. N-heterocyclic carbene coinage metal complexes as intense blue-green emitters. Organometallics. 2012;31(20):7146–57. https://doi.org/10.1021/om300571m.
Liu W, Bensdorf K, Proetto M, Hagenbach A, Abram U, Gust R. Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro studies of bis[1,3-diethyl-4,5-diarylimidazol-2-ylidene]gold(I/III) complexes. J Med Chem. 2012;55(8):3713–24. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm3000196.
Wróblewska AM, Samsonowicz-Górski J, Kamińska E, Drozd M, Matczuk M. Optimization of a CE-ICP-MS/MS method for the investigation of liposome–cisplatin nanosystems and their interactions with transferrin. J Anal At Spectrom. 2022;37(7):1442–9. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1JA00459J.
Massai L, Zoppi C, Cirri D, Pratesi A, Messori L. Reactions of medicinal gold(III) compounds with proteins and peptides explored by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and complementary biophysical methods. Front Chem. 2020;8: 581648. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.581648.
Zoppi C, Messori L, Pratesi A. ESI MS studies highlight the selective interaction of auranofin with protein free thiols. Dalton Trans. 2020;49(18):5906–13. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0DT00283F.
Colotti G, Baiocco P, Fiorillo A, et al. Structural insights into the enzymes of the trypanothione pathway: targets for antileishmaniasis drugs. Future Med Chem. 2013;5(15):1861–75. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.13.146.
Ilari A, Baiocco P, Messori L, et al. A gold-containing drug against parasitic polyamine metabolism: the X-ray structure of trypanothione reductase from Leishmania infantum in complex with auranofin reveals a dual mechanism of enzyme inhibition. Amino Acids. 2012;42(2):803–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0997-9.
Lamarche J, Bierla K, Ouerdane L, Szpunar J, Ronga L, Lobinski R. Mass spectrometry insights into interactions of selenoprotein P with auranofin and cisplatin. J Anal At Spectrom. 2022;37(5):1010–22. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2JA00090C.
Szpunar J. Advances in analytical methodology for bioinorganic speciation analysis: metallomics, metalloproteomics and heteroatom-tagged proteomics and metabolomics. Analyst. 2005;130(4):442–65. https://doi.org/10.1039/B418265K.
Nguyen TTTN, Østergaard J, Gammelgaard B. A method for studies on interactions between a gold-based drug and plasma proteins based on capillary electrophoresis with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry detection. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015;407(28):8497–503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8997-3.
Kupiec M, Tomaszewska A, Jakubczak W, Haczyk-Więcek M, Pawlak K. Speciation analysis highlights the interactions of auranofin with the cytoskeleton proteins of lung cancer cells. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022;15(10):1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101285.
Kallis GB, Holmgren A. Differential reactivity of the functional sulfhydryl groups of cysteine-32 and cysteine-35 present in the reduced form of thioredoxin from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980;255(21):10261–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)70458-X.
Giglione C, Boularot A, Meinnel T. Protein N-terminal methionine excision. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004;61(12):1455–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-3466-8.
Pratesi A, Cirri D, Ciofi L, Messori L. Reactions of auranofin and its pseudohalide derivatives with serum albumin investigated through ESI-Q-TOF MS. Inorg Chem. 2018;57(17):10507–10. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b02177.
Dupree EJ, Jayathirtha M, Yorkey H, Mihasan M, Petre BA, Darie CC. A critical review of bottom-up proteomics: the good, the bad, and the future of this field. Proteomes. 2020;8(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes8030014.
Tolbatov I, Coletti C, Marrone A, Re N. Reactivity of gold(I) monocarbene complexes with protein targets: a theoretical study. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(4):820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040820.
Funding
M. B. D. M. received from E2S-UPPA a PhD fellowship. Financial support of the CNR for “The Bioinorganic Drugs (BIDs) joint laboratory: A multidisciplinary platform promoting new molecular targets for drug discovery” is also received. M. M. and J. S. received from the Warsaw University of Technology financial support of the CE-ICP-MS/MS measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Published in the topical collection Elemental Mass Spectrometry for Bioanalysis with guest editors Jörg Bettmer, Mario Corte-Rodríguez, and Márcia Foster Mesko.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bernabeu De Maria, M., Matczuk, M., Tesauro, D. et al. Study of metalation of thioredoxin by gold(I) therapeutic compounds using combined liquid chromatography/capillary electrophoresis with inductively coupled plasma/electrospray MS/MS detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 416, 2819–2833 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05140-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05140-z