Abstract
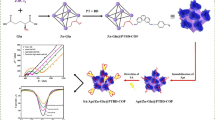
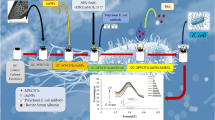
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is one of the most important pathogens that cause illness and food poisoning. In this research, using a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) modified with zeolite imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF 8) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), a sensitive electrochemical aptasensor has been made for the detection of the S. aureus bacteria. The morphology of the prepared AuNPs-ZIF 8 nanocomposite has been carefully characterized by means of transmission electron microscopy (TEM), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). In the manufacturing process, the S. aureus aptamer is immobilized on the AuNPs-ZIF 8 surface. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) method has been used for quantitative determination of S. aureus bacteria. The changes in the charge transfer resistance (Rct) of the aptamer due to the change in the concentration of bacteria are considered as the analytical signals. The proposed aptasensor has linear response in the concentration range of 1.5 × 101 to 1.5 × 107 CFU mL−1 of S. aureus bacteria. The detection limit of the method is 3.4 CFU mL−1. Using the developed aptasensor, it is possible to determine S. aureus bacteria in water and milk samples.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu S, Tang Y, Shi B, Zou W, Wang X, Wang C, Wu Y. Oligonucleotide-mediated the oxidase-mimicking activity of Mn3O4 nanoparticles as a novel colorimetric aptasensor for ultrasensitive and selective detection of Staphylococcus aureus in food. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2021;349:130809.
Huang Z, Yu X, Yang Q, Zhao Y, Wu W. Aptasensors for Staphylococcus aureus risk assessment in food. Front Microbiol. 2021;12:714265.
Ranjbar S, Shahrokhian S. Design and fabrication of an electrochemical aptasensor using Au nanoparticles/carbon nanoparticles/cellulose nanofibers nanocomposite for rapid and sensitive detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Bioelectrochemistry. 2018;123:70–6.
Abbaspour A, Norouz-Sarvestani F, Noori A, Soltani N. Aptamer-conjugated silver nanoparticles for electrochemical dual-aptamer-based sandwich detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;68:149–55.
Schmitz FRW, Valério A, de Oliveira D, Hotza D. An overview and future prospects on aptamers for food safety. Appl Microbio Biotech. 2020;104:6929–39.
Cai R, Zhang Z, Chen H, Tian Y, Zhou N. A versatile signal-on electrochemical biosensor for Staphylococcus aureus based on triple-helix molecular switch. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2021;326: 128842.
Zhu Z, Shi L, Feng H, Zhou HS. Single domain antibody coated gold nanoparticles as enhancer for clostridium difficile toxin detection by electrochemical impedance immunosensors. Bioelectrochem. 2015;101:153–8.
Jahangiri–Dehaghani F, Zare HR, Shekari Z, Benvidi A. Development of an electrochemical aptasensor based on Au nanoparticles decorated on metal–organic framework nanosheets and p-biphenol electroactive label for the measurement of aflatoxin B1 in a rice flour sample. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022:1–13.
Nameghi MA, Danesh NM, Ramezani M, Hassani FV, Abnous K, Taghdisi SM. A fluorescent aptasensor based on a DNA pyramid nanostructure for ultrasensitive detection of ochratoxin A. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016;408:5811–8.
Balaji Viswanath K, Krithiga N, Jayachitra A, Sheik Mideen AK, Amali AJ, Vasantha VS. Enzyme-free multiplex detection of pseudomonas aeruginosa and aeromonas hydrophila with ferrocene and thionine-labeled antibodies using ZIF-8/Au NPs as a platform. ACS Omega. 2018;3(12):17010–22.
Lu S, Hummel M, Chen K, Zhou Y, Kang S, Gu Z. Synthesis of Au@ ZIF-8 nanocomposites for enhanced electrochemical detection of dopamine. Electrochem Commun. 2020;114:106715.
Zhong T, Li S, Li X, JiYe Y, Mo Y, Chen L, Zhang Z, Wu H, Li M, Luo Q. A label-free electrochemical aptasensor based on AuNPs-loaded zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 for sensitive determination of aflatoxin B1. Food Chem. 2022;384: 132495.
Zhang Y, Zhang X, Song J, Jin L, Wang X, Quan C. Ag/H-ZIF-8 nanocomposite as an effective antibacterial agent against pathogenic bacteria. J Nanomater. 2019;9(11):1579.
Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Rong S, Yu H, Gao H, Ding P, Chang D, Pan H. Electrochemical immunoassay for the carcinoembryonic antigen based on Au NPs modified zeolitic imidazolate framework and ordered mesoporous carbon. Microchim Acta. 2020;187:1–9.
Fan G, Zheng X, Luo J, Peng H, Lin H, Bao M, Hong L, Zhou J. Rapid synthesis of Ag/AgCl@ ZIF-8 as a highly efficient photocatalyst for degradation of acetaminophen under visible light. J Chem Eng. 2018;351:782–90.
Jenkins JA, Wax TJ, Zhao J. Seed-mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles of controlled sizes to demonstrate the impact of size on optical properties. J Chem Educ. 2017;94(8):1090–3.
Shekari Z, Zare HR, Falahati A. Developing an impedimetric aptasensor for selective label–free detection of CEA as a cancer biomarker based on gold nanoparticles loaded in functionalized mesoporous silica films. J Electrochem Soc. 2017;164(13):B739.
Zhang Y, Jiang J, Zhang Z, Yu H, Rong S, Gao H, Pan H, Chang D. Electrochemical strategy with zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 and ordered mesoporous carbon for detection of xanthine. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020;14(2):120–5.
Yu X, Chen F, Wang R, Li Y. Whole-bacterium SELEX of DNA aptamers for rapid detection of E. coli O157: H7 using a QCM sensor. J. Biotechnol. 2018;266:39–49.
Kim YS, Song MY, Jurng J, Kim BC. Isolation and characterization of DNA aptamers against Escherichia coli using a bacterial cell–systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment approach. Anal Biochem. 2013;436(1):22–8.
Shekari Z, Zare HR, Falahati A. Dual assaying of breast cancer biomarkers by using a sandwich–type electrochemical aptasensor based on a gold nanoparticles–3D graphene hydrogel nanocomposite and redox probes labeled aptamers. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2021;332: 129515.
Han D, Yan Y, Wang J, Zhao M, Duan X, Kong L, Wu H, Cheng W, Min X, Ding S. An enzyme-free electrochemiluminesce aptasensor for the rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus by the quenching effect of MoS2-PtNPs-vancomycin to S2O82−/O2 system. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2019;288:586–93.
Sohouli E, Ghalkhani M, Zargar T, Joseph Y, Rahimi-Nasrabadi M, Ahmadi F, Plonska-Brzezinska ME, Ehrlich H. A new electrochemical aptasensor based on gold/nitrogen-doped carbon nano-onions for the detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Electrochim Acta. 2022;403: 139633.
Chen W, Chen Z, Lai Q, Zhang Y, Long M, Liang B, Liu Z. Specific and ultrasensitive detection of Staphylococcus aureus with a catechol-chitosan redox capacitor based electrochemical aptasensor. J Electroanal Chem. 2022;916:116357.
El-Wekil MM, Halby HM, Darweesh M, Ali ME, Ali R. An innovative dual recognition aptasensor for specific detection of Staphylococcus aureus based on Au/Fe3O4 binary hybrid. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):12502.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Morsalpour, H., Zare, H.R., Shekari, Z. et al. Development of an electrochemical sensitive aptasensor based on a zeolite imidazolate framework-8 and gold nanoparticles for the determination of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. Anal Bioanal Chem 416, 1229–1238 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-05115-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-05115-6