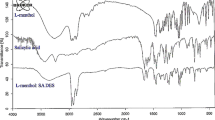
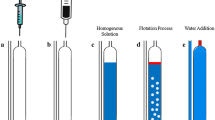
Abstract
This study presents a novel approach for the quantification of silver ions in environmental water through the utilization of liquid-liquid microextraction, employing natural deep eutectic solvents in conjunction with inductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopy. The extracted solvent was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). The impact of various extractant types, extractant molar ratio, extractant volume, extraction time, and salt concentration on the efficacy of silver ion extraction was investigated. The findings indicate that the optimal extraction efficiency was attained by utilizing a 5-mL aqueous solution volume, containing 1000 μL thymol/lactic acid NADES 1:3, a salt concentration of 1 mg mL−1, a pH value of 4, and a vortex time of 4 min. Upon implementing the optimized experimental conditions, the recovery of target metal ions was from 96.9 to 101.0%. The relative standard deviations were observed to be within the range of 1.5 to 2.7%. The present study demonstrates the reproducibility, accuracy, and reliability of the method for detecting silver ions in environmental water, with linear range of 5~1000 ng mL−1 and limits of detection (LOD) and limits of quantification (LOQ) of 1.52 ng mL−1 and 5.02 ng mL−1, respectively.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Jiang H, Tang CL, Wang Y, Mao LH, Sun Q, Zhang LB, Song HJ, Huang FL, Zuo CC. Low content and low-temperature cured silver nanoparticles/silver ion composite ink for flexible electronic applications with robust mechanical performance. Appl Surf Sci. 2021;564:150447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150447.
Xi JF, Kan WJ, Zhu Y, Huang SW, Wu LF, Wang J. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Eucommia ulmoides extract and their potential biological function in cosmetics. Heliyon. 2022;8:e10021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10021.
Mehmood I, Huang JC, Khan SA, Shah AH, Khan QU, Kiani M, Zhou DJ, Li GJ. Investigation of silver doped CdS co-sensitized TiO2/CISe/Ag–CdS heterostructure for improved optoelectronic properties. Opt Mater. 2021;111:110645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2020.110645.
García-Bonillo C, Texidó R, Gilabert-Porres J, Borrós S. Plasma-induced nanostructured metallic silver surfaces: study of bacteriophobic effect to avoid bacterial adhesion on medical devices. Heliyon. 2022;8:e10842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10842.
Mendes-Oliveira G, Luo YG, Zhou B, Gu GY, Teng Z, Bolten S, Park E, Pearlstein D, Turner ER, Millner PD, Nou XW. Use of a silver-based sanitizer to accelerate Escherichia coli die-off on fresh-cut lettuce and maintain produce quality during cold storage: laboratory and pilot-plant scale tests. Food Res Int. 2022;157:111170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111170.
Javed XW, Cuss XW, Shotyk XW. Dissolved versus particulate forms of trace elements in the Athabasca River, upstream and downstream of bitumen mines and upgraders. Appl Geochem. 2020;122:104706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104706.
Shotyk W, Bicalho B, Cuss CW, Donner MW, Grant-Weaver I, Haas-Neill S, Javed MB, Krachler M, Noernberg T, Pelletier R, Zaccone C. Trace metals in the dissolved fraction (<045μm) of the lower Athabasca River: analytical challenges and environmental implications. Sci Total Environ. 2017;580:660–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.012.
Jin Q, Feng C, Xia P, Bai Y. Hardness-dependent water quality criteria for protection of freshwater aquatic organisms for silver in China. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19:6067. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106067.
Beer C, Foldbjerg R, Hayashi Y, Sutherland DS, Autrup H. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles—nanoparticle or silver ion? Toxicol Lett. 2012;208:286–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2011.11.002.
Hadrup N, Sharma AK, Loeschner K. Toxicity of silver ions, metallic silver, and silver nanoparticle materials after in vivo dermal and mucosal surface exposure: a review. Regulatory. Toxicol Pharmacol. 2018;98:257–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2018.08.007.
Arai Y, Miyayama T, Hirano S. Difference in the toxicity mechanism between ion and nanoparticle forms of silver in the mouse lung and in macrophages. Toxicology. 2015;328:84–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2014.12.014.
Ryan J, Jacob P, Lee A, Gagnon Z, Pavel IE. Biodistribution and toxicity of antimicrobial ionic silver (Ag+) and silver nanoparticle (AgNP+) species after oral exposure, in Sprague-Dawley rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 2022;166:113228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2022.113228.
Huang YY, Wu YY, Ding W, Sun W, Hu C, Liu BZ, Liu HX, Zheng HL. Anion-synergistic adsorption enhances the selective removal of silver ions from complex wastewater by chitosan-coated magnetic silica core-shell nanoparticles. J Clean Prod. 2022;339:130777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130777.
Xu KQ, Liu YJ, Crespo GA, Cuartero M. Ultrathin ion-selective membranes for trace detection of lead, copper and silver ions. Electrochim Acta. 2022;427:140870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2022.140870.
Kamal S, Yang TCK. Silver enriched silver phosphate microcubes as an efficient recyclable SERS substrate for the detection of heavy metal ions. J Colloid Interf Sci. 2022;605:173–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.07.084.
Shah RV, Pandey AK, Bhushan KS, Kumar SJ, Rao RM, Jaison PG. Deep eutectic solvent-based extraction of uranium(vi) from a wide range acidity and subsequent determination by direct loading in thermal ionization mass spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom. 2021;36:590–7. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0JA00434K.
Wang RX, Zhang L, Zhang CL, Wang JW, Guan J, Jian ZM, Bu YT. Selective extraction of precious metals in the polar aprotic solvent system: experiment and simulation. Waste Manage. 2022;153:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2022.08.012.
Suresh PS, Singh PP, Anmol S, Kapoor YS. Upendra Sharma. Lactic acid-based deep eutectic solvent: an efficient green media for the selective extraction of steroidal saponins from Trillium govanianum. Sep Purif Technol. 2022;294:121105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121105.
Schaeffer N, Conceiçao JHF, Martins MAR, Neves MC, Erez-Sánchez MC, Gomes JRB, Papaiconomou N, Coutinho JAP. Non-ionic hydrophobic eutectics versatile solvents for tailored metal separation and valorization. Green Chem. 2020;22:2810–20. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0GC00793E.
Zhang M, Tian RB, Han H, Wu KJ, Wang BS, Liu YY, Zhu YM, Lu HF, Liang B. Preparation strategy and stability of deep eutectic solvents: a case study based on choline chloride-carboxylic acid. J Clean Prod. 2022;345:131028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131028.
Musarurwa H, Tavengwa NT. Deep eutectic solvent-based dispersive liquid-liquid micro-extraction of pesticides in food samples. Food Chem. 2021;342:127943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127943.
Kalyniukova A, Holuša J, Musiolek D, Sedlakova-Kadukova J, Płotka-Wasylka J, Andruch V. Application of deep eutectic solvents for separation and determination of bioactive compounds in medicinal plants. Ind Crop Prod. 2021;172:114047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.114047.
Kaoui S, Chebli B, Zaidouni S, Basaid K, Mir Y. Deep eutectic solvents as sustainable extraction media for plants and food samples: a review, Sustain. Chem Pharm. 2023;31:100937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2022.100937.
Wazeer I, Hizaddin HF, Hashim MA, Hadj-Kali MK. An overview about the extraction of heavy metals and other critical pollutants from contaminated water via hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents. J Environ Chem Eng. 2022;10:108574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108574.
Barzegar-Jalali MK, Jafari P, Jouyban A. Experimental determination and correlation of naproxen solubility in biodegradable low-toxic betaine-based deep eutectic solvents and water mixtures at 293.15 K to 313.15 K. Fluid Phase Equilibr. 2022;560:113508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fluid.2022.113508.
Jeong HH, Chen Z, Yadavali S, Xu J, Issadore D, Lee D. Large-scale production of compound bubbles using parallelized microfluidics for efficient extraction of metal ions. Lab Chip. 2019;19(4):665–73. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8LC01267A.
Abney CW, Gilhula JC, Lu K, Lin W. Metal-organic framework templated inorganic sorbents for rapid and efficient extraction of heavy metals. Adv Mater. 2014;26:7993–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201403428.
Zhao X, Zhang H, Yuan Y, Ren Y, Wang N. Ultra-fast and stable extraction of Li metal from seawater. Chem Commun (Camb). 2020;56:1577–80. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CC08927F.
Peng FX, Liu M, Wang XL, Ding XQ. Synthesis of low-viscosity hydrophobic magnetic deep eutectic solvent: selective extraction of DNA. Anal Chim Acta. 2021;1181:338899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.338899.
Rodriguez NR, Machiels L, Onghena B, Binnemans JSK. Selective recovery of zinc from goethite residue in the zinc industry using deep-eutectic solvents. RSC Adv. 2020;10:7328. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra00277a.
Surapong N, Pongpinyo P, Santaladchaiyakit Y, Burakham R. A biobased magnetic dual-dummy-template molecularly imprinted polymer using a deep eutectic solvent as a coporogen for highly selective enrichment of organophosphates. Food Chem. 2023;418:136045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.136045.
Osch DJGPV, Zubeir LF, Bruinhorst AVD, Rocha MAA, Kroon MC. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents as water-immiscible extractants. Green Chem. 2015;17:4518–21. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5GC01451D.
Santana-Mayor A, Socas-Rodríguez B, Rodríguez-Ramos R, Herrera-Herrera AV, Rodríguez-Delgado MÁ. Quality assessment of environmental water by a simple and fast non-ionic hydrophobic natural deep eutectic solvent-based extraction procedure combined with liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of plastic migrants. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021;413:1967–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03166-1.
Demmelmayer P, Steiner L, Weber H, Kienberger M. Thymol-menthol-based deep eutectic solvent as a modifier in reactive liquid–liquid extraction of carboxylic acids from pretreated sweet sorghum silage press juice. Sep Purif Technol. 2023;310:123060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.123060.
Sorouraddin SM, Farajzadeh MA, Dastoori H. Development of a dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method based on a ternary deep eutectic solvent as chelating agent and extraction solvent for preconcentration of heavy metals from milk samples. Talanta. 2020;208:120485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120485.
Durai L, Badhulika S. Stripping voltammetry and chemometrics assisted ultra-selective, simultaneous detection of trace amounts of heavy metal ions in aqua and blood serum samples. Sensor Actuator Rep. 2022;4:100097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snr.2022.100097.
Hatiboruah S, Biswas S, Sarma D, Nath P. A smartphone-based photometric and fluorescence sensing for accurate estimation of zinc ion in water. Sensor Actuat A-Phys. 2022;20:113586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2022.113586.
Gruszka J, Zambrzycka-Szelewa E, Kulpa JS, Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz B. Discrimination between ionic silver and silver nanoparticles in consumer products using graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom. 2018;33:2133–42. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8JA00310F.
Laborda F, Jiménez-Lamana J, Bolea E, Castillo JR. Selective identification, characterization and determination of dissolved silver(i) and silver nanoparticles based on single particle detection by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom. 2011;26:1362–71. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0JA00098A.
Bozorgzadeh JR, Pasdaran A, Ebrahimi-Najafabadi H. Determination of toxic heavy metals in fish samples using dispersive micro solid phase extraction combined with inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2021;346:128916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128916.
Zhang H, Zhou Y, Yoon J, Kim JS. Recent progress in fluorescent and colorimetric chemosensors for detection of precious metal ions (silver, gold and platinum ions). Chem Soc Rev. 2011;40:3416–29. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CS15028F.
Zheng WY, Wu XM, Li MX, Qiu SL, Yang TD, Yang R, Chen ZP, Wang SY, Liao L. Synergistic strongly coupled super-deamidation of wheat gluten by glucose-organic acid natural deep eutectic solvent and the efficaciousness of structure and functionality. Food Hydrocolloid. 2022;125:107437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107437.
Cherkashina K, Pochivalov A, Simonova V, Shakirova F, Shishov A, Bulatov A. A synergistic effect of hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents based on terpenoids and carboxylic acids for tetracycline microextraction. Analyst. 2021;146:3449–53. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1AN00096A.
Wang YF, Song YH, Li YF, Li J, Bao J, Zhang XW, Li B. Study on the extraction and separation of precious metals from wastewater using a hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent. J Environ Chem Eng. 2023;11:111102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.111102.
Yuan Y, Chen X, Chen Q, Jiang G, Wang H, Wang J. New switch on fluorescent probe with AIE characteristics for selective and reversible detection of mercury ion in aqueous solution. Anal Biochem. 2019;585:113403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2019.113403.
Soylak M, Koksal M. Deep eutectic solvent microextraction of lead(II), cobalt(II), nickel(II) and manganese(II) ions for the separation and preconcentration in some oil samples from Turkey prior to their microsampling flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination. Microchem J. 2019;147:832–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.04.006.
Liu M, Fu X, Lu M, Liu J, Xie H, Wei P, Zhang W, Xie Y, Qi Y. Colorimetric and visual determination of iodide ions via morphology transition of gold nanobipyramids. Anal Biochem. 2023;666:115077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2023.115077.
Mitani C, Anthemidis AN. An automatic countercurrent liquid-liquid micro-extraction system coupled with atomic absorption spectrometry for metal determination. Talanta. 2014;133:77–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.04.091.
Elmizadeh A, Soleimani M, Faridbod F, Bardajee GR. Fabrication of a nanomaterial-based fluorescence sensor constructed from ligand capped CdTe quantum dots for ultrasensitive and rapid detection of silver ions in aqueous samples. Spectrochim Acta A. 2019;211:291–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2018.12.016.
Bagheri N, Cinti S, Nobile E, Moscone D, Arduini F. Multi-array wax paper-based platform for the pre-concentration and determination of silver ions in drinking water. Talanta. 2021;232:122474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122474.
Chen HY, Wang S, Fu H, Xie HL, Lan W, Xu L, Zhang L, She YB. Dual-QDs ratios fluorescent probe for sensitive and selective detection of silver ions contamination in real sample. Spectrochim Acta A. 2020;234:118248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.118248.
Zhang LB, Zhang GW, Wang SX, Peng JH, Cui W. Sulfoethyl functionalized silica nanoparticle as an adsorbent to selectively adsorb silver ions from aqueous solutions. J Taiwan Inst Chem E. 2017;71:330–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.01.001.
Wang J, Lan Z, Hou S, Hou S. A novel symmetrical imidazole-containing framework as a fluorescence sensor for selectively detecting silver ions. Analyst. 2021;146:7618–26. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1AN01687C.
Acknowledgements
The authors also appreciate the facilities rendered by the National Coarse Cereals Engineering Research Center and Agricultural Products and Processed Products Supervision and Testing Center, Ministry of Agriculture, for the facilities rendered. We thank Home for Researchers (www.home-for-researchers.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the School Cultivation Subject of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University (No. PTJH201905, ZRCPY202124).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CW: conceptualization, methodology, validation, writing—original draft. SL: data curation, writing—original draft preparation. PS: supervision. XY: writing—reviewing and editing. ZY: software, validation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
All authors have seen and approved the submitted version of the manuscript to Journal of Food Composition and Analysis.
Consent for publication
All authors consented for publishing the work. All authors agree to publish an individual’s data or image in Journal of Food Composition and Analysis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Li, S., Sun, P. et al. Vortex-assisted hydrophobic natural deep eutectic solvent liquid-liquid microextraction for the removal of silver ions from environmental water. Anal Bioanal Chem 416, 873–882 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-05073-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-05073-z