Abstract
As two main types of liquid biopsy markers, both circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) play important roles in the diagnosis and prognosis of cancers. CTCs are malignant cells that detach from the original tumor tissue and enter the circulation of body fluids. sEVs are nanoscale vesicles secreted by normal cells or pathological cells. However, CTCs and sEVs in body fluids are scarce, leading to great difficulties in the accurate analysis of related diseases. For the sensitive detection of CTCs and sEVs in body fluids, various types of nucleic acid and nanomaterial-assisted signal amplification strategies have been developed. In this review, we summarize the recent advances in fluorescent detection of CTCs and sEVs in liquid biopsy based on nucleic acid and nanomaterial-assisted signal amplification strategies. We also discuss their advantages, challenges, and future prospects.
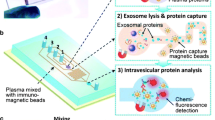
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49.
Zhao M, Mi D, Ferdows BE, Li Y, Wang R, Li J, et al. State-of-the-art nanotechnologies for the detection, recovery, analysis and elimination of liquid biopsy components in cancer. Nano Today. 2022;42: 101361.
Diamantis A, Magiorkinis E, Koutselini H. Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy: historical aspects. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2009;47(2):191–7.
Sumida Y, Nakajima A, Itoh Y. Limitations of liver biopsy and non-invasive diagnostic tests for the diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(2):475–85.
Nagrath S, Sequist LV, Maheswaran S, Bell DW, Irimia D, Ulkus L, et al. Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer patients by microchip technology. Nature. 2007;450(7173):1235-U10.
Ye M, Kong Y, Zhang C, Lv Y, Cheng S, Hou D, et al. Near-Infrared light controllable DNA walker driven by endogenous adenosine triphosphate for in situ spatiotemporal imaging of intracellular microRNA. ACS Nano. 2021;15(9):14253–62.
Shen Z, Wu A, Chen X. Current detection technologies for circulating tumor cells. Chem Soc Rev. 2017;46(8):2038–56.
Dai J, Su Y, Zhong S, Cong L, Liu B, Yang J, et al. Exosomes: key players in cancer and potential therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(3):1425–34.
Tkach M, Thery C. Communication by extracellular vesicles: where we are and where we need to go. Cell. 2016;164(6):1226–32.
Sullivan LB. Extracellular vesicles: taking metabolism on the road. Nat Chem Biol. 2017;13(9):924–5.
An T, Qin S, Xu Y, Tang Y, Huang Y, Situ B, et al. Exosomes serve as tumour markers for personalized diagnostics owing to their important role in cancer metastasis. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:27522.
Tsai WS, Nimgaonkar A, Segurado O, Chang Y, Hsieh B, Shao HJ, et al. Prospective clinical study of circulating tumor cells for colorectal cancer screening. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(4):556–556.
Cristofanilli M, Budd GT, Ellis MJ, Stopeck A, Matera J, et al. Circulating tumor cells, disease progression, and survival in metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:781–791.
Li P, Yu X, Han W, Kong Y, Bao W, Zhang J, et al. Ultrasensitive and reversible nanoplatform of urinary exosomes for prostate cancer diagnosis. ACS Sens. 2019;4(5):1433–41.
Kang YT, Hadlock T, Lo TW, Purcell E, Mutukuri A, Fouladdel S, et al. Dual-Isolation and profiling of circulating tumor cells and cancer exosomes from blood samples with melanoma using immunoaffinity-based microfluidic interfaces. Adv Sci. 2020;7(19):2001581.
Gallo M, De Luca A, Frezzetti D, Passaro V, Maiello MR, Normanno N. The potential of monitoring treatment response in non-small cell lung cancer using circulating tumour cells. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2019;19(8):683–94.
Haraszti RA, Didiot M-C, Sapp E, Leszyk J, Shaffer SA, Rockwell HE, et al. High-resolution proteomic and lipidomic analysis of exosomes and microvesicles from different cell sources. J Extracell Vesicles. 2016;5:32570.
Mellby LD, Nyberg AP, Johansen JS, Wingren C, Nordestgaard BG, Bojesen SE, et al. Serum biomarker signature-based liquid biopsy for diagnosis of early-stage pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(28):2887–94.
Wu L, Wang Y, Xu X, Liu Y, Lin B, Zhang M, et al. Aptamer-based detection of circulating targets for precision medicine. Chem Rev. 2021;121(19):12035–3105.
Onukwugha N-E, Kang Y-T, Nagrath S. Emerging micro-nanotechnologies for extracellular vesicles in immuno-oncology: from target specific isolations to immunomodulation. Lab Chip. 2022;22(18):3314–39.
Vajhadin F, Mazloum-Ardakani M, Sanati A, Haghniaz R, Travas-Sejdic J. Optical cytosensors for the detection of circulating tumour cells. J Mater Chem B. 2022;10(7):990–1004.
Wang X, Cheng S, Wang X, Wei L, Kong Q, Ye M, et al. pH-Sensitive dye-based nanobioplatform for colorimetric detection of heterogeneous circulating tumor cells. Acs Sens. 2021;6(5):1925–32.
Jiang Y, Shi M, Liu Y, Wan S, Cui C, Zhang L, et al. Aptamer/AuNP biosensor for colorimetric profiling of exosomal proteins. Angew. 2017;56(39):11916–20.
Cao Y, Yu X, Han B, Dong L, Xu J, Dai Y, et al. In situ programmable DNA circuit-promoted electrochemical characterization of stemlike phenotype in breast cancer. J Am Chem Soc. 2021;143(39):16078–86.
Wang X, Wang X, Cheng S, Ye M, Zhang C, Xian Y. Near-infrared light-switched MoS2 nanoflakes@gelatin bioplatform for capture, detection, and nondestructive release of circulating tumor cells. Anal Chem. 2020;92(4):3111–7.
Wang SS, Zhao XP, Liu FF, Younis MR, Xia XH, Wang C. Direct plasmon-enhanced electrochemistry for enabling ultrasensitive and label-free detection of circulating tumor cells in blood. Anal Chem. 2019;91(7):4413–20.
Li J, Li Y, Li P, Zhang Y, Du L, Wang Y, et al. Exosome detection via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for cancer diagnosis. Acta Biomater. 2022;144:1–14.
Kim WH, Lee JU, Jeon MJ, Park KH, Sim SJ. Three-dimensional hierarchical plasmonic nano-architecture based label-free surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy detection of urinary exosomal miRNA for clinical diagnosis of prostate cancer. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022;205: 114116.
Xu X, Lin J, Guo Y, Wu X, Xu Y, Zhang D, et al. TiO2-based surface-enhanced raman scattering bio-probe for efficient circulating tumor cell detection on microfilter. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022;210: 114305.
Tang Q, Xiao X, Li R, He H, Li S, Ma C. Recent advances in detection for breast-cancer-derived exosomes. Molecules. 2022;27(19):6673.
Yu D, Li Y, Wang M, Gu J, Xu W, Cai H, et al. Exosomes as a new frontier of cancer liquid biopsy. Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):56.
Wu D, Sedgwick AC, Gunnlaugsson T, Akkaya EU, Yoon J, James TD. Fluorescent chemosensors: the past, present and future. Chem Soc Rev. 2017;46(23):7105–23.
Wang C, Ye M, Cheng L, Li R, Zhu W, Shi Z, et al. Simultaneous isolation and detection of circulating tumor cells with a microfluidic silicon-nanowire-array integrated with magnetic upconversion nanoprobes. Biomater. 2015;54:55–62.
Rodrigues M, Richards N, Ning B, Lyon CJ, Hu TY. Rapid lipid-based approach for normalization of quantum-dot-detected biomarker expression on extracellular vesicles in complex biological samples. Nano Lett. 2019;19(11):7623–31.
Hussain SH, Huertas CS, Mitchell A, Deman AL, Laurenceau E. Biosensors for circulating tumor cells (CTCs)-biomarker detection in lung and prostate cancer: trends and prospects. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022;197: 113770.
Wu L, Wang Y, Zhu L, Liu Y, Wang T, Liu D, et al. Aptamer-based liquid biopsy. Acs Appl Bio Mater. 2020;3(5):2743–64.
Mei T, Lu X, Sun N, Li X, Chen J, Liang M, et al. Real-time quantitative PCR detection of circulating tumor cells using tag DNA mediated signal amplification strategy. J Pharm Anal. 2018;158:204–8.
Singh N, Huang L, Wang DB, Shao N, Zhang XE. Simultaneous detection of a cluster of differentiation markers on leukemia-derived exosomes by multiplex immuno-polymerase chain reaction via capillary electrophoresis analysis. Anal Chem. 2020;92(15):10569–77.
Ko J, Wang Y, Sheng K, Weitz DA, Weissleder R. Sequencing-based protein analysis of single extracellular vesicles. ACS Nano. 2021;15(3):5631–8.
Mohsen MG, Kool ET. The discovery of rolling circle amplification and rolling circle transcription. Acc Chem Res. 2016;49(11):2540–50.
Gao X, Teng X, Dai Y, Li J. Rolling circle amplification-assisted flow cytometry approach for simultaneous profiling of exosomal surface proteins. ACS Sens. 2021;6(10):3611–20.
Wang J, Dong HY, Zhou Y, Han LY, Zhang T, Lin M, et al. Immunomagnetic antibody plus aptamer pseudo-DNA nanocatenane followed by rolling circle amplication for highly-sensitive CTC detection. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;122:239–46.
Zhao X, Luo C, Mei Q, Zhang H, Zhang W, Su D, et al. Aptamer-cholesterol-mediated proximity ligation assay for accurate identification of exosomes. Anal Chem. 2020;92(7):5411–4518.
Chen T, Fu X, Zhang Q, Mao D, Song Y, Feng C, et al. A DNA logic gate with dual-anchored proximity aptamers for the accurate identification of circulating tumor cells. Chem Commun. 2020;56(51):6961–4.
Gao Q, Zhao Y, Xu K, Zhang C, Ma Q, Qi L, et al. Highly specific, single-step cancer cell isolation with multi-aptamer-mediated proximity ligation on live cell membranes. Angew. 2020;59(52):23564–8.
Yurke B, Turberfield AJ, Mills AP, Simmel FC, Neumann JL. A DNA-fuelled molecular machine made of DNA. Nature. 2000;406(6796):605–8.
Miao P, Tang Y. Cascade toehold-mediated strand displacement reaction for ultrasensitive detection of exosomal microRNA. CCS Chem. 3(7):2331–2339.
Dirks MR, Pierce NA. Triggered amplification by hybridization chain reaction. PNAS 2004;101(43):15275–15278.
Ding C, Zhang C, Yin X, Cao X, Cai M, Xian Y. Near-infrared fluorescent Ag2S nanodot-based signal amplification for efficient detection of circulating tumor cells. Anal Chem. 2018;90(11):6702–9.
Shen W, Guo K, Adkins GB, Jiang Q, Liu Y, Sedano S, et al. A single extracellular vesicle (EV) flow cytometry approach to reveal EV heterogeneity. Angew. 2018;57(48):15675–80.
Rafiee SD, Kocabey S, Mayer M, List J, Ruegg C. Detection of HER2(+) breast cancer cells using bioinspired DNA-based signal amplification. ChemMedChem. 2020;15(8):661–6.
Wang X, Shang H, Ma C, Chen L. A fluorescence assay for exosome detection based on bivalent cholesterol anchor triggered target conversion and enzyme-free signal amplification. Anal Chem. 2021;93(24):8493–500.
Wang H, Zeng J, Huang J, Cheng H, Chen B, Hu X, et al. A self-serviced-track 3D DNA walker for ultrasensitive detection of tumor exosomes by glycoprotein profiling. Angew. 2022;61(19): e202116932.
Cheng S, Kong Q, Hu X, Zhang C, Xian Y. An ultrasensitive strand displacement signal amplification-assisted synchronous fluorescence assay for surface proteins of small extracellular vesicle analysis and cancer identification. Anal Chem. 2022;94(2):1085–91.
Yu Y, Zhang WS, Guo Y, Peng H, Zhu M, Miao D, et al. Engineering of exosome-triggered enzyme-powered DNA motors for highly sensitive fluorescence detection of tumor-derived exosomes. Biosens Bioelectron. 2020;167: 112482.
Zhao Y, Chen F, Li Q, Wang L, Fan C. Isothermal amplification of nucleic acids. Chem Rev. 2015;115(22):12491–545.
Liu H, You Y, Zhu Y, Zheng H. Recent advances in the exonuclease III-assisted target signal amplification strategy for nucleic acid detection. Anal Methods. 2021;13(43):5103–19.
Li P, Wang J, Gao M, Wang J, Ma Y, Gu Y. Membrane feature-inspired profiling of extracellular vesicles for pancreatic cancer diagnosis. Anal Chem. 2021;93(28):9860–8.
Miao P, Chai H, Tang Y. DNA hairpins and dumbbell-wheel transitions amplified walking nanomachine for ultrasensitive nucleic acid detection. ACS Nano. 16 (3):4726–4733.
Kong Q, Cheng S, Hu X, You J, Zhang C, Xian Y. Ultrasensitive detection of tumor-derived small extracellular vesicles based on nonlinear hybridization chain reaction fluorescence signal amplification and immunomagnetic separation. Analyst. 2022;147(9):1859–65.
Sun S, Yang S, Hu X, Zheng C, Song H, Wang L, et al. Combination of immunomagnetic separation with aptamer-mediated double rolling circle amplification for highly sensitive circulating tumor cell detection. ACS Sens. 2020;5(12):3870–8.
Huang R, He L, Li S, Liu H, Jin L, Chen Z, et al. A simple fluorescence aptasensor for gastric cancer exosome detection based on branched rolling circle amplification. Nanoscale. 2020;12(4):2445–51.
He L, Yu X, Huang R, Jin L, Liu Y, Deng Y, et al. A novel specific and ultrasensitive method detecting extracellular vesicles secreted from lung cancer by padlock probe-based exponential rolling circle amplification. Nano Today. 2022;42: 101334.
Gao ML, He F, Yin BC, Ye BC. A dual signal amplification method for exosome detection based on DNA dendrimer self-assembly. Analyst. 2019;144(6):1995–2002.
Li F, Zhou Y, Yin H, Ai S. Recent advances on signal amplification strategies in photoelectrochemical sensing of microRNAs. Biosens Bioelectron. 2020;166: 112476.
Miao P, Tang Y. Dumbbell hybridization chain reaction based electrochemical biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of exosomal miRNA. Anal Chem. 92 (17):12026–12032.
Tabata M, Miyahara Y. Liquid biopsy in combination with solid-state electrochemical sensors and nucleic acid amplification. J Mater Chem B. 2019;7(43):6655–69.
Miao P, Tang Y. Gold nanoparticles-based multipedal DNA walker for ratiometric detection of circulating tumor cell. Anal Chem. 91 (23):15187–15192.
Zhou M, Li C, Wang B, Huang L. Rapid and sensitive leukemia-derived exosome quantification via nicking endonuclease-assisted target recycling. Anal Methods. 2021;13(35):4001–7.
Huang L, Wang DB, Singh N, Yang F, Gu N, Zhang XE. A dual-signal amplification platform for sensitive fluorescence biosensing of leukemia-derived exosomes. Nanoscale. 2018;10(43):20289–95.
Li Z, Wang G, Shen Y, Guo N, Ma N. DNA-templated magnetic nanoparticle-quantum dot polymers for ultrasensitive capture and detection of circulating tumor cells. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28(14):1707152.
Chen H, Luo D, Shang B, Cao J, Wei J, Chen Q, et al. Immunoassay-type biosensor based on magnetic nanoparticle capture and the fluorescence signal formed by horseradish peroxidase catalysis for tumor-related exosome determination. Mikrochim Acta. 2020;187(5):282.
He F, Wang J, Yin BC, Ye BC. Quantification of exosome based on a copper-mediated signal amplification strategy. Anal Chem. 2018;90(13):8072–9.
Tan J, Yang N, Hu Z, Su J, Zhong J, Yang Y, et al. Aptamer-functionalized fluorescent silica nanoparticles for highly sensitive detection of leukemia cells. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2016;11.298.
Wang Z, Sun N, Liu H, Chen C, Ding P, Yue X, et al. High-efficiency isolation and rapid identification of heterogeneous circulating tumor cells (CTCs) using dual-antibody-modified fluorescent-magnetic nanoparticles. Acs Appl Mater. 2019;11(43):39586–93.
Kalogianni DP. Nanotechnology in emerging liquid biopsy applications. Nano Converg. 2021;8:13.
Arshad F, Nabi F, Iqbal S, Khan RH. Applications of graphene-based electrochemical and optical biosensors in early detection of cancer biomarkers. Colloids Surf B. 2022;212.112356.
Pourmadadi M, Dinani HS, Tabar FS, Khassi K, Janfaza S, Tasnim N, et al. Properties and applications of graphene and its derivatives in biosensors for cancer detection: a comprehensive review. Biosensors. 2022;12(5):269.
Lu CH, Li J, Lin MH, Wang YW, Yang HH, Chen X, et al. Amplified aptamer-based assay through catalytic recycling of the analyte. Angew. 2010;49(45):8454–7.
Wang H, Chen H, Huang Z, Li T, Deng A, Kong J. DNase I enzyme-aided fluorescence signal amplification based on graphene oxide-DNA aptamer interactions for colorectal cancer exosome detection. Talanta. 2018;184:219–26.
Jin D, Yang F, Zhang Y, Liu L, Zhou Y, Wang F, et al. ExoAPP: exosome-oriented, aptamer nanoprobe-enabled surface proteins profiling and detection. Anal Chem. 2018;90(24):14402–11.
Xiao K, Liu J, Chen H, Zhang S, Kong J. A label-free and high-efficient GO-based aptasensor for cancer cells based on cyclic enzymatic signal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;91:76–81.
Li B, Pan W, Liu C, Guo J, Shen J, Feng J, et al. Homogenous magneto-fluorescent nanosensor for tumor-derived exosome isolation and analysis. ACS Sens. 2020;5(7):2052–60.
Robinson JT, Tabakman SM, Liang Y, Wang H, Casalongue HS, Daniel V, et al. Ultrasmall reduced graphene oxide with high near-infrared absorbance for photothermal therapy. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133(17):6825–31.
Zhang H, Zhang H, Aldalbahi A, Zuo X, Fan C, Mi X. Fluorescent biosensors enabled by graphene and graphene oxide. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;89:96–106.
Wang L, Pan Y, Liu Y, Sun Z, Huang Y, Li J, et al. Fabrication of an aptamer-coated liposome complex for the detection and profiling of exosomes based on terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated signal amplification. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2020;12(1):322–9.
Zhang J, Zhu Y, Shi J, Zhang K, Zhang Z, Zhang H. Sensitive signal amplifying a diagnostic biochip based on a biomimetic periodic nanostructure for detecting dancer exosomes. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2020;12(30):33473–82.
Ding C, Zhang C, Cheng S, Xian Y. Multivalent aptamer functionalized Ag2S nanodots/hybrid cell membrane-coated magnetic nanobioprobe for the ultrasensitive isolation and detection of circulating tumor cells. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(16):1909781.
Sforzi J, Palagi L, Aime S. Liposome-based bioassays. Biology. 2020;9(8):202.
Wang L, Yang Y, Liu Y, Ning L, Xiang Y, Li G. Bridging exosome and liposome through zirconium-phosphate coordination chemistry: a new method for exosome detection. Chem Commun. 2019;55(18):2708–11.
Zhang L, Gu C, Wen J, Liu G, Liu H, Li L. Recent advances in nanomaterial-based biosensors for the detection of exosomes. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021;413(1):83–102.
Resch-Genger U, Grabolle M, Cavaliere-Jaricot S, Nitschke R, Nann T. Quantum dots versus organic dyes as fluorescent labels. Nat Methods. 2008;5(9):763–75.
Liang Z, Khawar MB, Liang J, Sun H. Bio-conjugated quantum dots for cancer research: detection and imaging. Front Oncol. 2021;11: 749970.
Wu LL, Tang M, Zhang ZL, Qi CB, Hu J, Ma XY, et al. Chip-assisted single-cell biomarker profiling of heterogeneous circulating tumor cells using multifunctional nanospheres. Anal Chem. 2018;90(17):10518–26.
Lei J, Ju H. Signal amplification using functional nanomaterials for biosensing. Chem Soc Rev. 2012;41(6):2122–34.
Safarpour H, Dehghani S, Nosrati R, Zebardast N, Alibolandi M, Mokhtarzadeh A, et al. Optical and electrochemical-based nano-aptasensing approaches for the detection of circulating tumor cells (CTCs). Biosen Bioelectron. 2020;148.111833.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22274054, 21974050, and 11727810), the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (20ZR1418000), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Published in the topical collection Young Investigators in (Bio-)Analytical Chemistry 2023 with guest editors Zhi-Yuan Gu, Beatriz Jurado-Sánchez, Thomas H. Linz, Leandro Wang Hantao, Nongnoot Wongkaew, and Peng Wu.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Tan, W., Cheng, S. et al. Nucleic acid and nanomaterial-assisted signal-amplified strategies in fluorescent analysis of circulating tumor cells and small extracellular vesicles. Anal Bioanal Chem 415, 3769–3787 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04509-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04509-2