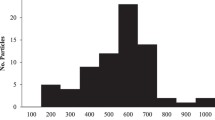
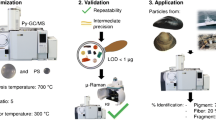
Abstract
Microplastics (MPs) are considered as contaminants of emerging concern to the environment and our food chains in recent years. In this study, we presented a multi-technique-based analytical method for detection of MPs through a combination of microscope-FTIR (μ-FTIR) with pyrolysis-GC/MS (Py-GC/MS) to achieve 3-dimensional (3D) information for the identification of polymer type, characterization of particle size and morphology, and quantification of MPs based on both particle number and mass of plastics. Plastics that are commonly used and disposed of, including polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), poly vinyl chloride (PVC), polyamide (PA), and poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), were covered in this study. Sample extraction and separation procedures were optimized for these microplastics in table salts where good recoveries (> 75%) were achieved. To further enhance the detection sensitivity in simultaneous quantification of multiple polymers in a sample, a serial dissolution approach with different solvents was developed for the detection of all 7 types of plastics. The established sample preparation process and multi-technique-based analytical method were validated with polymer standards in table salts, resulting in satisfactory qualification and quantification for all samples tested. A retail survey of MPs in table salts was conducted with the developed analytical method, revealing that MPs were present in all commercially available table salts. The total number of MP particles varied from 20 to 125 particles/kg and the total mass contents of seven types of plastics ranged from 30 to 530 µg/kg in table salts.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bond T, Ferrandiz-Mas V, Felipe-Sotelo M, van Sebille E. The occurrence and degradation of aquatic plastic litter based on polymer physicochemical properties: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol. 2018;48(7–9):685–722. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2018.1483155.
Dehaut A, Cassone AL, Frere L, Hermabessiere L, Himber C, Rinnert E, Riviere G, Lambert C, Soudant P, Huvet A, Duflos G, Paul-Pont I. Microplastics in seafood: benchmark protocol for their extraction and characterization. Environ Pollut. 2016;215:223–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.05.018.
Law KL, Thompson RC. Microplastics in the seas. Science. 2014;345(6193):144–5. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1254065.
Eriksen M, Lebreton LCM, Carson HS, Thiel M, Moore CJ, Borerro JC, Galgani F, Ryan PG, Reisser J. Plastic pollution in the world’s oceans: more than 5 trillion plastic pieces weighing over 250,000 tons afloat at sea. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(12): e0111913. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0111913.
Barnes DKA, Galgani F, Thompson RC, Barlaz M. Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos Trans R Soc B-Biol Sci. 2009;364(1526):1985–98. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2008.0205.
Cole M, Lindeque P, Halsband C, Galloway TS. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: a review. Mar Pollut Bull. 2011;62(12):2588–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.09.025.
Wright SL, Thompson RC, Galloway TS. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: a review. Environ Pollut. 2013;178:483–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.02.031.
Bessa F, Barria P, Neto JM, Frias J, Otero V, Sobral P, Marques JC. Occurrence of microplastics in commercial fish from a natural estuarine environment. Mar Pollut Bull. 2018;128:575–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.01.044.
Ribeiro F, Okoffo ED, O’Brien JW, Fraissinet-Tachet S, O’Brien S, Gallen M, Samanipour S, Kaserzon S, Mueller JF, Galloway T, Thomas KV. Quantitative analysis of selected plastics in high-commercial-value Australian seafood by pyrolysis gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Environ Sci Technol. 2020;54(15):9408–17. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c02337.
Liebezeit G, Liebezeit E. Non-pollen particulates in honey and sugar. Food Addit Contam Part A-Chem. 2013;30(12):2136–40. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2013.843025.
Kosuth M, Mason SA, Wattenberg EV. Anthropogenic contamination of tap water, beer, and sea salt. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(4): e0194970. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0194970.
Karami A, Golieskardi A, Choo CK, Larat V, Galloway TS, Salamatinia B. The presence of microplastics in commercial salts from different countries. Sci Rep. 2017;7:46173. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46173.
Iniguez ME, Conesa JA, Fullana A. Microplastics in Spanish table salt. Sci Rep. 2017;7:8620. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09128-x.
Yang DQ, Shi HH, Li L, Li JN, Jabeen K, Kolandhasamy P. Microplastic pollution in table salts from China. Environ Sci Technol. 2015;49(22):13622–7. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b03163.
Selvam S, Manisha A, Venkatramanan S, Chung SY, Paramasivam CR, Singaraja C. Microplastic presence in commercial marine sea salts: a baseline study along Tuticorin Coastal salt pan stations, Gulf of Mannar, South India. Mar Pollut Bull. 2020;150: 110675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110675.
Ossmann BE, Sarau G, Holtmannspotter H, Pischetsrieder M, Christiansen SH, Dicke W. Small-sized microplastics and pigmented particles in bottled mineral water. Water Res. 2018;141:307–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.05.027.
Schymanski D, Goldbeck C, Humpf HU, Furst P. Analysis of microplastics in water by micro-Raman spectroscopy: release of plastic particles from different packaging into mineral water. Water Res. 2018;129:154–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.11.011.
Hernandez LM, Xu EG, Larsson HCE, Tahara R, Maisuria VB, Tufenkji N. Plastic teabags release billions of microparticles and nanoparticles into tea. Environ Sci Technol. 2019;53(21):12300–10. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b02540.
Cox KD, Covernton GA, Davies HL, Dower JF, Juanes F, Dudas SE. Human consumption of microplastics. Environ Sci Technol. 2019;53(12):7068–74. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b01517.
Schwabl P, Koppel S, Konigshofer P, Bucsics T, Trauner M, Reiberger T, Liebmann B. Detection of various microplastics in human stool: a prospective case series. Ann Intern Med. 2019;171(7):453–7. https://doi.org/10.7326/m19-0618.
Huang W, Song BA, Liang J, Niu QY, Zeng GM, Shen MC, Deng JQ, Luo YA, Wen XF, Zhang YF. Microplastics and associated contaminants in the aquatic environment: a review on their ecotoxicological effects, trophic transfer, and potential impacts to human health. J Hazard Mater. 2021;405: 124187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124187.
Laborda F, Trujillo C, Lobinski R. Analysis of microplastics in consumer products by single particle-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry using the carbon-13 isotope. Talanta. 2021;221:8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121486.
Bolea-Fernandez E, Rua-Ibarz A, Velimirovic M, Tirez K, Vanhaecke F. Detection of microplastics using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) operated in single-event mode. J Anal At Spectrom. 2020;35(3):455–60. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ja00379g.
Jimenez-Lamana J, Marigliano L, Allouche J, Grassl B, Szpunar J, Reynaud S. A novel strategy for the detection and quantification of nanoplastics by single particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Anal Chem. 2020;92(17):11664–72. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c01536.
Lin YE, Huang X, Liu Q, Lin ZY, Jiang GB. Thermal fragmentation enhanced identification and quantification of polystyrene micro/nanoplastics in complex media. Talanta. 2020;208: 120478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120478.
Peez N, Imhof W. Quantitative(1)H-NMR spectroscopy as an efficient method for identification and quantification of PVC, ABS and PA microparticles. Analyst. 2020;145(15):5363–71. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0an00879f.
Corami F, Rosso B, Bravo B, Gambaro A, Barbante C. A novel method for purification, quantitative analysis and characterization of microplastic fibers using micro-FTIR. Chemosphere. 2020;238: 124564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124564.
Primpke S, Lorenz C, Rascher-Friesenhausen R, Gerdts G. An automated approach for microplastics analysis using focal plane array (FPA) FTIR microscopy and image analysis. Anal Methods. 2017;9(9):1499–511. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ay02476a.
Karami A, Golieskardi A, Ho YB, Larat V, Salamatinia B. Microplastics in eviscerated flesh and excised organs of dried fish. Sci Rep. 2017;7:5473. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-05828-6.
Qiu QX, Tan Z, Wang JD, Peng JP, Li MM, Zhan ZW. Extraction, enumeration and identification methods for monitoring microplastics in the environment. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci. 2016;176:102–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2016.04.012.
Penalver R, Arroyo-Manzanares N, Lopez-Garcia I, Hernandez-Cordoba M. An overview of microplastics characterization by thermal analysis. Chemosphere. 2020;242: 125170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125170.
Fischer M, Scholz-Bottcher BM. Simultaneous trace identification and quantification of common types of microplastics in environmental samples by pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Environ Sci Technol. 2017;51(9):5052–60. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b06362.
Duemichen E, Eisentraut P, Celina M, Braun U. Automated thermal extraction-desorption gas chromatography mass spectrometry: a multifunctional tool for comprehensive characterization of polymers and their degradation products. J Chromatogr A. 2019;1592:133–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.01.033.
Fries E, Dekiff JH, Willmeyer J, Nuelle MT, Ebert M, Remy D. Identification of polymer types and additives in marine microplastic particles using pyrolysis-GC/MS and scanning electron microscopy. Environ Sci-Process Impacts. 2013;15(10):1949–56. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3em00214d.
Fischer M, Scholz-Bottcher BM. Microplastics analysis in environmental samples—recent pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method improvements to increase the reliability of mass-related data. Anal Methods. 2019;11(18):2489–97. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ay00600a.
Hermabessiere L, Himber C, Boricaud B, Kazour M, Amara R, Cassone AL, Laurentie M, Paul-Pont I, Soudant P, Dehaut A, Duflos G. Optimization, performance, and application of a pyrolysis-GC/MS method for the identification of microplastics. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018;410(25):6663–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1279-0.
Okoffo ED, Ribeiro F, O’Brien JW, O’Brien S, Tscharke BJ, Gallen M, Samanipour S, Mueller JF, Thomas KV. Identification and quantification of selected plastics in biosolids by pressurized liquid extraction combined with double-shot pyrolysis gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Sci Total Environ. 2020;715: 136924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136924.
Dierkes G, Lauschke T, Becher S, Schumacher H, Földi C, Ternes T. Quantification of microplastics in environmental samples via pressurized liquid extraction and pyrolysis-gas chromatography. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411(26):6959–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02066-9.
Hendrickson E, Minor EC, Schreiner K. Microplastic abundance and composition in Western Lake Superior as determined via microscopy, Pyr-GC/MS, and FTIR. Environ Sci Technol. 2018;52(4):1787–96. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b05829.
Primpke S, Fischer M, Lorenz C, Gerdts G, Scholz-Bottcher BM. Comparison of pyrolysis gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and hyperspectral FTIR imaging spectroscopy for the analysis of microplastics. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020;412(30):8283–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02979-w.
Kappler A, Fischer M, Scholz-Bottcher BM, Oberbeckmann S, Labrenz M, Fischer D, Eichhorn KJ, Voit B. Comparison of µ-ATR-FTIR spectroscopy and py-GCMS as identification tools for microplastic particles and fibers isolated from river sediments. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018;410(21):5313–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1185-5.
Rodrigues MO, Goncalves AMM, Goncalves FJM, Nogueira H, Marques JC, Abrantes N. Effectiveness of a methodology of microplastics isolation for environmental monitoring in freshwater systems. Ecol Indic. 2018;89:488–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.02.038.
Steinmetz Z, Kintzi A, Munoz K, Schaumann GE. A simple method for the selective quantification of polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene plastic debris in soil by pyrolysis-gas chromatography/massspectrometry. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2020;147: 104803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2020.104803.
Karami A, Golieskardi A, Choo CK, Romano N, Bin Ho Y, Salamatinia B. A high-performance protocol for extraction of microplastics in fish. Sci Total Environ. 2017;578:485–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.213.
Lares M, Ncibi MC, Sillanpaa M, Sillanpaa M. Intercomparison study on commonly used methods to determine microplastics in wastewater and sludge samples. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2019;26(12):12109–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04584-6.
Peixoto D, Pinheiro C, Amorim J, Oliva-Teles L, Guilhermino L, Vieira MN. Microplastic pollution in commercial salt for human consumption: a review. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci. 2019;219:161–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2019.02.018.
Kim JS, Lee HJ, Kim SK, Kim HJ. Global pattern of microplastics (MPs) in commercial food-grade salts: sea salt as an indicator of seawater MP pollution. Environ Sci Technol. 2018;52:12819–28. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b04180.
Lee H, Kunz A, Shim WJ, Walther BA. Microplastic contamination of table salts from Taiwan, including a global review. Sci Rep. 2019;9:10145. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46417-z.
Lee HJ, Song NS, Kim Ji-Su, Kim SK. Variation and uncertainty of microplastics in commercial table salts: critical review and validation. J Hazard Mater. 2021;402:123743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123743
Kooi M, Reisser J, Slat B, Ferrari FF, Schmid MS, Cunsolo S, Brambini R, Noble K, Sirks LA, Linders TEW, Schoeneich-Argent RI, Koelmans AA. The effect of particle properties on the depth profile of buoyant plastics in the ocean. Sci Rep. 2016;6:33882. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep33882.
Khuyen VTK, Le DV, Anh L, Fischer AR, Dornack C. Investigating the correlation of microplastic pollution between seawater and marine salt using micro-Raman spectroscopy. Front Mar Sci. 2021;8: 735975. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2021.735975.
Zhang Q, Xu EG, Li JN, Chen QQ, Ma LP, Zeng EY, Shi HH. A review of microplastics in table salt, drinking water, and air: direct human exposure. Environ Sci Technol. 2020;54(7):3740–51. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b04535.
World Health Organization (2012) Guideline: sodium intake for adults and children. https://www.who.int/nutrition/publications/guidelines/sodium_intake_printversion.pdf. Accessed 16 Mar 2022.
Vandermeersch G, Van Cauwenberghe L, Janssen CR, Marques A, Granby K, Fait G, Kotterman MJJ, Diogene J, Bekaert K, Robbens J, Devriese L. A critical view on microplastic quantification in aquatic organisms. Environ Res. 2015;143:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2015.07.016.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Chemical Specialist Team, Food Contact Material Team, and Inorganic Contaminants Team of the National Centre for Food Science, Singapore Food Agency for providing some standards and samples.
Funding
This research was carried out with financial support from the Singapore Food Agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Wu, Q., Ng, J. et al. Identification and quantification of common microplastics in table salts by a multi-technique-based analytical method. Anal Bioanal Chem 414, 6647–6656 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04226-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04226-w