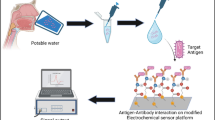
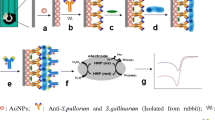
Abstract
Infectious diseases caused by Aeromonas salmonicida (A. salmonicida) have a huge impact and produce significant losses in aquaculture and fish farming. Fish pathogen early detection is a critical step for the rapid identification and prevention of these problems. This work presents a novel portable label-free ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for A. salmonicida detection in seawater. It consists of a fluidic integrated electrochemical-cell-chip (ECC) with independent chambers enclosing three electrochemical cells (ECs). Anti-A. salmonicida (AbSalm) antibodies were covalently attached to the gold surface of the microfabricated electrodes and were used for the sensitive detection of A. salmonicida. The antibody-antigen immunoreaction was studied by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and the surface functionalization was characterized by using quartz crystal microbalance (QCM), differential pulse voltammetry (DPV), and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The performance of the developed immunosensor, in terms of sensitivity, repeatability, and specificity, was also studied. The linear working range varied between 1 and 107 CFU mL−1, with a limit of detection (LOD) as low as 1 CFU mL−1. The suitability of the immunosensor for real sample detection was successfully demonstrated via recovery studies performed in spiked seawater samples. The proposed technology supports the use of low-cost and portable instrumentation that concedes the ultrasensitive, simple, and fast quantification of the A. salmonicida. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first portable sensing system for the detection of A. salmonicida in seawater samples, which provides a promising online monitoring platform for the detection of this bacterium in aquaculture facilities.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnemo M, Kavaliauskis A, Gjøen T. Effects of TLR agonists and viral infection on cytokine and TLR expression in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Dev Comp Immunol. 2014;46:139–45.
Salehi MR, Shadvar S, Sadeghian M, Doomanlou M, Abdollahi A, Manshadi SAD, Sardari A, Rahdar HA, Feizabadi MM. Endocarditis with Aeromonas salmonicida IDCases. 2019;18: e00625.
Austin B, Austin DA. Bacterial fish pathogens: disease of farmed and wild fish. 4th ed. Netherlands: Springer; 2007.
Reith ME, Singh RK, Curtis B, Boyd JM, Bouevitch A, Kimball J, Munholland J, Murphy C, Sarty D, Williams J. The genome of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida A449: insights into the evolution of a fish pathogen. BMC Genomics. 2008;9:1–15.
AQUAVETPLAN disease strategy furunculosis (Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida) version 2, https://www.awe.gov.au/sites/default/files/sitecollectiondocuments/animal-plant/aquatic/aquavetplan/furunc.pdf (accessed 2009). no date.
Boily F, Malcolm G, Johnson SC. Characterization of Aeromonas salmonicida and furunculosis to inform pathogen transfer risk assessments in British Columbia. DFO Can Sci Advis Sec Res Doc. 2019/016. vi + 39 p.
Toranzo AE. Report about fish bacterial diseases. Mediterr Aquac Lab Ed 2004; 49–89 Report about fish bacterial diseases. In : Alvarez-Pellitero P, Barja JL, Basurco B, Berthe F, Toranzo AE, editors. Mediterranean aquaculture diagnostic laboratories. Zaragoza : CIHEAM, 2004. p. 49–89 (Options Méditerranéennes : Série B. Etudes et Recherches; n. 49).
Coscelli GA, Bermúdez R, Losada AP, Faílde LD, Santos Y, Quiroga MI. Acute Aeromonas salmonicida infection in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Histopathological and immunohistochemical studies Aquaculture. 2014;430:79–85.
Toranzo AE, Barja JL. First report of furunculosis in turbot reared in floating cages in northwest Spain. Bull-Eur Assoc Fish Pathol. 1992;12:147–147.
Lago EP, Nieto TP, Farto R. Virulence factors of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida strains associated with infections in turbot Psetta maxima. Dis Aquat Organ. 2012;99:145–51.
Santos Y, García-Marquez S, Pereira PG, Pazos F, Riaza A, Silva R, El Morabit A, Ubeira FM. Efficacy of furunculosis vaccines in turbot, Scophthalmus maximus (L.): evaluation of immersion, oral and injection delivery. J Fish Dis. 2005;28:165–72.
Toranzo AE, Magariños B, Romalde JL. A review of the main bacterial fish diseases in mariculture systems. Aquaculture. 2005;246:37–61.
Torres-Corral Y, Girons A, González-Barreiro O, Seoane R, Riaza A, Santos Y. Effect of bivalent vaccines against Vibrio anguillarum and Aeromonas salmonicida subspecie achromogenes on health and survival of turbot. Vaccines. 2021;9:906.
Chapela M-J, Ferreira M, Ruiz-Cruz A, Martin-Varela I, Fernández-Casal J, Garrido-Maestu A. Application of real-time PCR for early diagnosis of diseases caused by Aeromonas salmonicida, Vibrio anguillarum, and Tenacibaculum maritimum in turbot: a field study. J Appl Aquac. 2018;30:76–89.
Balcazar JL, Vendrell D, de Blas I, Ruiz-Zarzuela I, Girones O, Muzquiz JL. Quantitative detection of Aeromonas salmonicida in fish tissue by real-time PCR using self-quenched, fluorogenic primers. J Med Microbiol. 2007;56:323–8.
Gulla S, Duodu S, Nilsen A, Fossen I, Colquhoun DJ. Aeromonas salmonicida infection levels in pre-and post-stocked cleaner fish assessed by culture and an amended qPCR assay. J Fish Dis. 2016;39:867–77.
Keeling SE, Brosnahan CL, Johnston C, Wallis R, Gudkovs N, McDonald WL. Development and validation of a real-time PCR assay for the detection of Aeromonas salmonicida. J Fish Dis. 2013;36:495–503.
Goodwin AE, Merry GE. Are all Koi ulcer cases associated with infection by atypical Aeromonas salmonicida? Polymerase chain reaction assays of Koi carp skin swabs submitted by hobbyists. J Aquat Anim Health. 2009;21:98–103.
Del Cerro A, Marquez I, Guijarro JA. Simultaneous detection of Aeromonas salmonicida, Flavobacterium psychrophilum, and Yersinia ruckeri, three major fish pathogens, by multiplex PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2002;68:5177–80.
Onuk EE, Ciftci A, Findik A, Durmaz Y. Development and evaluation of a multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of Flavobacterium psychrophilum, Yersinia ruckeri and Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida in culture fisheries. J Vet Sci. 2010;11:235–41.
Cesewski E, Johnson BN. Electrochemical biosensors for pathogen detection. Biosens Bioelectron. 2020;159: 112214.
Clark KD, Zhang C, Anderson JL. Sample preparation for bioanalytical and pharmaceutical analysis. Anal Chem. 2016;88:11262–70.
Kaya HO, Cetin AE, Azimzadeh M, Topkaya SN. Pathogen detection with electrochemical biosensors: advantages, challenges and future perspectives. J Electroanal Chem Lausanne Switz. 2021;882: 114989.
Dos Santos MB, Azevedo S, Agusil JP, Prieto-Simón B, Sporer C, Torrents E, Juárez A, Teixeira V, Samitier J. Label-free ITO-based immunosensor for the detection of very low concentrations of pathogenic bacteria. Bioelectrochemistry. 2015;101:146–52.
Dos Santos MB, Agusil JP, Prieto-Simón B, Sporer C, Teixeira V, Samitier J. Highly sensitive detection of pathogen Escherichia coli O157: H7 by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Biosens Bioelectron. 2013;45:174–80.
Katz E, Willner I. Probing biomolecular interactions at conductive and semiconductive surfaces by impedance spectroscopy: routes to impedimetric immunosensors, DNA-sensors, and enzyme biosensors. Electroanal Int J Devoted Fundam Pract Asp Electroanal. 2003;15:913–47.
Azzaroni O, Salvarezza RC. Chemisorbed self-assembled monolayers. Supramol Chem Mol Nanomater. 2012;7:3445–61.
Dos Santos MB, Queirós RB, Geraldes Á, Marques C, Vilas-Boas V, Dieguez L, Paz E, Ferreira R, Morais J, Vasconcelos V. Portable sensing system based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for the simultaneous quantification of free and total microcystin-LR in freshwaters. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;142: 111550.
Flauzino JMR, Nguyen EP, Yang Q, Rosati G, Panáček D, Brito-Madurro AG, Madurro JM, Bakandritsos A, Otyepka M, Merkoçi A. Label-free and reagentless electrochemical genosensor based on graphene acid for meat adulteration detection. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022;195: 113628.
K’Owino IO, Sadik OA. Impedance spectroscopy: a powerful tool for rapid biomolecular screening and cell culture monitoring. Electroanal Int J Devoted Fundam Pract Asp Electroanal. 2005;17:2101–13.
Ben Messaoud N, Ghica ME, Dridi C, Ben Ali M, Brett CM. Electrochemical sensor based on multiwalled carbon nanotube and gold nanoparticle modified electrode for the sensitive detection of bisphenol A. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2017;253:513–22.
Zhong M, Yang L, Yang H, Cheng C, Deng W, Tan Y, Xie Q, Yao S. An electrochemical immunobiosensor for ultrasensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 using CdS quantum dots-encapsulated metal-organic frameworks as signal-amplifying tags. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;126:493–500.
Hu W-C, Pang J, Biswas S, Wang K, Wang C, Xia X-H. Ultrasensitive detection of bacteria using a 2D MOF nanozyme-amplified electrochemical detector. Anal Chem. 2021;93:8544–52.
Tan X, Yang M, Zhu L, Gunathilaka G, Zhou Z, Chen P-Y, Zhang Y, Cheng MM-C. Ultrasensitive and selective bacteria sensors based on functionalized graphene transistors. IEEE Sens J. 2022;22:5514–20.
Bu S, Liu X, Wang Z, Wei H, Yu S, Li Z, Hao Z, Liu W, Wan J. Ultrasensitive detection of pathogenic bacteria by CRISPR/Cas12a coupling with a primer exchange reaction. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2021;347: 130630.
International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use ICH Harmonised Guideline. Validation of Analytical Procedures Q2(R2) 31 March 2022 EMA/CHMP/ICH/82072/2006
Efs EFSA. Food safety considerations of animal welfare aspects of husbandry systems for farmed fish-scientific opinion of the panel on biological hazards. EFSA J. 2008;6:867.
Rozen Y, Belkin S. Survival of enteric bacteria in seawater. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2001;25:513–29.
Ederveen J. A practical approach to biological assay validation. Progress report number 08090. Sponsored by the Dutch Ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning and the Environment (VROM), The Netherlands; 2010.
Du Y, Liu Y, Xiao P, Meng L, Liu P. Development and application of a quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection of Aeromonas salmonicida. J World Aquac Soc. 2017;48:574–82.
Fernández-Álvarez C, González SF, Santos Y. Development of a SYBR green I real-time PCR assay for specific identification of the fish pathogen Aeromonas salmonicida subspecies salmonicida. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016;100:10585–95.
Lian Z, Bai J, Hu X, Lü A, Sun J, Guo Y, Song Y. Detection and characterization of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida infection in crucian carp Carassius auratus. Vet Res Commun. 2020;44:61–72.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Centro Tecnológico Gallego de Acuicultura — CETGA, A Coruña, Spain, for providing water samples from the farm tanks.
Funding
This work was funded by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF), under the Interreg Atlantic Area funding programme [EAPA_595/2016, 2017].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Najib Ben Messaoud: investigation, methodology, formal analysis, validation, writing — original draft, review and editing. Marília dos Santos: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, formal analysis, writing — original draft, review and editing. Ana Vieira: investigation, formal analysis, writing — review and editing. Alejandro Garrido-Maestu: resources, methodology, writing — review and editing. Begoña Espiña: conceptualization, funding acquisition, project management, supervision, writing — review and editing. Raquel Queirós: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, formal analysis, project management, supervision, writing — original draft, review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Messaoud, N.B., dos Santos, M.B., Vieira, A. et al. A novel portable label-free electrochemical immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of Aeromonas salmonicida in aquaculture seawater. Anal Bioanal Chem 414, 6591–6600 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04219-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04219-9