Abstract
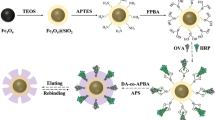
Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) can exhibit antibody-level affinity for target molecules. However, the nonspecific adsorption of non-imprinted regions for non-target molecules limits the application range of MIPs. Herein, we fabricated PEGylated boronate-affinity-oriented ellagic acid-imprinting magnetic nanoparticles (PBEMN), which first integrated boronate-affinity-oriented surface imprinting and sequential PEGylation for small molecule-imprinted MIPs. The resultant PBEMN possess higher adsorption capacity and faster adsorption rate for template ellagic acid (EA) molecules than the non-PEGylated control. To prove the excellent performance, the PBEMN were linked with hydrophilic boronic acid-modified/fluorescein isothiocyanate-loaded graphene oxide (BFGO), because BFGO could selectively label cis-diol-containing substances by boronate-affinity and output ultrasensitive fluorescent signals. Based on a dual boronate-affinity synergy, the PBEMN first selectively captured EA molecules by boronate-affinity-oriented molecular imprinted recognition, and then the EA molecules were further labeled with BFGO through boronate-affinity. The PBEMN linked BFGO (PBPF) strategy provided ultrahigh sensitivity for EA molecules with a limit of detection of 39.1 fg mL−1, resulting from the low nonspecific adsorption of PBEMN and the ultrasensitive fluorescence signal of BFGO. Lastly, the PBPF strategy was successfully employed in the determination of EA concentration in a spiked beverage sample with recovery and relative standard deviation in the range of 96.5 to 104.2% and 3.8 to 5.1%, respectively. This work demonstrates that the integration of boronate-affinity-oriented surface imprinting and sequential PEGylation may be a universal tool for improving the performance of MIPs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu D, Zhou JJ, Creyer MN, Yim W, Chen Z, Messersmith PB, Jokerst JV. Phenolic-enabled nanotechnology: versatile particle engineering for biomedicine. Chem Soc Rev. 2021;50(7):4432–83. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0cs00908c.
Hsu CC, Chao YY, Wang SW, Chen YL. Polyethylenimine-capped silver nanoclusters as fluorescent sensors for the rapid detection of ellagic acid in cosmetics. Talanta. 2019;204:484–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.06.047.
Zhang MW, Cui SM, Mao BY, Zhang QX, Zhao JX, Zhang H, Tang X, Chen W. Ellagic acid and intestinal microflora metabolite urolithin A: a review on its sources, metabolic distribution, health benefits, and biotransformation. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2022.2036693.
An JY, Wang LT, Lv MJ, Wang JD, Cai ZH, Wang YQ, Zhang S, Yang Q, Fu YJ. An efficiency strategy for extraction and recovery of ellagic acid from waste chestnut shell and its biological activity evaluation. Microchem J. 2021;160:7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.105616.
Lin CH, Zou ZF, Lei ZW, Wang L, Song YH. Fluorescent metal-organic frameworks MIL-101 (Al)-NH2 for rapid and sensitive detection of ellagic acid. Spectroc Acta Pt A-Molec Biomolec Spectr. 2020;242:7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.118739.
You Q, Chen F, Sharp JL, Wang X, You YR, Zhang CJ. High-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and evaporative light-scattering detector to compare phenolic profiles of muscadine grapes. J Chromatogr A. 2012;1240:96–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2012.03.086.
Guo YM, Zhao W. Hydrothermal synthesis of highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots with good biocompatibility and the application for sensing ellagic acid. Spectroc Acta Pt A-Molec Biomolec Spectr. 2020;240:7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.118580.
Peng LQ, Li Q, Chang YX, An MR, Yang R, Tan ZJ, Hao J, Cao J, Xu JJ, Hu SS. Determination of natural phenols in olive fruits by chitosan assisted matrix solid-phase dispersion microextraction and ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography with quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2016;1456:68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.06.011.
Cuartero M, Ortuno JA, Truchado P, Garcia MS, Tomas-Barberan FA, Albero MI. Voltammetric behaviour and square-wave voltammetric determination of the potent antioxidant and anticarcinogenic agent ellagic acid in foodstuffs. Food Chem. 2011;128(2):549–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.03.064.
Arabi M, Ostovan A, Li JH, Wang XY, Zhang ZY, Choo J, Chen LX. Molecular imprinting: green perspectives and strategies. Adv Mater. 2021;33(30):33. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202100543.
Xu JJ, Miao HH, Wang JX, Pan GQ. Molecularly imprinted synthetic antibodies: from chemical design to biomedical applications. Small. 2020;16(27):21. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201906644.
Wang S, Ye J, Bie Z, Liu Z (2014) Affinity-tunable specific recognition of glycoproteins via boronate affinity-based controllable oriented surface imprinting. Chemical Science 5 (3). doi:https://doi.org/10.1039/c3sc52986j
Bie Z, Chen Y, Ye J, Wang S, Liu Z. Boronate-affinity glycan-oriented surface imprinting: a new strategy to mimic lectins for the recognition of an intact glycoprotein and its characteristic fragments. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015;54(35):10211–5. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201503066.
Xing RR, Wang SS, Bie ZJ, He H, Liu Z. Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers specific to glycoproteins, glycans and monosaccharides via boronate affinity controllable-oriented surface imprinting. Nat Protoc. 2017;12(5):964–87. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2017.015.
Guo ZC, Xing RR, Zhao MH, Li Y, Lu HF, Liu Z. Controllable engineering and functionalizing of nanoparticles for targeting specific proteins towards biomedical applications. Adv Sci. 2021;8(24):12. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202101713.
Xing R, Guo Z, Lu H, Zhang Q, Liu Z. Molecular imprinting and cladding produces antibody mimics with significantly improved affinity and specificity. Science Bulletin. 2022;67(3):278–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2021.10.006.
Liu LK, Dong CY, Li XW, Li SW, Ma BF, Zhao BF, Li X, Liang Z, Yang KG, Zhang LH, Zhang YK. Antibody-free hydrogel with the synergistic effect of cell imprinting and boronate affinity: toward the selective capture and release of undamaged circulating tumor cells. Small. 2020;16(7):6. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201904199.
Zhang LX, Duan R, Yang YS, Peng C, Dong LY, Wang XH. Rapid and ultrasensitive detection of ellagic acid by integrating boronate-affinity controllable-oriented imprinted magnetic nanoparticle and boronic acid-modified/polyethylene glycol-coated allochroic-graphene oxide. Sens Actuator B-Chem. 2021;345:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130400.
Duan R, Peng C, Sun L, Zhang LX, Bai CC, Dong LY, Wang XH. Integrating boronate affinity controllable-oriented surface imprinting nylon wire and pH-triggered allochroic-graphene oxide for ultrasensitive detection of glycoprotein. Sens Actuator B-Chem. 2021;330:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.129310.
Bai CC, Wang D, Liu MX, Ma YR, Sun Y, Duan R, Dong LY, Wang XH. Ultrasensitive and specific detection of glycoprotein with boronic acid-modified/fluorescein isothiocyanate-loaded graphene oxide as signal amplification matrix. Sens Actuator B-Chem. 2021;344:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130327.
Pan ZH, Yu SS, Bai CC, Yin WY, Ma YR, Xue ZA, Lu QY, Dong LY, Wang XH. Poly(caffeic acid)-coated molecularly imprinted magnetic nanoparticles for specific and ultrasensitive detection of glycoprotein. Talanta. 2022;241:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123240.
Marszall MP, Baczek T, Kaliszan R. Reduction of silanophilic interactions in liquid chromatography with the use of ionic liquids. Anal Chim Acta. 2005;547(2):172–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2005.05.045.
Pochechueva T, Chinarev A, Bovin N, Fedier A, Jacob F, Heinzelmann-Schwarz V. PEGylation of microbead surfaces reduces unspecific antibody binding in glycan-based suspension array. J Immunol Methods. 2014;412:42–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2014.06.015.
Han X, Han WY, Zhang ST, Liu ZQ, Fu GQ. PEGylation of protein-imprinted nanocomposites sandwiching CdTe quantum dots with enhanced fluorescence sensing selectivity. RSC Adv. 2019;9(65):38165–73. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra08556d.
Yang X, Sun Y, Xiang Y, Qiu FT, Fu GQ. Controlled synthesis of PEGylated surface protein-imprinted nanoparticles. Analyst. 2019;144(18):5439–48. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9an01221d.
Luo Y, Bai CC, Liu MX, Wang D, Chen MY, Yu SS, Bu XY, Wang XH. PEGylation of boronate-affinity-oriented surface imprinting magnetic nanoparticles with improved performance. Talanta. 2022;238:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122992.
Zhao M, Chen X, Zhang H, Yan H, Zhang H. Well-defined hydrophilic molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres for efficient molecular recognition in real biological samples by facile RAFT coupling chemistry. Biomacromol. 2014;15(5):1663–75. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm500086e.
Montagna V, Haupt K, Gonzato C. RAFT coupling chemistry: a general approach for post-functionalizing molecularly imprinted polymers synthesized by radical polymerization. Polym Chem. 2020;11(5):1055–61. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9py01629e.
Moczko E, Guerreiro A, Piletska E, Piletsky S. PEG-stabilized core-shell surface-imprinted nanoparticles. Langmuir. 2013;29(31):9891–6. https://doi.org/10.1021/la401891f.
Pei XM, Zhang B, Tang J, Liu BQ, Lai WQ, Tang DP. Sandwich-type immunosensors and immunoassays exploiting nanostructure labels: a review. Anal Chim Acta. 2013;758:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2012.10.060.
Yilmaz E, Sarp G, Uzcan F, Ozalp O, Soylak M. Application of magnetic nanomaterials in bioanalysis. Talanta. 2021;229:20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122285.
Salman AD, Juzsakova T, Akos R, Ibrahim RI, Al-Mayyahi MA, Mohsen S, Abdullah TA, Domokos E. Synthesis and surface modification of magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles and its application in uptake of scandium (III) ions from aqueous media. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2021;28(22):28428–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12170-4.
Hashemi E, Mahdavi H, Khezri J, Razi F, Shamsara M, Farmany A. Enhanced gene delivery in bacterial and mammalian cells using pegylated calcium doped magnetic nanograin. Int J Nanomed. 2019;14:9879–91. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.S228396.
Kook JK, Phung VD, Koh DY, Lee SW. Facile synthesis of boronic acid-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for efficient dopamine extraction. Nano Converg. 2019;6(1):8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40580-019-0200-7.
Han YM, Ye ZJ, Chen LX, Xiao LH. Gold nanoparticles enumeration with dark-field optical microscope for the sensitive glycoprotein sandwich assay. Anal Chim Acta. 2020;1109:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.02.066.
He PY, Zhu HJ, Ma Y, Li N, Niu XH, Wei MB, Pan JM. Rational design and fabrication of surface molecularly imprinted polymers based on multi-boronic acid sites for selective capture glycoproteins. Chem Eng J. 2019;367:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.140.
Ying LL, Wang DY, Yang HP, Deng XY, Peng C, Zheng C, Xu B, Dong LY, Wang X, Xu L, Zhang YW, Wang XH. Synthesis of boronate-decorated polyethyleneimine-grafted porous layer open tubular capillaries for enrichment of polyphenols in fruit juices. J Chromatogr A. 2018;1544:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.02.044.
Li W, Zhang Q, Wang YJ, Ma YY, Guo ZC, Liu Z. Controllably prepared aptamer-molecularly imprinted polymer hybrid for high-specificity and high-affinity recognition of target proteins. Anal Chem. 2019;91(7):4831–7. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b00465.
Wang P, Zhu HJ, Liu JX, Ma Y, Yao JT, Dai XH, Pan JM. Double affinity integrated MIPs nanoparticles for specific separation of glycoproteins: a combination of synergistic multiple bindings and imprinting effect. Chem Eng J. 2019;358:143–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.168.
Li PF, Qin LT, Wang T, Dai LX, Li H, Jiang JX, Zhou JY, Li H, Cheng XQ, Lei FH. Preparation and adsorption characteristics of rosin-based polymer microspheres for berberine hydrochloride and separation of total alkaloids from coptidis rhizoma. Chem Eng J. 2020;392:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123707.
Gao RX, Mu XR, Hao Y, Zhang LL, Zhang JJ, Tang YH. Combination of surface imprinting and immobilized template techniques for preparation of core-shell molecularly imprinted polymers based on directly amino-modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles for specific recognition of bovine hemoglobin. J Mat Chem B. 2014;2(12):1733–41. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tb21684e.
Kong XJ, Zheng C, Lan YH, Chi SS, Dong Q, Liu HL, Peng C, Dong LY, Xu L, Wang XH. Synthesis of multirecognition magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer by atom transfer radical polymerization and its application in magnetic solid-phase extraction. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018;410(1):247–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0716-9.
Chen ZJ, Wu HL, Xiao ZL, Fu HJ, Shen YD, Luo L, Wang H, Lei HT, Hongsibsong S, Xu ZL. Rational hapten design to produce high-quality antibodies against carbamate pesticides and development of immunochromatographic assays for simultaneous pesticide screening. J Hazard Mater. 2021;412:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125241.
Kim TH, Shin HY, Park SY, Kim H, Chung DK. Development and validation of a method for determining the quercetin-3-O-glucuronide and ellagic acid content of common evening primrose (Oenothera biennis) by HPLC-UVD. Molecules. 2021;26(2):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020267.
Iwaoka Y, Suzuki S, Kato N, Hayakawa C, Kawabe S, Ganeko N, Uemura T, Ito H. Characterization and identification of bioactive polyphenols in the Trapa bispinosa Roxb. Pericarp Extract Molecules. 2021;26(19):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26195802.
Urun I, Attar SH, Sonmez DA, Gundesli MA, Ercisli S, Kafkas NE, Bandic LM, Duralija B. Comparison of polyphenol, sugar, organic acid, volatile compounds, and antioxidant capacity of commercially grown strawberry cultivars in Turkey. Plants-Basel. 2021;10(8):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10081654.
Wu SH, Li HB, Li GL, Lv N, Qi YJ. Metabolite identification of gut microflora-cassia seed interactions using UPLC-QTOF/MS. Exp Ther Med. 2020;19(5):3305–15. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2020.8585.
Song XC, Canellas E, Dreolin N, Nerin C, Goshawk J. Discovery and characterization of phenolic compounds in bearberry (Arctostaphylos uva-ursi) leaves using liquid chromatography-ion mobility-high-resolution mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem. 2021;69(37):10856–68. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c02845.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21605114) and Tianjin Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 17JCQNJC13300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, MY., Lang, JY., Bai, CC. et al. Construction of PEGylated boronate-affinity-oriented imprinting magnetic nanoparticles for ultrasensitive detection of ellagic acid from beverages. Anal Bioanal Chem 414, 6557–6570 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04213-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04213-1