Abstract
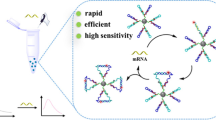
The accurate and sensitive detection of survivin mRNA is of great significance for cancer diagnosis and treatment. However, limited by the low-abundance mRNA in live cells, most strategies of survivin mRNA detection that were one-to-one signal-triggered model (one target triggered one signal) were inapplicable in practice. Here, we reported a binding-induced DNAzyme motor triggered by the survivin mRNA, which was a one-to-more signal-triggered model (one target triggered more signals), amplifying the detection signal and enhancing the sensitivity. The nanomotor is constructed by assembling several DNAzyme motor strands silenced by the blocker strands, and dozens of FAM-labeled substrate strands on a single gold nanoparticle (AuNP), forming three-dimensional DNA tracks. Through building the survivin mRNA bridge between the blocker and the DNAzyme motor strand, the binding-induced DNA nanomotor could be triggered by survivin mRNA. The operation of the DNAzyme motor was self-powered. And each walking step of the DNAzyme motor was fueled by DNAzyme-catalyzed substrate cleavage, along with the cleavage of the fluorescent molecule, resulting in autonomous and progressive walking along the AuNP-based tracks, and the fluorescence increase. The DNAzyme motor exhibited excellent sensitivity and remarkable specificity for survivin mRNA, providing the potential for cell image.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu M, Fu J, Hejesen C, Yang Y, Woodbury NW, Gothelf K, Liu Y. A DNA tweezer-actuated enzyme nanoreactor. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2127.
Yurke B, Turberfield AJ, Mills AP, Simmel FC, Neumann JL. A DNA-fuelled molecular machine made of DNA. Nature. 2000;406:605–8.
Cha TG, Pan J, Chen H, Salgado J, Li X, Mao C, Choi JH. A synthetic DNA motor that transports nanoparticles along carbon nanotubes. Nat Nanotech. 2014;9:39–43.
Yin P, Yan H, Daniell XG, Turberfield AJ, Reif JH. A unidirectional DNA walker that moves autonomously along a track. Angew Chem. 2004;116:5014–9.
Thomas JM, Yu HZ, Sen D. A mechano-electronic DNA switch. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:13738–48.
Wang F, Liu X, Willner I. DNA switches: from principles to applications. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2015;54:1098–129.
Bujold KE, Lacroix A, Sleiman HF. DNA nanostructures at the interface with biology. Chem. 2018;4:495–521.
Zhao J, Chu H, Zhao Y, Lu Y, Li L. A NIR light gated DNA nanodevice for spatiotemporally controlled imaging of microRNA in cells and animals. J Am Chem Soc. 2019;141:7056–62.
Zhang S, Chen C, Xue C, Chang D, Xu H, Salena BJ, Li Y, Wu ZS. Ribbon of DNA lattice on gold nanoparticles for selective drug delivery to cancer cells. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2020;59:14584–92.
Qing ZH, Xu JY, Hu JL, Zheng J, He L, Zou Z, Yang S, Tan WH, Yang RH. In situ amplification-based imaging of RNA in living cells. Angew Chem. 2019;131:11698–709.
Fong FY, Oh SS, Hawker CJ, Soh HT. In vitro selection of pH-activated DNA nanostructures. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2016;55:15258–62.
You M, Chen Y, Zhang X, Liu H, Wang R, Wang K, Williams KR, Tan W. An autonomous and controllable light-driven DNA walking device. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2012;51:2457–60.
Wang W, Satyavolu NSR, Wu Z, Zhang JR, Zhu JJ, Lu Y. Near-infrared photothermally activated DNAzyme-gold nanoshells for imaging metal ions in living cells. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2017;56:6798–802.
Peng HY, Newbigging AM, Reid MS, Uppal JS, Xu JY, Zhang HQ, Le XC. Signal amplification in living cells: a review of microRNA detection and imaging. Anal Chem. 2020;92:292–308.
Ratajczak K, Krazinski BE, Kowalczyk AE, Dworakowska B, Jakiela S, Stobiecka M. Hairpin−hairpin molecular beacon interactions for detection of survivin mRNA in malignant SW480 cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:17028–39.
Seferos DS, Giljohann DA, Hill HD, Prigodich AE, Mirkin CA. Nano-flares: probes for transfection and mRNA detection in living cells. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:15477–9.
Khan S, Burciu B, Filipe CDM, Li Y, Dellinger K, Didar TF. DNAzyme-based biosensors: immobilization strategies, applications, and future prospective. ACS Nano. 2021;15:13943–69.
Cheng X, Sun R, Yin L, Chai Z, Shi H, Gao M. Light-triggered assembly of gold nanoparticles for photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging of tumors in vivo. Adv Mater. 2017;29:1604894.
Zheng D, Seferos DS, Giljohann DA, Patel PC, Mirkin CA. Aptamer nano-flares for molecular detection in living cells. Nano Lett. 2009;9:3258–61.
Li N, Chang C, Pan W, Tang B. A multicolor nanoprobe for detection and imaging of tumor-related mRNAs in living cells. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2012;51:7426–30.
Kyriazi ME, Giust D, El-Sagheer AH, Lackie PM, Muskens OL, Brown T, Kanaras AG. Multiplexed mRNA sensing and combinatorial-targeted drug delivery using DNA-Gold nanoparticle dimers. ACS Nano. 2018;12:3333–40.
Huang J, He Y, Yang X, Wang K, Ying L, Quan K, Yang Y, Yin B. I-motif-based nano-flares for sensing pH changes in live cells. Chem Commun. 2014;50:15768–71.
Li J, Huang J, Yang X, Yang Y, Quan K, Xie N, Wu Y, Ma C, Wang K. Two-color-based nanoflares for multiplexed microRNAs imaging in live cells. Nanotheranostics. 2018;2:96–105.
Zhao XJ, Zhu ZC, Zou R, Wang LY, Gong H, Cai CQ. An enzyme-free three-dimensional DNA walker powered by catalytic hairpin assembly for H5N1 DNA ratiometric detection. Microchem J. 2021;17:106728.
Du H, Yang P, Hou X, Hou XD, Chen JB. Accelerating DNA nanomotor by branched DNAzyme for ultrasensitive optical detection of thrombin. Microchem J. 2018;139:260–7.
Liu Z, Zhao J, Zhang R, Han G, Zhang C, Liu B, Zhang Z, Han MY, Gao X. Cross-platform cancer cell identification using telomerase-specific spherical nucleic acids. ACS Nano. 2018;12:3629–37.
He X, Zeng T, Li Z, Wang G, Ma N. Catalytic molecular imaging of microRNA in living cells by DNA-programmed nanoparticle disassembly. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2016;55:3073–6.
Liang CP, Ma PQ, Liu H, Guo X, Yin BC, Ye BC. Rational engineering of a dynamic, entropy-driven DNA nanomachine for intracellular microRNA imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2017;56:9077–81.
Wang J, Huang J, Quan K, Li J, Wu Y, Wei Q, Yang X, Wang K. Hairpin-fuelled catalytic nanobeacons for amplified microRNA imaging in live cells. Chem Commun. 2018;54:10336–9.
Yang Y, Huang J, Yang X, Quan K, Wang H, Ying L, Xie N, Ou M, Wang K. Aptazyme-Gold nanoparticle sensor for amplified molecular probing in living cells. Anal Chem. 2016;88:5981–7.
Liu J, Cui M, Zhou H, Yang W. DNAzyme based nanomachine for in situ detection of microRNA in living cells. ACS Sensors. 2017;2:1847–53.
Yang Y, Huang J, Yang X, He X, Quan K, Xie N, Ou M, Wang K. Gold nanoparticle based hairpin-locked-DNAzyme probe for amplified miRNA imaging in living cells. Anal Chem. 2017;89:5850–6.
Hu N, Wang Y, Liu C, He M, Nie C, Zhang J, Yu Q, Zhao C, Chen T, Chu X. An enzyme-initiated DNAzyme motor for RNase H activity imaging in living cell. Chem Commun. 2020;56:639–42.
Wu Y, Huang J, Yang X, Yang Y, Quan K, Xie N, Li J, Ma C, Wang K. Gold nanoparticle loaded split-DNAzyme probe for amplified miRNA detection in living cells. Anal Chem. 2017;89:8377–83.
Peng H, Li XF, Zhang H, Le XC. A microRNA-initiated DNAzyme motor operating in living cells. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14378.
Liu C, Hu Y, Pan Q, Yi J, Zhang J, He M, He M, Chen T, Chu X. A microRNA-triggered self-powered DNAzyme walker operating in living cells. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;136:31–7.
Liu C, Hu Y, Pan Q, Yi J, Zhang J, He M, He M, Nie C, Chen T, Chu X. A photocontrolled and self-powered bipedal DNA walking machine for intracellular microRNA imaging. Chem Commun. 2020;56:3496–9.
Wu Z, Liu GQ, Yang XL, Jiang JH. Electrostatic nucleic acid nanoassembly enables hybridization chain reaction in living cells for ultrasensitive mRNA imaging. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137:6829–36.
Wang J, Wang DX, Tang AN, Kong DM. Highly integrated, biostable, and self-powered DNA motor enabling autonomous operation in living bodies. Anal Chem. 2019;91:5244–51.
Liu YH, Gao JL, Liu JX, Liu D, Fang WK, Zheng B, Tang HW, Li CY. Photo-gated and self-powered three-dimensional DNA motors with boosted biostability for exceptionally precise and efficient tracing of intracellular survivin mRNA. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021;190:113445.
Zhang H, Lai M, Zuehlke A, Peng H, Li XF, Le XC. Binding-induced DNA nanomachines triggered by proteins and nucleic acids. Angew Chem. 2015;127:14534–8.
Grabar KC, Freeman RG, Hommer MB, Natan MJ. Preparation and characterization of Au colloid monolayers. Anal Chem. 1995;67:735–43.
Gao P, Wei R, Chen Y, Liu X, Zhang J, Pan W, Li N, Tang B. Multicolor covalent organic framework-DNA nanoprobe for fluorescence imaging of biomarkers with different locations in living cells. Anal Chem. 2021;93:13734–41.
Piao Y, Liu F, Seo TS. A novel molecular beacon bearing a graphite nanoparticle as a nanoquencher for in situ mRNA detection in cancer cells. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2012;4:6785–9.
Ren K, Xu Y, Liu Y, Yang M, Ju H. A responsive “nano string light” for highly efficient mRNA imaging in living cells via accelerated DNA cascade reaction. ACS Nano. 2018;12:263–71.
Qian GS, Kang B, Zhang ZL, Li XL, Zhao W, Xu JJ, Chen HY. Plasmonic nanohalo optical probes for highly sensitive imaging of survivin mRNA in living cells. Chem Commun. 2016;52:11052–5.
Funding
Financial support from the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (21C0566, 21A0455), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2020JJ2012), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81874332), and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (2020JJ5593).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Deng, J., Yi, J. et al. A novel binding-induced DNAzyme motor triggered by survivin mRNA. Anal Bioanal Chem 414, 6167–6175 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04183-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04183-4