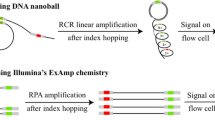
Abstract
The rapid development of high-throughput parallel sequencing poses new challenges for large-scale barcoding and sequencing library construction. Here, we present droplet combinational indexed transposon insertion sequencing (dCITI-Seq), in which samples are indexed by the direct insertion of index-containing adaptors through transposition. The random combination of two sets of adaptors with known barcodes and massively parallel transposition was realized via a robust droplet pairing and merging platform. This strategy potentially enlarges the indexing capacity and decreases index crosstalk. Also, dCITI-Seq exhibited a lower GC base preference than conventional in-tube transposition library preparation. With a custom bioinformatic processing, it could be further applied to large-scale single-cell sequencing.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Quail MA, Smith M, Jackson D, Leonard S, Skelly T, Swerdlow HP, et al. SASI-Seq: sample assurance Spike-Ins, and highly differentiating 384 barcoding for Illumina sequencing. Bmc Genomics. 2014;15:110.
Mezger A, Klemm S, Mann I, Brower K, Mir A, Bostick M, et al. High-throughput chromatin accessibility profiling at single-cell resolution. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):3647.
Shang L, Cheng Y, Zhao Y. Emerging droplet microfluidics. Chem Rev. 2017;117(12):7964–8040.
Salafi T, Zeming KK, Zhang Y. Advancements in microfluidics for nanoparticle separation. Lab Chip. 2017;17(1):11–33.
Jackson JM, Witek MA, Kamande JW, Soper SA. Materials and microfluidics: enabling the efficient isolation and analysis of circulating tumour cells. Chem Soc Rev. 2017;46(14):4245–80.
Du G, Fang Q, den Toonder JMJ. Microfluidics for cell-based high throughput screening platformsd-a review. Anal Chim Acta. 2016;903:36–50.
Trantidou T, Friddin MS, Salehi-Reyhani A, Ces O, Elani Y. Droplet microfluidics for the construction of compartmentalised model membranes. Lab Chip. 2018;18(17):2488–509.
Klein AM, Mazutis L, Akartuna I, Tallapragada N, Veres A, Li V, et al. Droplet barcoding for single-cell transcriptomics applied to embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2015;161(5):1187–201.
Zheng W, Zhao S, Yin Y, Zhang H, Needham DM, Evans ED, et al. Microbe-seq: high-throughput, single-microbe genomics with strain resolution, applied to a human gut microbiome. bioRxiv. 2020;422699. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.14.422699.
Lareau CA, Duarte FM, Chew JG, Kartha VK, Burkett ZD, Kohlway AS, et al. Droplet-based combinatorial indexing for massive-scale single-cell chromatin accessibility. Nat Biotechnol. 2019;37(8):916–24.
Macosko EZ, Basu A, Satija R, Nemesh J, Shekhar K, Goldman M, et al. Highly parallel genome-wide expression profiling of individual cells using nanoliter droplets. Cell. 2015;161(5):1202–14.
Delley CL, Abate AR. Modular barcode beads for microfluidic single cell genomics. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):10857.
Zheng H, Pomyen Y, Hernandez MO, Li C, Livak F, Tang W, et al. Single-cell analysis reveals cancer stem cell heterogeneity in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2018;68(1):127–40.
Muller S, Kohanbash G, Liu SJ, Alvarado B, Carrera D, Bhaduri A, et al. Single-cell profiling of human gliomas reveals macrophage ontogeny as a basis for regional differences in macrophage activation in the tumor microenvironment. Genome Biol. 2017;18:14.
Savage P, Blanchet-Cohen A, Revil T, Badescu D, Saleh SMI, Wang YC, et al. A targetable EGFR-dependent tumor-initiating program in breast cancer. Cell Rep. 2017;21(5):1140–9.
Sinha R, Stanley G, Gulati GS, Ezran C, Weissman IL. Index switching causes “spreading-of-signal” among multiplexed samples in Illumina HiSeq 4000 DNA sequencing. bioRxiv. 2017;125724. https://doi.org/10.1101/125724.
Lan F, Demaree B, Ahmed N, Abate AR. Single-cell genome sequencing at ultra-high-throughput with microfluidic droplet barcoding. Nat Biotechnol. 2017;35(7):640–6.
Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(14):1754–60.
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, et al. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(16):2078–9.
Okonechnikov K, Conesa A, Garcia-Alcalde F. Qualimap 2: advanced multi-sample quality control for high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2016;32(2):292–4.
Tarasov A, Vilella AJ, Cuppen E, Nijman IJ, Prins P. Sambamba: fast processing of NGS alignment formats. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(12):2032–4.
Li J, Lu N, Tao Y, Duan M, Qiao Y, Xu Y, et al. Accurate and sensitive single-cell-level detection of copy number variations by micro-channel multiple displacement amplification (μcMDA). Nanoscale. 2018;10(37):17933–41.
Delley CL, Abate ARJLoaC. Microfluidic particle zipper enables controlled loading of droplets with distinct particle types. Lab Chip. 2020;20(14):2465–72.
Qiao Y, Fu J, Yang F, Duan M, Huang M, Tu J, et al. An efficient strategy for a controllable droplet merging system for digital analysis. RSC Advances. 2018;8(60):34343–9.
Siebert PD, Chenchik A, Kellogg DE, Lukyanov KA, Lukyanov SA. An improved PCR method for walking in uncloned genomic DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995;23(6):1087–8.
Sidore AM, Lan F, Lim SW, Abate AR. Enhanced sequencing coverage with digital droplet multiple displacement amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(7):e66.
Li J, Lu N, Shi X, Qiao Y, Chen L, Duan M, et al. 1D-reactor decentralized MDA for uniform and accurate whole genome amplification. Anal Chem. 2017;89(19):10147–52.
Green B, Bouchier C, Fairhead C, Craig NL, Cormack BP. Insertion site preference of Mu, Tn5, and Tn7 transposons. Mobile DNA. 2012;3:3.
Lan F, Haliburton JR, Yuan A, Abate AR. Droplet barcoding for massively parallel single-molecule deep sequencing. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11784.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20211513), National Natural Science Foundation of China (61971125), and Six Talent Peaks Project of Jiangsu Province (2019-SWYY-004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Jing Tu. Investigation and methodology: Yi Qiao, Zheyun Xu, Naiyun Long. Data curation and formal analysis: Zheyun Xu, Na Lu. Resources and supervision: Jing Tu, Zuhong Lu. Writing—original draft: Jing Tu, Yi Qiao, Zheyun Xu. Writing, review, and editing: Jing Tu, Yi Qiao.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 15360 KB)
Supplementary file2 (MP4 6272 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tu, J., Qiao, Y., Xu, Z. et al. dCITI-Seq: droplet combinational indexed transposon insertion sequencing. Anal Bioanal Chem 414, 2661–2670 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-03902-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-03902-1