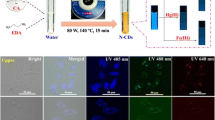
Abstract
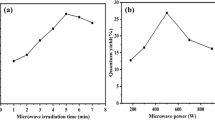
Microwave-assisted solid-phase synthesis method was simple, convenient, and fast, and herein adopted to produce nitrogen-doping carbon dots (N-CDs) in only 3 min. The N-CDs possessed high fluorescence quantum yield up to 15.9% with satisfactory stability to the environmental pH, ionic strength, and ultraviolet radiation. Particularly, the N-CDs had excellent dispersibility in both water and water-compatible organic solvents with similar fluorescence properties. Sunitinib, a small-molecule tyrosine inhibitor effective for some solid tumors, was found to quench the fluorescence of N-CDs in these media via the inner-filter effect. Hence, it was convenient to combine the proper sample pretreatment with the N-CD probe for sensing sunitinib avoiding the medium incompatibility problem. For rat plasma sample, salting-out liquid-liquid extraction was employed to minimize the sample matrix and concentrate the target sunitinib from aqueous to acetonitrile. The fluorescence detection of sunitinib was then achieved in acetonitrile by the addition of the proper amount of N-CDs. The method provided a good linearity of 0.1 μg/mL to 7 μg/mL with a limit of detection of 30 ng/mL, which met the requirement of the therapeutic drug monitoring of sunitinib. The developed method was potential for on-site detection of sunitinib.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Quintás-Cardama A, Cortes J. Molecular biology of bcr-abl1-positive chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2009;113:1619–30. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-03-144790.
Scheffler M, Gion PD, Doroshyenko O, Wolf J, Fuhr U. Clinical pharmacokinetics of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2011;50:371–403.
Soria J-C, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:113–25. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1713137.
Schmidinger M, Zielinski CC, Vogl UM, Bojic A, Bojic M, Schukro C, et al. Cardiac toxicity of sunitinib and sorafenib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:5204–12. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2007.15.6331.
Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 2010;141:1117–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.06.011.
Petrelli A, Giordano S. From single- to multi-target drugs in cancer therapy: when aspecificity becomes an advantage. Curr Med Chem. 2008;15:422–32. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986708783503212.
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:115–24. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa065044.
FDA (2006) Sutent® (sunitinib malate) capsules. Drugs@FDA: FDA-Approved Drugs. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2006/021968lbl.pdf. Accessed 26 January 2006.
Ma L, Li J, Zhao J, Liao H, Xu L, Shi Z-G. Penetrable silica microspheres for immobilization of bovine serum albumin and their application to the study of the interaction between imatinib mesylate and protein by frontal affinity chromatography. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016;408:805–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-9163-7.
Negreira N, López de Alda M, Barceló D. On-line solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of 17 cytostatics and metabolites in waste, surface and ground water samples. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1280:64–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.01.031.
Li J, Huang Y, Huang L, Ye L, Zhou Z, Xiang G, et al. Determination of imatinib mesylate and related compounds by field amplified sample stacking with large volume sample injection capillary electrophoresis. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012;70:26–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2012.05.010.
Ye L, Huang Y, Li J, Xiang G, Xu L. Nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis of imatinib mesylate and related substances. J Sep Sci. 2012;35:2108–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201200114.
Liao S, Huang Y, Zuo J, Yan Z. The interaction of CuInS2/ZnS/TGA quantum dots with tyrosine kinase inhibitor and its application. Luminescence. 2014;30:362–70. https://doi.org/10.1002/bio.2740.
Yan Z, Zhang Z, Chen J. Biomass-based carbon dots: synthesis and application in imatinib determination. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2016;225:469–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.10.107.
Zhang Z, Liu Y, Yan Z, Chen J. Simultaneous determination of temperature and erlotinib by novel carbon-based sensitive nanoparticles. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;255:986–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.08.153.
Hu Z, Jiao X-Y, Xu L. The N,S co-doped carbon dots with excellent luminescent properties from green tea leaf residue and its sensing of gefitinib. Microchem J. 2020;154:104588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104588.
Kashani HM, Madrakian T, Afkhami A. Highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots as a green, economical and facile sensor for the determination of sunitinib in real samples. New J Chem. 2020;41:6875–82. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nj00262a.
Zhang Z, Chen J, Yang Q, Lan K, Yan Z, Chen J. Eco-friendly intracellular microalgae synthesis of fluorescent CdSe QDs as a sensitive nanoprobe for determination of imatinib. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;263:625–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.02.169.
Zong J, Yang X, Trinchi A, Hardin S, Cole I, Zhu Y, et al. Carbon dots as fluorescent probes for “off–on” detection of Cu2+ and L-cysteine in aqueous solution. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014;51:330–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.07.042.
Long R, Tang C, Li T, Tong X, Tong C, Guo Y, et al. Dual-emissive carbon dots for dual-channel ratiometric fluorometric determination of pH and mercury ion and intracellular imaging. Microchim Acta. 2020;187:307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04287-7.
Simões EFC, Leitão JMM, da Sliva Esteves JCG. Carbon dots prepared from citric acid and urea as fluorescent probes for hypochlorite and peroxynitrite. Microchim Acta. 2016;183:1769–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1807-6.
Zhang H, Chen Y, Liang M, Xu L, Qi S, Chen H, et al. Solid-phase synthesis of highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots for sensitive and selective probing ferric ions in living cells. Anal Chem. 2014;86:9846–52. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac502446m.
Liang Y, Xu L, Tang K, Guan Y, Wang T, Wang H, et al. Nitrogen-doped carbon dots used as an “on–off–on” fluorescent sensor for Fe3+ and glutathione detection. Dyes Pigments. 2020;178:108358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2020.108358.
Khavlyuk PD, Stepanidenko EA, Bondarenko DP, Danilov DV, Koroleva AV, Baranov AV, et al. The influence of thermal treatment conditions (solvothermal versus microwave) and solvent polarity on the morphology and emission of phloroglucinol-based nitrogen-doped carbon dots. Nanoscale. 2020;13:3070–8. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nr07852b.
Pan L, Sun S, Zhang A, Jiang K, Zhang L, Dong C, et al. Truly fluorescent excitation-dependent carbon dots and their applications in multicolor cellular imaging and multidimensional sensing. Adv Mater. 2016;27:7782–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201503821.
He J, He Y, Chen Y, Lei B, Zhuang J, Xiao Y, et al. Solid-state carbon dots with red fluorescence and efficient construction of dual-fluorescence morphologies. Small. 2017;13:1700075. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201700075.
Sun S, Zhang L, Jiang K, Wu A, Lin H. Toward high-efficient red emissive carbon dots: facile preparation, unique properties, and applications as multifunctional theranostic agents. Chem Mater. 2016;28:8659–68. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b03695.
Zhang R, Liu Y, Yu L, Li Z, Sun S. Preparation of high-quality biocompatible carbon dots by extraction, with new thoughts on the luminescence mechanisms. Nanotechnology. 2013;24:225601. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/24/22/225601.
Kudo Y, Kino S, Matsuura Y. Vacuum ultraviolet absorption spectroscopy analysis of breath acetone using a hollow optical fiber gas cell. Sensors. 2020;21:478. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020478.
Gion PD, Kanefendt F, Lindauer A, Scheffler M, Doroshyenko O, Fuhr U, et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2011;50:551–603. https://doi.org/10.2165/11593320-000000000-00000.
Balan M, Trusohamn M, Ning FC, Jacob S, Pietras K, Eriksson U, et al. Noninvasive intravital high-resolution imaging of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours. Sci Rep. 2019;9:14636. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51093-0.
Shi Y, Sun Y, Qu W, Zhou L, Yue T, Yuan Y. Preparation of species-specific monoclonal antibody and development of fluorescence immunoassay based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer of carbon dots for accurate and sensitive detection of Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris in apple juice. Food Chem. 2021;347:129069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129069.
Liu J, Jiang M, Li G, Xu L, Xie M. Miniaturized salting-out liquid–liquid extraction of sulfonamides from different matrices. Anal Chim Acta. 2010;679:74–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2010.09.013.
Niknafs M, Kaviani R, Gharekhani A, Jouyban A, Shayanfar A. Salting-out liquid–liquid microextraction to the determination of mycophenolic acid in plasma samples. Chem Pap. 2020;74:1663–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-019-01018-y.
Padervand M, Ghaffari S, Attar H, Nejad MM. Reverse phase HPLC determination of sunitinib malate using UV detector, its isomerisation study, method development and validation. J Anal Chem. 2017;72:567–74. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934817050082.
Haouala A, Zanolari B, Rochat B, Montemurro M, Zaman K, Duchosal MA, et al. Therapeutic drug monitoring of the new targeted anticancer agents imatinib, nilotinib, dasatinib, sunitinib, sorafenib and lapatinib by LC tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B. 2009;877:1982–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2009.04.045.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support to this research by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2172019kfyRCPY112), Program for HUST Academic Frontier Youth Team (No. 2019QYTD09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Compliance with ethical standards
All the tests were performed in compliance with the relevant laws and institutional guidelines, and were approved by the ethics committee of Huazhong University of Science and Technology.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Z., Zhang, C., Yu, X. et al. Microwave-assisted solid-phase synthesis of nitrogen-doping carbon dot with good solvent compatibility and its sensing of sunitinib. Anal Bioanal Chem 413, 6435–6447 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03609-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03609-9