Abstract
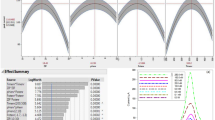
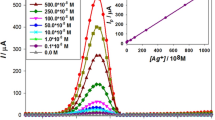
An electroanalytical sensor was constructed constituted on a carbon paste electrode (CPE) with a ZIF-67 modifier and devoted to the quantification of Tl(I). Several characterization tests including XRD, BET, FT-IR, SEM/EDS/mapping, TEM, impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and cyclic voltammetry (CV) were performed on the synthesized ZIF-67 nanocrystals and CPE matrix. Central composite design (CCD) was used to assess the impact of variables affecting the sensor response, including the weight percent of ZIF-67 (14%), the pH of the thallium accumulation solution (6.4), and accumulation time (315 s) as well as the accumulation potential (−1.2 V). The direct linear relationship between the sensor response and the concentration of Tl(I) is in the interval of 1.0×10−10 to 5.0×10-7 M (coefficient of determination = 0.9994). The detection limit is approximately 1.0 × 10−11 M. The right selection of the MOF makes this sensor highly resistant to the interference of other ions. High selectivity against common interferences in the measurement of thallium (such as Pb(II) and Cd(II)) is an important feature of this sensor. To confirm the performance of the prepared sensor, the amount of thallium in the real sample was determined.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Du L, Xing L, Zhang G, Sun S. Metal–organic framework derived carbon materials for electrocatalytic oxygen reactions: recent progress and future perspectives. Carbon. 2020;156:77–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.09.029.
Li J, Wang H, Yuan X, Zhang J, Wei CJ. Metal–organic framework membranes for wastewater treatment and water regeneration. Coord Chem Rev. 2020;404(213116):1–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2019.213116.
Anumah A, Louis H, Hamzate AT, Amusan OO, Pigveh AI, Akakuru OU, et al. Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs): recent advances in synthetic methodologies and some applications. Chem Method. 2019;3:283–305. https://doi.org/10.22034/CHEMM.2018.139807.1067.
Ramanayaka S, Vithanage M, Sarmah A, An T, Kim KH, Sik OY. Performance of metal–organic frameworks for the adsorptive removal of potentially toxic elements in a water system: a critical review. RSC Adv. 2019;9:34359–76. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra06879a.
Yang Y, Shijie Y, Jiannan D, Zipeng X. ZIF-67-derived CoO (tetrahedral Co2+)@nitrogen-doped porous carbon protected by oxygen vacancies-enriched SnO2 as highly active catalyst for oxygen reduction and Pt co-catalyst for methanol oxidation. Appl Catal B. 2019;259(118043):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118043.
Chu C, Rao S, Ma Z, Han H. Copper and cobalt nanoparticles doped nitrogen-containing carbon frameworks derived from CuO-encapsulated ZIF-67 as high-efficiency catalyst for hydrogenation of 4-nitrophenol. Appl Catal B. 2019;256(117792):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.117792.
Tuan DD, Lin KYA. Ruthenium supported on ZIF-67 as an enhanced catalyst for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Chem Eng J. 2018;351:48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.06.082.
Lin B, Wang A, Guo Y, Ding Y, Guo Y, Wang L, et al. Ambient temperature NO adsorber derived from pyrolysis of Co-MOF (ZIF-67). ACS Omega. 2019;4:9542–51. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b00763.
Song X, Yu J, Wei M, Li R, Pan X, Yang G, et al. Ionic liquids-functionalized zeolitic imidazolate framework for carbon dioxide adsorption. Materials. 2019;12(2361):1–8. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12152361.
Ethiraj J, Palla S, Reinsch H. Insights into high pressure gas adsorption properties of ZIF-67: experimental and theoretical studies. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020;294(109867):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109867.
Xuan X, Qian M, Han L, Wan L, Li Y, Lu T, et al. In-situ growth of hollow NiCo layered double hydroxide on carbon substrate for flexible supercapacitor. Electrochim Acta. 2019;321(134710):1–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.134710.
Cai P, Liu T, Zhang L, Cheng B, Yu J. ZIF-67 derived nickel cobalt sulfide hollow cages for high-performance supercapacitors. Appl Surf Sci. 2020;504(144501):1–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144501.
Gu J, Sun L, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Li X, Si H, et al. MOF-derived Ni-doped CoP@C grown on CNTs for high-performance supercapacitors. Chem Eng J. 2020;385(123454):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123454.
Xie Y, Chen L, Jin Q, Yun J, Liang X. MoS2-Co3S4 hollow polyhedrons derived from ZIF-67 towards hydrogen evolution reaction and hydrodesulfurization. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2019;44:24246–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.07.160.
Zhang Y, Yu H, Liu T, Li W, Hao X, Lu Q, et al. Highly sensitive detection of Pb2+ and Cu2+ based on ZIF-67/MWCNT/Nafion-modified glassy carbon electrode. Anal Chim Acta. 2020;1124:166–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.05.023.
Sohouli E, Sadeghpour Karimi M, Marzi Khosrowshahi E, Rahimi-Nasrabadi M, Ahmadi F. Fabrication of an electrochemical mesalazine sensor based on ZIF-67. Measurement. 2020;165:108140–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108140.
Jin Y, Li X, Ge C, Ma J, Li Y, Zhao E, et al. Carbon nanotube hollow polyhedrons derived from ZIF-8@ZIF-67 coupled to electro-deposited gold nanoparticles for voltammetric determination of acetaminophen. Microchim Acta. 2020;187(6):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3814-x.
Zhang H, Cai X, Zhao H, Sun W, Wang Z, Lan M. Enzyme-free electrochemical sensor based on ZIF-67 for the detection of superoxide anion radical released from SK-BR-3 cells. J Electroanal Chem. 2019;855(113653):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.113653.
Shang H, Xu H, Jin L, Chen C, Song T, Wang C, et al. Electrochemical-photoelectrochemical dual-mode sensing platform based on advanced Cu9S8/polypyrrole/ZIF-67 heterojunction nanohybrid for the robust and selective detection of hydrogen sulfide. Sensor Actuat B-chem. 2019;301(127060):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127060.
Xu Q, Chen Sh XJ, Duan X, Lu L, Tian Q, et al. Facile synthesis of hierarchical MXene/ZIF-67/CNTs composite for electrochemical sensing of luteolin. J. of Electroanal. Chem. 2021;880(114765):1–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.114765.
Sun S, Tang Y, Wu C, Wan C. Phytic acid functionalized ZIF-67 decorated graphene nanosheets with remarkably boosted electrochemical sensing performance. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2020;1107:55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.02.014.
Tu NTT, Sy PC, Thien TV, Toan TTT, Phong NH, Long HT, et al. Microwave-assisted synthesis and simultaneous electrochemical determination of dopamine and paracetamol using ZIF-67-modified electrode. J. Mater. Sci. 2019;54:11654–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03709-z.
Li D, Tian X, Wang Z, Guan Zh, Li X, Qiao H, et al. Multifunctional adsorbent based on metal-organic framework modified bacterial cellulose/chitosan composite aerogel for high efficient removal of heavy metal ion and organic pollutant. Chem. Eng. J. 2020; 383(123127):1−9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123127.
Zhao M, Reda AT, Zhang D. Reduced graphene oxide/ZIF-67 aerogel composite material for uranium adsorption in aqueous solutions. ACS Omega 2020; 5:8012−8022. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c00089.
Ma L, Zhang X, Ikram M, Ullah M, Wu H, Shi K. Controllable synthesis of an intercalated ZIF-67/EG structure for the detection of ultratrace Cd2+, Cu2+, Hg2+ and Pb2+ ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2020; 395(125216):1−12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125216.
Bhattacharjee S, Jang MS, Kwon HJ, Ahn WS. Zeolitic imidazolate frameworks: synthesis, functionalization, and catalytic/adsorption applications. Catal. Surv. Asia. 2014;18:101–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10563-014-9169-8.
Bhattacharjee S, Lee YR, Ahn WS. Post-synthesis functionalization of a zeolitic imidazolate structure ZIF-90: a study on removal of Hg (II) from water and epoxidation of alkenes. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2015;17:2575–82. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE02555E.
Silva M, Morante-Zarcero S, Pérez-Quintanilla D, Sierra I. Simultaneous determination of pindolol, acebutolol and metoprolol in waters by differential-pulse voltammetry using an efficient sensor based on carbon paste electrode modified with amino-functionalized mesostructured silica. Sensor Actuat B-chem. 2019;283:434–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.12.058.
Sherino B, Mohamad S. Nadiah Abdul Halim S, Suhana Abdul Manan N. Electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide on a new microporous Ni–metal organic framework material-carbon paste electrode. Sensor Actuat B-chem. 2018;254:1148–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.08.002.
Wang H, Hu Q, Meng Y, Jin Z, Fang Z, Fu Q, et al. Efficient detection of hazardous catechol and hydroquinone with MOF-rGO modified carbon paste electrode. J Hazard Mater. 2018;353:151–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.02.029.
De Benedetto GE, Di Masi S, Pennetta A, Malitesta C. Response surface methodology for the optimization of electrochemical biosensors for heavy metals detection. Biosens. 2019;9(26):1–11. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010026.
Korolev I, Altınkaya P, Halli P, Hannula PM, Yliniemi K, Lundström M. Electrochemical recovery of minor concentrations of gold from cyanide-free cupric chloride leaching solutions. J Clean Prod. 2018;186:840–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.177.
Shah A, Nisar A, Khan K, Nisar J, Niaz A, Naeem Ashiq M, et al. Amino acid functionalized glassy carbon electrode for the simultaneous detection of thallium and mercuric ions. Electrochim Acta. 2019;321(134658):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.134658.
Karbowska B, Rębis’ T, Milczarek G. Mercury-modified lignosulfonate-stabilized gold nanoparticles as an alternative material for anodic stripping voltammetry of thallium. Electroanalysis. 2017;29:2090–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201700090.
Ahmed SA, Bagchi D, Katouah HA, Hasan MN, Altass HM, Kumar PS. Enhanced water stability and photoresponsivity in metal-organic framework (MOF): a potential tool to combat drug-resistant bacteria. Sci Rep. 2019;9(19372):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-55542-8.
Banerjee R, Phan A, Wang B, Knobler C, Keeffe M, Yaghi OM, et al. High-throughput synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks and application to CO2 capture. Science. 2008;319:939–43. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1152516.
Asadi F, Azizi SN, Ghasemi S. A novel non-precious catalyst containing transition metal in nanoporous cobalt based metal-organic framework (ZIF-67) for electrooxidation of methanol. J Electroanal Chem. 2019;847(113181):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.05.063.
Zhou K, Mousavi B, Luo Zh, Phatanasri Sh, Chaemchuen S, Verpoort F. Characterization and properties of Zn/Co zeolitic imidazolate frameworks vs. ZIF-8 and ZIF-67, J Mater Chem. A. 2017;5:952–957. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta07860e.
Sundriyal S, Shrivastav V, Kaur H, Mishra S, Deep A. High-performance symmetrical supercapacitor with a combination of a ZIF-67/rGO composite electrode and a redox additive electrolyte. ACS. Omega. 2018;3:17348–58. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b02065.
Payra S, Challagulla S, Chakraborty C, Roy S. A hydrogen evolution reaction induced unprecedentedly rapid electrocatalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol over ZIF-67 compare to ZIF-8. J Electroanal Chem. 2019;853(113545):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.113545.
Truong T, Hoang TM. CHK Nguyen, Huynh QTN, Phan NTS. Expanding applications of zeolite imidazolate frameworks in catalysis: synthesis of quinazolines using ZIF-67 as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst. RSC Adv. 2015;5:24769–76. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra16168h.
Tan TTY, Cham JTM, Reithofer MR, Andy Hor TS, Chin JM. Motorized Janus metal organic framework crystals. Chem Commun. 2014;50(15175):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cc06952h.
Qian J, Sun F, Qin L. Hydrothermal synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 (ZIF-67) nanocrystals. Mater Lett. 2012;82:220–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2012.05.077.
Ammar M, Jiang S, Ji S. Heteropoly acid encapsulated into zeolite imidazolate framework (ZIF-67) cage as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for Friedel–Crafts acylation. J Solid State Chem. 2016;233:303–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2015.11.014.
Dong Y, Duan C, Sheng Q, Zheng J. Preparation of Ag@zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 at room temperature for electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide. Analyst. 2019;144:521–9. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8an01641k.
Song F, Cao Y, Zhao Y, Jiang R, Xu Q, Yan J, et al. Ion-exchanged ZIF-67 synthesized by one-step method for enhancement of CO2 adsorption. J Nanomater. 2020;2020:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1508574.
Li X, Niu Z, Jiang J, Ai L. Cobalt nanoparticles embedded in porous N-rich carbon as an efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for water splitting. J Mater Chem A. 2016;4:3204–9. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta00223d.
Li X, Qiao Y, Wang C, Shen T, Zhang X, Wang H, et al. MOF-derived Co/C nanocomposites encapsulated by Ni(OH)2 ultrathin nanosheets shell for high performance supercapacitors. J Alloys Compd. 2019;770:803–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.08.164.
Wang Y, Hou P, Wang Z, Kang P. Zinc imidazolate metal–organic frameworks (ZIF-8) for electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO. Chem Phys Chem. 2017;18:3142–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.201700716.
Li Y, Huangfu Ch DH, Liu W, Li Y, Ye J. Electrochemical behavior of metal–organic framework MIL-101 modified carbon paste electrode: an excellent candidate for electroanalysis. J Electroanal Chem. 2013;709:65–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2013.09.017.
Xu Q, Wang Y, Jin G, Jin D, Li K, Mao A, et al. Photooxidation assisted sensitive detection of trace Mn2+ in tea by NH2-MIL-125 (Ti) modified carbon paste electrode. Sensor Actuat B-chem. 2014;201:274–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.05.017.
Meng W, Wen Y, Dai L, He Z, Wang L. A novel electrochemical sensor for glucose detection based onAg@ZIF-67 nanocomposite. Sensor Actuat B-chem. 2018;260:852–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.01.109.
Jin Yf, Ge Chy, Li Xb, Zhang M, Xu Gr, Li Dh. A sensitive electrochemical sensor based on ZIF-8–acetylene black–chitosan nanocomposites for rutin detection. RSC Adv. 2018;8:32740–32746. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra06452k.
Hu X, Lou X, Li C, Chen Q, Yang Q, Hu B. Amorphization and disordering of metal–organic framework materials for rechargeable batteries by thermal treatment. New J Chem. 2017;41:6415–9. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NJ04021G.
Wang Y, Wu Y, Xie J, Hu X. Metal–organic framework modified carbon paste electrode for lead sensor. Sensor Actuat B-chem. 2013;177:1161–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.12.048.
Wang Y, Ge H, Wu Y, Ye G, Chen H, Hu X. Construction of an electrochemical sensor based on amino-functionalized metal-organic frameworks for differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetric determination of lead. Talanta. 2014;129:100–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.05.014.
Du XD, Wang CC, Liu JG, Zhao XD, Zhong J, Li YX, et al. Extensive and selective adsorption of ZIF-67 towards organic dyes: performance and mechanism. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017;506:437–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.07.073.
Mostafazadeh N, Ghoreyshi AA, Pirzadeh K. Optimization of solvothermally synthesized ZIF-67 metal organic framework and its application for Cr (VI) adsorption from aqueous solution. Iranian Journal of Chemical Engineering. 2018;15(4):27–47.
Wang Y, Du K, Chen Y, Li Y, He X. Electrochemical determination of lead based on metal-organic framework MIL-101(Cr) by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry. Anal Methods. 2016;8:32633–269. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6AY00183A.
Worrall SD, Mann H, Rogers A, Bissett MA, Attfield MP, Dryfe RAW. Electrochemical deposition of zeolitic imidazolate framework electrode coatings for supercapacitor electrodes. Electrochim Acta. 2016;197:228–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.02.145.
Nasiri-Majd M, Taher MA, Fazelirad H. Synthesis and application of nano-sized ionic imprinted polymer for the selective voltammetric determination of thallium. Talanta. 2015;144:204–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.05.058.
Asadi F, Azizi SN, Ghasemi S. Preparation of Ag nanoparticles on nano cobalt-based metal organic framework (ZIF-67) as catalyst support for electrochemical determination of hydrazine. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. 2019;30(6):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00834-y.
Hosseinian A, Amjad AH, Hosseinzadeh-Khanmiri R, Ghorbani-Kalhor E, Babazadeh M, Vessally E. Nanocomposite of ZIF-67 metal–organic framework with reduced graphene oxide nanosheets for high-performance supercapacitor applications. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. 2017;28:18040–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7747-z.
Kielland J. Individual activity coefficients of ions in aqueous solutions. J Am Chem Soc. 1937;59:1675–8. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01288a032.
Jorge EO, Neto MMM, Rocha MM Rocha. A mercury-free electrochemical sensor for the determination of thallium(I) based on the rotating-disc bismuth film electrode. Talanta. 2007;72:1392–1399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2007.01.047.
Kahlert H, Komorsky-Lovrić Š, Hermes M, Scholz F. A Prussian blue-based reactive electrode (reactrode) for the determination of thallium ions. Fresenius J Anal Chem. 1996;356:204–8.
Lu TH, Yang HY, Wen SI. Square-wave anodic stripping voltammetric determination of thallium(I) at a Nafion:mercury film modified electrode. Talanta. 1999;49:59–68.
Mohammadi S, Taher MA, Beitollahi H. Mercury nanodroplets immobilized on the surface of a chitosan-modified carbon paste electrode as a new thallium sensor in aqueous samples. J Electrochem Soc. 2017;164(9):476–81. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.1581709jes.
Mnyipika SH, Nomngongo phN. Square wave anodic stripping voltammetry for simultaneous determination of trace Hg (II) and Tl(I) in surface water samples using SnO2@MWCNTs modified glassy carbon electrode. Int J Electrochem Sci. 2017;12:4811–4827. https://doi.org/10.20964/2017.06.36
Khieu DQ, Thanh MT, Thien TV, Phong NH, Van DH, Du PD, et al. Synthesis and voltammetric determination of Pb(II) using a ZIF-8-based electrode. Hindawi, J Chem. 2018;2018:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5395106.
Bagheri H, Afkhami A, Shirzadmehr A, Khoshsafar H. A new nano-composite modified carbon paste electrode as a high performance potentiometric sensor for nanomolar Tl (I) determination. J Mol Liq. 2014;197:52–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2014.04.023.
Cheraghi S, Taher MA, Fazelirad H. Voltammetric sensing of thallium at a carbon paste electrode modified with a crown ether. Microchim Acta. 2013;180:1157–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1038-z.
Tarasova VA. Voltammetric determination of thallium(I) at a mechanically renewed Bi-graphite electrode. J Anal Chem. 2007;62:157–60. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934807020104.
Dong H, Zheng H, Lin L, Ye B. Determination of thallium and cadmium on a chemically modified electrode with Langmuir-Blodgett film of p-allylcalix[4]arene. Sensor Actuat B-chem. 2006;115:303–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2005.09.017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All participants who provided hair and urine samples were given full information about this study and their consent was obtained. This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committees of Islamic Azad University- Khomeinishahr Branch, Iran, (Approval ID: IR.IAU.KHSH.REC.1400.008).
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 5349 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hashemi, F., Zanganeh, A.R., Naeimi, F. et al. Construction of a Tl(I) voltammetric sensor based on ZIF-67 nanocrystals: optimization of operational conditions via response surface design. Anal Bioanal Chem 413, 5215–5226 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03493-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03493-3