Abstract
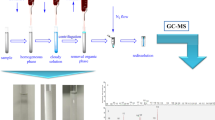
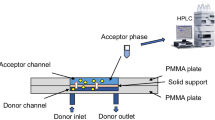
In this work, hippuric acid (log P = 0.5), anthranilic acid (log P = 1.3), ketoprofen (log P = 3.6), and naproxen (log P = 3.0) were simultaneously extracted by a green microfluidic device based on the principles of liquid-phase microextraction (LPME). Different deep eutectic solvents (DESs) were investigated as supported liquid membrane (SLM), and a mixture of camphor and menthol as eutectic solvents in the molar ratio 1:1 was found to be highly efficient for the simultaneous extraction of non-polar and polar acidic drugs. LPME was conducted for 6 min per sample. Urine sample was delivered to the system at 1 μL min−1, and target analytes were extracted exhaustively (75–100% recovery) across the DES SLM, and into pure aqueous phosphate buffer pH 11.0 delivered as acceptor at 1 μL min−1. The acceptor was analyzed with liquid chromatography-UV detection. Interestingly, the DES enabled extraction of both the polar and non-polar model analytes at the same time; all chemicals were green and non-hazardous, and the chemical waste was less than 1 mg per sample.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Petersen NJ, Jensen H, Hansen SH, Foss ST, Snakenborg D, Pedersen-Bjergaard S. On-chip electro membrane extraction. Microfluid Nanofluid. 2010;9:881–8.
Sikanen T, Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Jensen H, Kostiainen R, Rasmussen KE, Kotiaho T. Implementation of droplet-membrane-droplet liquid-phase microextraction under stagnant conditions for lab-on-a-chip applications. Anal Chim Acta. 2010;658:133–40.
Asl YA, Yamini Y, Seidi S. Development of a microfluidic-chip system for liquid–phase microextraction based on two immiscible organic solvents for the extraction and preconcentration of some hormonal drugs. Talanta. 2016;160:592–9.
Petersen NJ, Foss ST, Jensen H, Hansen SH, Skonberg C, Snakenborg D, et al. On-chip electro membrane extraction with online ultraviolet and mass spectrometric detection. Anal Chem. 2011;83:44–51.
Petersen NJ, Pedersen JS, Poulsen NN, Jensen H, Skonberg C, Hansen SH, et al. On-chip electromembrane extraction for monitoring drug metabolism in real time by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Analyst. 2012;137:3321–7.
Wang X, Saridara C, Mitra S. Microfluidic supported liquid membrane extraction. Anal Chim Acta. 2005;543:92–8.
Ramos Payán M. Liquid - phase microextraction and electromembrane extraction in millifluidic devices: a tutorial. Anal Chim Acta. 2019;1080:12–21.
Seidi S, Yamini Y, Rezazadeh M, Esrafili A. Low-voltage electrically-enhanced microextraction as a novel technique for simultaneous extraction of acidic and basic drugs from biological fluids. J Chromatogr A. 2012;1243:6–13.
Huang C, Seip KF, Gjelstad A, Shen X, Pedersen-Bjergaard S. Combination of electromembrane extraction and liquid-phase microextraction in a single step: simultaneous group separation of acidic and basic drugs. Anal Chem. 2015;87:6951–7.
Karami M, Yamini Y. On-disc electromembrane extraction-dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction: a fast and effective method for extraction and determination of ionic target analytes from complex biofluids by GC/MS. Anal Chim Acta. 2020;1105:95–104.
Vakh C, Likanov G, Bulatov A. Stir flat sheet membrane liquid phase microextraction for the selective chemiluminescence determination of ofloxacin and fleroxacin in human urine. Microchem J. 2021;163:105913.
Maghsoudi M, Nojavan S, Alexovič M, Tabani H. Two-phase agarose gel-electromembrane extraction: effect of organic solvent as an acceptor phase in electroendosmosis flow phenomenon. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2021;195:113862.
Rahimi A, Nojavan S, Maghsoudi M. Analysis of basic drugs in biological samples using dynamic single-interface hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction combined with fast electromembrane extraction. Microchem J. 2020;157:105001.
Mahdavi P, Nojavan S, Asadi S. Sugaring-out assisted electromembrane extraction of basic drugs from biological fluids: improving the efficiency and stability of extraction system. J Chromatogr A. 2019;1608:460411.
Sobhi HR, Ghambarian M, Behbahani M, Esrafili A. Application of modified hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction in conjunction with chromatography-electron capture detection for quantification of acrylamide in waste water samples at ultra-trace levels. J Chromatogr A. 2017;1487:30–5.
Ramos Payán M, López MÁ, Fernández-Torres R, Callejón Mochón M, Gómez Ariza JL. Application of hollow fiber-based liquid-phase microextraction (HF-LPME) for the determination of acidic pharmaceuticals in wastewaters. Talanta. 2010;82:854–8.
Drouin N, Rudaz S, Schappler J. New supported liquid membrane for electromembrane extraction of polar basic endogenous metabolites. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018;159:53–9.
Ramos Payán M, López MÁ, Fernández Torres R, González JAO, Callejón Mochón M. Hollow fiber-based liquid phase microextraction (HF-LPME) as a new approach for the HPLC determination of fluoroquinolones in biological and environmental matrices. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2011;55:332–41.
Tabani H, Fakhari AR, Shahsavani A. Simultaneous determination of acidic and basic drugs using dual hollow fibre electromembrane extraction combined with CE. Electrophoresis. 2013;34:269–76.
Li B, Petersen NJ, Ramos Payán M, Hansen SH, Pedersen-Bjergaard S. Design and implementation of an automated liquid-phase microextraction-chip system coupled on-line with high performance liquid chromatography. Talanta. 2014;120:224–9.
Ramos Payán M, Maspoch S, Llobera A. A simple and fast double-flow microfluidic device based liquid-phase microextraction (DF-μLPME) for the determination of parabens in water samples. Talanta. 2017;165:496–501.
Santigosa-Murillo E, Muñoz-Berbel X, Maspoch S, Muñoz M, Ramos Payán M. Impedance model for voltage optimization of parabens extraction in an electromembrane millifluidic device. J Chromatogr A. 1625;2020:461270.
Santigosa-Murillo E, Maspoch S, Ramos Payán M. Liquid phase microextraction integrated into a microchip device for the extraction of fluoroquinolones from urine samples. Microchem J. 2019;145:280–6.
Ramos Payán M, Maspoch S, Llobera A. An effective microfluidic based liquid-phase microextraction device (μLPME) for extraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from biological and environmental samples. Anal Chim Acta. 2016;946:56–63.
Ramos Payán M, Santigosa-Murillo E, Coello J, López MÁ. A comprehensive study of a new versatile microchip device based liquid phase microextraction for stopped-flow and double-flow conditions. J Chromatogr A. 2018;1556:29–36.
Ramos Payán M, Jensen H, Petersen NJ, Hansen SH, Pedersen-Bjergaard S. Liquid-phase microextraction in a microfluidic-chip – high enrichment and sample clean-up from small sample volumes based on three-phase extraction. Anal Chim Acta. 2012;735:46–53.
Kamankesh M, Mollahosseini A, Mohammadi A, Seidi S. Haas in grilled meat: determination using an advanced lab-on-a-chip flat electromembrane extraction coupled with on-line HPLC. Food Chem. 2020;311:125876.
Asl YA, Yamini Y, Seidi S. A novel approach to the consecutive extraction of drugs with different properties via on chip electromembrane extraction. Analyst. 2016;141:311–8.
Baharfar M, Yamini Y, Seidi S, Arain MB. Approach for downscaling of electromembrane extraction as a lab on-a-chip device followed by sensitive red-green-blue detection. Anal Chem. 2018;90:8478–86.
Karami M, Yamini Y, Abdossalami Asl Y, Rezazadeh M. On-chip pulsed electromembrane extraction as a new concept for analysis of biological fluids in a small device. J Chromatogr A. 2017;1527:1–9.
Asl YA, Yamini Y, Seidi S, Rezazadeh M. Simultaneous extraction of acidic and basic drugs via on-chip electromembrane extraction. Anal Chim Acta. 2016;937:61–8.
Ramos Payán M, Santigosa-Murillo E, Fernández Torres R, López MÁ. A new microchip design. A versatile combination of electromembrane extraction and liquid-phase microextraction in a single chip device. Anal Chem. 2018;90:10417–24.
Zarghampour F, Yamini Y, Baharfar M, Faraji M. Simultaneous extraction of acidic and basic drugs via on-chip electromembrane extraction using a single-compartment microfluidic device. Analyst. 2019;144:1159–66.
Román C, Martín Valero MJ, Fernández Torres R, López MÁ. Use of polymer inclusion membranes (PIMs) as support for electromembrane extraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and highly polar acidic drugs. Talanta. 2018;179:601–7.
Hansen FA, Santigosa-Murillo E, Ramos Payán M, Muñoz M, Leere Øiestad E, Pedersen-Bjergaard S. Electromembrane extraction using deep eutectic solvents as the liquid membrane. Anal Chim Acta. 2021;1143:109–16.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Agencia de Gestió d’Ajusts Universitaris i the Recerca (2017-SGR-329). Elia Santigosa thanks Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) for the PIF fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics declarations
The urine sample was provided voluntarily and with informed consent.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santigosa, E., Pedersen-Bjergaard, S., Muñoz, M. et al. Green microfluidic liquid-phase microextraction of polar and non-polar acids from urine. Anal Bioanal Chem 413, 3717–3723 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03320-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03320-9