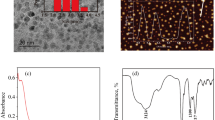
Abstract
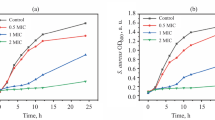
Novel carbon dots (CDs) were synthesized by a one-pot hydrothermal approach using ampicillin as a precursor, and the as-prepared CDs exhibited a high quantum yield (23%). The CDs were found to possess abundant surface functional groups, thus providing good permeability to the cell, and the antibacterial activity of CDs was evaluated. S. aureus and L. monocytogenes were selected as model bacteria, and our results showed that the CDs exhibited antibacterial activity against S. aureus and L. monocytogenes under visible light illumination, even at low concentrations. The antibacterial mechanism is believed to be the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) from CDs under visible light irradiation, which attacked the bacterial cell membranes, resulting in the death of the bacteria. In addition, because of the multicolor fluorescence properties of CDs, staining of S. aureus and L. monocytogenes obtained multicolor fluorescence images at different excitation wavelengths. Based on these results, CDs are a promising candidate material for biological applications.

Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zeng XK, Wang ZY, Meng N, McCarthy DT, Deletic A, Pan JH, et al. Highly dispersed TiO2 nanocrystals and carbon dots on reduced graphene oxide: ternary nanocomposites for accelerated photocatalytic water disinfection. Appl Catal B Environ. 2017;202:33–41.
Wang WJ, Li GY, Xia DH, An TC, Zhao HJ, Wong PK. Photocatalytic nanomaterials for solar-driven bacterial inactivation: recent progress and challenges. Environ Sci Nano. 2017;4(4):782–99.
Li H, Huang J, Song YX, Zhang ML, Wang HB, Lu F, et al. Degradable carbon dots with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(32):26936–46.
Liu WD, Liu JL, Triplett L, Leach JE, Wang GL. Novel insights into rice innate immunity against bacterial and fungal pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2014;52:213–41.
Moradi M, Kalantary RR, Esrafili A, Jafari AJ, Gholami M. Visible light photocatalytic inactivation of Escherichia coli by natural pyrite assisted by oxalate at neutral pH. J Mol Liq. 2017;248:880–9.
Wang R, Wang X, Sun Y. One-step synthesis of self-doped carbon dots with highly photoluminescence as multifunctional biosensors for detection of iron ions and pH. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017;241:73–9.
Wang H, Liu S, Xie Y, Bi J, Li Y, Song Y, et al. Facile one-step synthesis of highly luminescent N-doped carbon dots as efficient fluorescence probe for chromium (VI) detection based on inner filter effect. New J Chem. 2018;42(5):3729–35.
Dang DK, Chandrasekaran S, Ngo YLT, Chung JS, Kim EJ, Hur SH. One pot solid-state synthesis of highly fluorescent N and S co-doped carbon dots and its use as fluorescent probe for Ag+ detection in aqueous solution. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;255:3284–91.
Naaz S, Poddar S, Bayen SP, Mondal MK, Roy D, Mondal SK, et al. Tenfold enhancement of fluorescence quantum yield of water soluble silver nanoclusters for nano-molar level glucose sensing and precise determination of blood glucose level. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;255:332–40.
Jijie R, Barras A, Bouckaert J, Dumitrascu N, Szunerits S, Boukherroub R. Enhanced antibacterial activity of carbon dots functionalized with ampicillin combined with visible light triggered photodynamic effects. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;170:347–54.
Zhang LY, Wang DH, Huang HW, Liu LF, Zhou Y, Xia XD, et al. Preparation of gold-carbon dots and Ratiometric fluorescence cellular imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(10):6646–55.
Guo Y, Cao F, Li Y. Solid phase synthesis of nitrogen and phosphor co-doped carbon quantum dots for sensing Fe3+ and the enhanced photocatalytic degradation of dyes. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017;255:1105–11.
Jhonsi MA, Ananth DA, Nambirajan G, Sivasudha T, Yamini R, Bera S, et al. Antimicrobial activity, cytotoxicity and DNA binding studies of carbon dots. Spectroc Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2018;196:295–302.
Chen J, Liu J, Li J, Xu L, Qiao Y. One-pot synthesis of nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots and its application for sensor and multicolor cellular imaging. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017;485:167–74.
Wang D, Wang X, Guo Y, Liu W, Qin W. Luminescent properties of milk carbon dots and their sulphur and nitrogen doped analogues. RSC Adv. 2014;4(93):51658–65.
Du J, Yun Z, Chen J, Ping Z, Gao L, Wang M, et al. Difunctional cu-doped carbon dots: catalytic activity and fluorescence indication for the reduction reaction of p-nitrophenol. RSC Adv. 2017;7(54):33929–36.
Meng A, Xu QH, Zhao K, Li ZJ, Liang J, Li QD. A highly selective and sensitive "on-off-on" fluorescent probe for detecting hg(II) based on au/N-doped carbon quantum dots. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;255:657–65.
Kung ML, Lin PY, Hsieh CW, Tai MH, Wu DC, Kuo CH, et al. Bifunctional peppermint oil nanoparticles for antibacterial activity and fluorescence imaging. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2014;2(7):1769–75.
Das P, Ganguly S, Bose M, Mondal S, Choudhary S, Gangopadhyay S, et al. Zinc and nitrogen ornamented bluish white luminescent carbon dots for engrossing bacteriostatic activity and Fenton based bio-sensor. Mater Sci Eng C. 2018;88:115–29.
Meziani MJ, Dong X, Zhu L, Jones LP, Lecroy GE, Yang F, et al. Visible-light-activated bactericidal functions of carbon "quantum" dots. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(17):10761–6.
Travlou NA, Giannakoudakis DA, Algarra M, Labella AM, Rodriguez-Castellon E, Bandosz TJ. S- and N-doped carbon quantum dots: surface chemistry dependent antibacterial activity. Carbon. 2018;135:104–11.
Venkateswarlu S, Viswanath B, Reddy AS, Yoon M. Fungus-derived photoluminescent carbon nanodots for ultrasensitive detection of Hg2+ ions and photoinduced bactericidal activity. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017;258:172–83.
Fang BY, Li C, Song YY, Tan F, Cao YC, Zhao YD. Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot for direct fluorescence detection of Al3+ in aqueous media and living cells. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;100:41–8.
Ren G, Zhang Q, Li S, Fu S, Chai F, Wang C, et al. One pot synthesis of highly fluorescent N doped C-dots and used as fluorescent probe detection for Hg2+ and Ag+ in aqueous solution. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017;243:244–53.
Gu D, Shang S, Yu Q, Jie S. Green synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon dots from lotus root for Hg(II) ions detection and cell imaging. Appl Surf Sci. 2016;390:38–42.
Tabaraki R, Sadeghinejad N. Microwave assisted synthesis of doped carbon dots and their application as green and simple turn off-on fluorescent sensor for mercury (II) and iodide in environmental samples. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018;153:101–6.
Wang Z, Fan Z. Cu(2+) modulated nitrogen-doped grapheme quantum dots as a turn-off/on fluorescence sensor for the selective detection of histidine in biological fluid. Spectroc Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2017;189:195–201.
Xu H, Yang X, Li G, Zhao C, Liao X. Green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots for selective detection of tartrazine in food samples. J Agric Food Chem. 2015;63(30):6707–14.
Lu JH, Fu YQ, Wang DM, Lu CL. A facile synthesis of thermo-responsive copolymer stabilized fluorescent silver nanoclusters and their application in pH sensing. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;254:996–1004.
Ganganboina AB, Chowdhury AD, Doong RA. N-doped graphene quantum dots-decorated V2O5 Nanosheet for fluorescence turn off-on detection of cysteine. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(1):614–24.
Ankireddy SR, Kim J. Highly selective and sensitive detection of calcium (II) ions in human serum using novel fluorescent carbon dots. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;255:3425–33.
Borse V, Thakur M, Sengupta S, Srivastava R. N-doped multi-fluorescent carbon dots for ‘turn off-on’ silver-biothiol dual sensing and mammalian cell imaging application. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017;248:481–92.
Xu JW, Gao ZD, Han K, Liu Y, Song YY. Synthesis of magnetically separable Ag3PO4/TiO2/Fe3O4 heterostructure with enhanced photocatalytic performance under visible light for photoinactivation of bacteria. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(17):15122–31.
Yang JJ, Gao G, Zhang XD, Ma YH, Chen XK, Wu FG. One-step synthesis of carbon dots with bacterial contact-enhanced fluorescence emission: fast gram-type identification and selective gram-positive bacterial inactivation. Carbon. 2019;146:827–39.
Zhao CF, Wang XW, Wu LN, Wu W, Zheng YJ, Lin LQ, et al. Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots as an antimicrobial agent against Staphylococcus for the treatment of infected wounds. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019;179:17–27.
Bunz UH, Han J, Cheng H, Wang B, Braun M, Fan X, et al. Polymer/peptide complex-based sensor array discriminates bacteria in urine. Angew Chem. 2017;56:15246–51.
Shariati MR, Samadi-Maybodi A, Colagar AH. Dual Cocatalysts Loaded Reverse Type-I Core/Shell Quantum Dots for Photocatalytic Antibacterial Applications. J Mater Chem A. 2018;6(41).
Karthik K, Revathi V, Tatarchuk T. Microwave-assisted green synthesis of SnO2 nanoparticles and their optical and photocatalytic properties. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst. 2018;671:17–23.
Karthik K, Vijayalakshmi S, Phuruangrat A, Revathi V, Science UVJJoC. Multifunctional applications of microwave-assisted biogenic TiO2 nanoparticles. J Clust Sci. 2019;30:965–72.
Karthik K, Naik MM, Shashank M, Vinuth M, Revathi V. Microwave-assisted ZrO2 nanoparticles and its photocatalytic and antibacterial studies. J Clust Sci. 2019;30:311–8.
Karthik K, Revathi V, Crystals TTJM, Crystals L. Facile microwave-assisted green synthesis of NiO nanoparticles from Andrographis paniculata leaf extract and evaluation of their photocatalytic and anticancer activities. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst. 2019;673(1):70–80.
Nagaraju G, Karthik K, Shashank M. Ultrasound-assisted Ta2O5 nanoparticles and their photocatalytic and biological applications. Microchem J. 2019;147:749–54.
Revathi V, Karthik KJCDC. Physico-chemical properties and antibacterial activity of hexakis (thiocarbamide) nickel(II) nitrate single crystal. Chemical Data Collections. 2019;21:100229.
Wang R, Kong X, Zhang W, Zhu W, Huang L, Wang J, et al. Mechanism insight into rapid photocatalytic disinfection of Salmonella based on vanadate QDs-interspersed g-C3N4 heterostructures. Appl Catal B Environ. 2017;225:228–37.
Yu HL, Xu X, Ma APY, Liu F, Ng AMC, Shen Z, et al. Toxicity of ZnO and TiO2 to Escherichia coli cells. Sci Rep. 2016;6:35243.
Hua XW, Bao YW, Wang HY, Chen Z, Wu FG. Bacteria-derived fluorescent carbon dots for microbial live/dead differentiation. Nanoscale. 2017;9(6):2150–61.
Yang J, Zhang X, Ma YH, Gao G, Chen X, Jia HR, et al. Carbon dot-based platform for simultaneous bacterial distinguishment and antibacterial applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(47):32170–81.
Acknowledgements
This work was strongly supported by the Analysis and Testing Foundation of Kunming University of Science and Technology (2018 M20172118081).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Z., Yang, D., Wan, Y. et al. One-step synthesis of carbon dots for selective bacterial inactivation and bacterial differentiation. Anal Bioanal Chem 412, 871–880 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02293-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02293-0