Abstract
Methamphetamine (METH) is one of the most highly addictive illicit drugs abused all over the world. Much evidence indicates that METH abuse leads to major toxicity, medical consequences, and even severe public health consequences. Existing studies usually focus on the pathomechanism of METH-induced toxicity; therefore, data on metabolites and elements correlating with particular toxicity remain scarce. The objective of the present study is to develop appropriate analytical procedures to identify the differential metabolic and elemental biomarkers on METH-induced hepatic injury to rats. The rats were administrated with METH (15 mg/mL/kg, two times per day) via intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections for four consecutive days. The alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase activity levels of in the rat serum of the METH group increase significantly compared with those of the control group, suggesting obvious hepatic injury. The results are further confirmed by the histopathological microscopic observation. A total of 18 small molecular metabolites and 19 elements are selected to perform the simultaneous quantification based on the combination of liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Sample preparation was optimized to cover all the analytes. Both methods are optimized and validated according to developed guidelines such as limits of detection, limits of quantification, linearity, precision, and recovery. All the obtained data are within the satisfactory range. The normalized data were processed according to the partial least squares discrimination analysis (PLS-DA) model. Five differential metabolic and six elemental markers are identified in rat plasma based on the variable importance in projection (VIP) (> 1) and t test results. Overall, the results obtained in this study demonstrate the developed methods are suitable for simultaneous determination of metabolic and elemental markers in the hepatic injury to rats induced by METH.

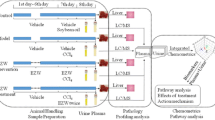
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mills EM, Banks ML, Sprague JE, Finkel T. Pharmacology: uncoupling the agony from ecstasy. Nature. 2003;426(6965):403–4.
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC). World drug report. 2018. http://www.unodc.org/wdr2018/index.html. Accessed 3 Dec 2018.
Krasnova IN, Cadet JL. Methamphetamine toxicity and messengers of death. Brain Res. 2009;60(2):379–407.
Kwon N, Han E. A commentary on the effects of methamphetamine and the status of methamphetamine abuse among youths in South Korea, Japan, and China. Forensic Sci Int. 2018;286:81–5.
Matsumoto RR, Seminerio MJ, Turner RC, Robson MJ, Nguyen L, Miller DB, et al. Methamphetamine-induced toxicity: an updated review on issues related to hyperthermia. Pharmacol Ther. 2014;144(1):28–40.
Romach MK, Schoedel KA, Sellers EM. Human abuse liability evaluation of CNS stimulant drugs. Neuropharmacology. 2014;87:81–90.
National Institutes of Health (NIH). National survey of drug use and health. 2016. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/NSDUH-DetTabs-2016/NSDUH-DetTabs-2016.htm. Accessed 3 Dec 2018.
Rommel N, Rohleder NH, Wagenpfeil S, Haertel-Petri R, Kesting MR. Evaluation of methamphetamine-associated socioeconomic status and addictive behaviors, and their impact on oral health. Addict Behav. 2015;50:182–7.
Roohbakhsh A, Shirani K, Karimi GK. Methamphetamine-induced toxicity: the role of autophagy. Chem Biol Interact. 2016;260:163–7.
Aizenman E, McCord MC, Saadi RA, Hartnett KA, He K. Complex role of zinc in methamphetamine toxicity in vitro. Neuroscience. 2010;171(1):31–9.
Wang Q, Wei LW, Xiao HQ, Xue Y, Du SH, Liu YG, et al. Methamphetamine induces hepatotoxicity via inhibiting cell division, arresting cell cycle and activating apoptosis: in vivo and in vitro studies. Food Chem Toxicol. 2017;105(105):61–72.
Xue Z, Siemian JN, Johnson BN, Zhang Y, Li JX. Methamphetamine-induced impulsivity during chronic methamphetamine treatment in rats: effects of the TAAR 1 agonist RO5263397. Neuropharmacology. 2018;129:36–46.
Choi MR, Chun JW, Kwak SM, Bang SH, Jin YB, Lee Y, et al. Effects of acute and chronic methamphetamine administration on cynomolgus monkey hippocampus structure and cellular transcriptome. Toxicol Appl Pharm. 2018;355:68–79.
London ED, Kohno M, Morales AM, Ballard ME. Chronic methamphetamine abuse and corticostriatal deficits revealed by neuroimaging. Brain Res. 2015;1628:174–85.
Prakash MD, Tangalakis K, Antonipillai J, Stojanovska L, Nurgali K, Apostolopoulos V. Methamphetamine: effects on the brain, gut and immune system. Pharmacol Res. 2017;120:60–7.
Cirulli ET, Guo L, Swisher CL, Shah N, Huang L, Napier LA, et al. Profound perturbation of the metabolome in obesity is associated with health risk. Cell Metab. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2018.09.022.
Vogiatzis CG, Zachariadis GA. Tandem mass spectrometry in metallomics and the involving role of ICP-MS detection: a review. Anal Chim Acta. 2014;819:1–14.
Pavlova NN, Thompson CB. The emerging hallmarks of cancer metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016;23(1):27–47.
Liu R, Li Q, Ma R, Lin X, Xu H, Bi K. Determination of polyamine metabolome in plasma and urine by ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method: application to identify potential markers for human hepatic cancer. Anal Chim Acta. 2013;791:36–45.
Cross AJ, Moore SC, Boca S, Huang WY, Xiong X, Stolzenberg-Solomon R, et al. A prospective study of serum metabolites and colorectal cancer risk. Cancer. 2014;120(19):3049–57.
Auslander N, Yizhak K, Weinstock A, Budhu A, Tang W, Wang XW, et al. A joint analysis of trascriptomic and metabolomic data uncovers enhanced enzyme-metabolite coupling in breast cancer. Sci Rep. 2016;6:29662.
Takeda SHK, Kuno R, Jr FB, Gouveia N. Trace element levels in blood and associated factors in adults living in the metropolitan area of São Paulo, Brazil. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2017;44:307–14.
Lubes G, Goodarzi M. GC-MS based metabolomics used for the identification of cancer volatile organic compounds as biomarkers. J Pharm Biomed. 2018;147:313–22.
Lee S, Park Y, Yang W, Han E, Choe S, In S, et al. Development of a reference material using methamphetamine abusers’ hair samples for the determination of methamphetamine and amphetamine in hair. J Chromatogr B. 2008;865(1–2):33–9.
Chou CC, Lee MR. Solid phase microextraction with liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry for analysis of amphetamine and methamphetamine in serum. Anal Chim Acta. 2005;538(1):49–56.
Bu Q, Lv L, Yan G, Deng P, Wang Y, Zhou J, et al. NMR-based metabonomic in hippocampus, nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex of methamphetamine-sensitized rats. NeuroToxicology. 2013;36(9):17–23.
Chatziioannou AC, Wolters JC, Sarafidis K, Thomaidou A, Agakidis C, Govorukhina N, et al. Targeted LC-MS/MS for the evaluation of proteomics biomarkers in the blood of neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis and late-onset sepsis. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018;410(27):7163–75.
McClay JL, Adkins DE, Vunck SA, Batman AM, Vann RE, Clark SL, et al. Large-scale neurochemical metabolomics analysis identifies multiple compounds associated with methamphetamine exposure. Metabolomics. 2013;9(2):392–402.
Tomita M, Katsuyama H, Watanabe Y, Okuyama T, Fushimi S, Ishikawa T, et al. Does methamphetamine affect bone metabolism? Toxicology. 2014;319:63–8.
Luo R, Zhang S, Xiang P, Shen B, Zhuo X, Ma D. Elements concentrations in the scalp hair of methamphetamine abusers. Forensic Sci Int. 2015;249:112–5.
Roberts SM, Harbison RD, Westhouse RA, James RC. Exacerbation of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in the rat by methamphetamine. Toxicol Lett. 1995;76(1):77–83.
Roberts SM, Harbison RD, James RC. Mechanistic studies on the potentiation of carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity by methamphetamine. Toxicology. 1995;97(1–3):49–57.
Pereira LSA, Lisboa FLC, Neto JC, Valladão FN, Sena MM. Screening method for rapid classification of psychoactive substances in illicit tablets using mid infrared spectroscopy and PLS-DA. Forensic Sci Int. 2018;288:227–35.
Song H, Peng JS, Yao DS, Liu DL, Yang ZL, Du YP, et al. Metabolic disorders of fatty acids and fatty acid amides associated with human gastric cancer morbidity. Chin Med J. 2012;125(5):757–63.
Huang BM, Zha QL, Chen TB, Xiao SY, Xie Y, Luo P, et al. Discovery of markers for discriminating the age of cultivated ginseng by using UHPLC-QTOF/MS coupled with OPLS-DA. Phytomedicine. 2018;45:8–17.
Zhang Y, Li L, Xing X, Zhou Z, Ma A. Analysis of methamphetamine and amphetamine chiral enantiomers in hair by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Chin J Chromatogr. 2018;36(12):1290–6.
Boorman GA, Eustis SL, Elwell MR, Montgomery CA, MacKenzie WF. Pathology of the fisher rat, reference and atlas. London: Academic Press Inc.; 1990. p. 24–8.
Guidance for Industry. Bioanalytical method validation (updated). 2018. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatory Information/Guidances/UCM070107.pdf. Accessed 3 Dec 2018.
Bastiaensen M, Xu F, Been F, Eede NV, Covaci A. Simultaneous determination of 14 urinary biomarkers of exposure to organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers by LC-MS/MS. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018;410(30):7871–80.
Borland L, Brickhouse M, Thomas T, Fountian AW III. Review of chemical signature databases. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010;397(3):1019–28.
Yan H, Qiao Z, Shen B, Xiang P, Shen M. Plasma metabolic profiling analysis of toxicity induced by brodifacoum using metabonomics coupled with multivariate data analysis. Forensic Sci Int. 2016;267:129–35.
Liu WZ, Wang JM, Zhang H, Huang HT. Health effects of cobalt and its compounds. Occup Health Emerg Rescue. 2016;34(2):111–3.
Shima N, Miyawaki I, Bando K, Horie H, Zaitsu K, Katagi M, et al. Influences of methamphetamine-induced acute intoxication on urinary and plasma metabolic profiles in the rat. Toxicology. 2011;287(1–3):29–37.
Wu MJ, Wang M, Zhang GQ, Yang RQ, Zhang DM. Metabonomics study of serum in methamphetamine dependent rats. Chin J Drug Depend. 2013;22(6):419–22.
Gatiatulina ER, Popova EV, Polyakova VS, Skalnaya AA, Agletdinov EF, Nikonorov AA, et al. Evaluation of tissue metal and trace element content in a rat model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease using ICP-DRC-MS. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2017;39:91–9.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2017A030310051) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81703438 and 81501629).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards and approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Southern Medical University (approval no. L2017184).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1.75 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Li, L., Wang, Q. et al. Simultaneous determination of metabolic and elemental markers in methamphetamine-induced hepatic injury to rats using LC-MS/MS and ICP-MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 411, 3361–3372 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01810-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01810-5