Abstract
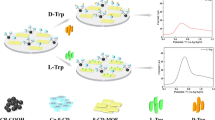
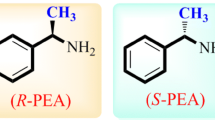
We describe the synthesis of new chiral calix[4]arene derivatives having (R)-1-phenylethylamine, (S)-1-phenylethylamine, (R)-2-phenylglycinol, and (S)-2-phenylglycinol moieties, and chiral recognition studies for enantiomers of some selected α-amino acid derivatives such as alanine, phenylalanine, serine, and tryptophan using a quartz crystal microbalance (QCM). Initial experiments indicated that the highest selective chiral recognition factor was 1.42 for alanine enantiomers. The sensitivity, limit of detection, and time constant for l-alanine were calculated as 0.028 Hz/μM, 60.9 μM, and 36.2 s, respectively. The results indicated that real-time, sensitive, selective, and effective chiral recognition of alanine enantiomers was achieved with a QCM sensor coated with a chiral calix[4]arene derivative having (R)-2-phenylglycinol moieties.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yoshio O, Eiji Y. Polysaccharide derivatives for chromatographic separation of enantiomers. Angew Chem Int Ed. 1998;37(8):1020–43. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19980504)37:8<1020::AID-ANIE1020>3.0.CO;2-5.
Gawley RE, Aubé J. Practical aspects of asymmetric synthesis. In: Principles of asymmetric synthesis. 2nd ed. Oxford: Elsevier; 2012. p. 63–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-044860-2.00002-7.
Dewick PM. Medicinal natural products: a biosynthetic approach. 2nd ed. Chichester: Wiley; 2001.
Gasparrini F, Pierini M, Villani C, Filippi A, Speranza M. Induced-fit in the gas phase: conformational effects on the enantioselectivity of chiral tetra-amide macrocycles. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130(2):522–34. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja073287+.
Sambasivan S, Kim D-s, Ahn KH. Chiral discrimination of α-amino acids with a C2-symmetric homoditopic receptor. Chem Commun. 2010;46(4):541–3. https://doi.org/10.1039/B919957H.
Bi Q, Dong S, Sun Y, Lu X, Zhao L. An electrochemical sensor based on cellulose nanocrystal for the enantioselective discrimination of chiral amino acids. Anal Biochem. 2016;508:50–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2016.05.022.
Ilisz I, Péter A, Lindner W. State-of-the-art enantioseparations of natural and unnatural amino acids by high-performance liquid chromatography. Trends Anal Chem. 2016;81:11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2016.01.016.
Sánchez-Hernández L, Bernal JL, Nozal MJ, Toribio L. Chiral analysis of aromatic amino acids in food supplements using subcritical fluid chromatography and Chirobiotic T2 column. J Supercrit Fluids. 2016;107:519–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2015.06.027.
Yu X, Yao Z-P. Chiral differentiation of amino acids through binuclear copper bound tetramers by ion mobility mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta. 2017;981:62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.05.026.
Tabakcı M, Tabakcı B, Yılmaz M. Design and synthesis of new chiral calix[4]arenes as liquid phase extraction agents for α-amino acid methylesters and chiral α-amines. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem. 2005;53(1–2):51–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-005-0697-8.
Erdemir S. Synthesis of novel chiral Schiff base and amino alcohol derivatives of calix[4]arene and chiral recognition properties. J Mol Struct. 2012;1007:235–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2011.10.053.
Zhang X, Chen S, Xu P, Yu Q, Dai Z. Synthesis of new chiral fluorescent sensors and their applications in enantioselective discrimination. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017;58(29):2850–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2017.06.025.
Gao G, Lv C, Li Q, Ai L, Zhang J. Enantiomeric discrimination of α-hydroxy acids and N-Ts-α-amino acids by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015;56(48):6742–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2015.10.060.
Yin X, Ding J, Zhang S, Kong J. Enantioselective sensing of chiral amino acids by potentiometric sensors based on optical active polyaniline films. Biosens Bioelectron. 2006;21(11):2184–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2005.10.010.
Fu YQ, Luo JK, Nguyen NT, Walton AJ, Flewitt AJ, Zu XT, et al. Advances in piezoelectric thin films for acoustic biosensors, acoustofluidics and lab-on-chip applications. Prog Mater Sci. 2017;89:31–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2017.04.006.
Sayin S, Ozbek C, Okur S, Yilmaz M. Preparation of the ferrocene-substituted 1,3-distal p-tert-butylcalix[4]arene based QCM sensors array and utilization of its gas-sensing affinities. J Organomet Chem. 2014;771:9–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jorganchem.2014.06.004.
Baldini L, Sansone F, Faimani G, Massera C, Casnati A, Ungaro R. Self-assembled Chiral dimeric capsules from difunctionalized N,C-linked peptidocalix[4]arenes: scope and limitations. Eur J Org Chem. 2008;5:869–86. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.200700943.
Pirondini L, Dalcanale E. Molecular recognition at the gas–solid interface: a powerful tool for chemical sensing. Chem Soc Rev. 2007;36(5):695–706. https://doi.org/10.1039/B516256B.
Koshets IA, Kazantseva ZI, Shirshov YM, Cherenok SA, Kalchenko VI. Calixarene films as sensitive coatings for QCM-based gas sensors. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2005;106(1):177–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2004.05.054.
Miah M, Pavey KD, Gun'ko VM, Sheehan R, Cragg PJ. Observation of transient alkali metal inclusion in oxacalix[3]arenes. Supramol Chem. 2004;16(3):185–92. https://doi.org/10.1080/10610270310001644473.
Wang C, He X-W, Chen L-X. A piezoelectric quartz crystal sensor array self assembled calixarene bilayers for detection of volatile organic amine in gas. Talanta. 2002;57(6):1181–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-9140(02)00193-5.
Sharma K, Cragg P. Calixarene based chemical sensors. Chem Senses. 2011;1(9):1–18.
Hao R-Z, Song H-B, Zuo G-M, Yang R-F, Wei H-P, Wang D-B, et al. DNA probe functionalized QCM biosensor based on gold nanoparticle amplification for Bacillus anthracis detection. Biosens Bioelectron. 2011;26(8):3398–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2011.01.010.
Jearanaikoon P, Prakrankamanant P, Leelayuwat C, Wanram S, Limpaiboon T, Promptmas C. The evaluation of loop-mediated isothermal amplification-quartz crystal microbalance (LAMP-QCM) biosensor as a real-time measurement of HPV16 DNA. J Virol Methods. 2016;229:8–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2015.12.005.
Karaseva N, Ermolaeva T, Mizaikoff B. Piezoelectric sensors using molecularly imprinted nanospheres for the detection of antibiotics. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2016;225:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.11.045.
Pei Z, Saint-Guirons J, Käck C, Ingemarsson B, Aastrup T. Real-time analysis of the carbohydrates on cell surfaces using a QCM biosensor: a lectin-based approach. Biosens Bioelectron. 2012;35(1):200–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.02.047.
Sauerbrey G. Use of quartz vibrator for weighing thin layers and as a microbalance. Z Phys. 1959;155:206–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01337937.
Fakhrullin RF, Vinter VG, Zamaleeva AI, Matveeva MV, Kourbanov RA, Temesgen BK, et al. Quartz crystal microbalance immunosensor for the detection of antibodies to double-stranded DNA. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007;388(2):367–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-007-1230-2.
Lee S-W, Hinsberg WD, Kanazawa KK. Determination of the viscoelastic properties of polymer films using a compensated phase-locked oscillator circuit. Anal Chem. 2002;74(1):125–31. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac0108358.
Arnau A, Sogorb T, Jiménez Y. Circuit for continuous motional series resonant frequency and motional resistance monitoring of quartz crystal resonators by parallel capacitance compensation. Rev Sci Instrum. 2002;73(7):2724–37. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1484254.
Nwankwo E, Durning CJ. Impedance analysis of thickness-shear mode quartz crystal resonators in contact with linear viscoelastic media. Rev Sci Instrum. 1998;69(6):2375–84. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1148963.
Su X-L, Li Y. A QCM immunosensor for Salmonella detection with simultaneous measurements of resonant frequency and motional resistance. Biosens Bioelectron. 2005;21(6):840–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2005.01.021.
Singh AK, Singh M. Molecularly imprinted Au-nanoparticle composite-functionalized EQCM sensor for l-serine. J Electroanal Chem. 2016;780:169–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.09.021.
Mirmohseni A, Shojaei M, Farbodi M. Application of a quartz crystal nanobalance to the molecularly imprinted recognition of phenylalanine in solution. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng. 2008;13(5):592–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-008-0028-1.
Nakanishi T, Yamakawa N, Asahi T, Osaka T, Ohtani B, Uosaki K. Enantioselective adsorption of phenylalanine onto self-assembled monolayers of 1,1‘-binaphthalene-2,2‘-dithiol on gold. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124(5):740–1. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja012084x.
Bodenhofer K, Hierlemann A, Seemann J, Gauglitz G, Koppenhoefer B, Gopel W. Chiral discrimination using piezoelectric and optical gas sensors. Nature. 1997;387(6633):577–80.
Yılmaz A, Tabakcı B, Tabakcı M. New diamino derivatives of p-tert-butylcalix[4]arene for oxyanion recognition: synthesis and complexation studies. Supramol Chem. 2009;21(6):435–41. https://doi.org/10.1080/10610270802165969.
Gutsche CD, Dhawan B, No KH, Muthukrishnan R. Calixarenes. 4. The synthesis, characterization, and properties of the calixarenes from p-tert-butylphenol. J Am Chem Soc. 1981;103(13):3782–92. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00403a028.
Ovsyannikov A, Solovieva S, Antipin I, Ferlay S. Coordination polymers based on calixarene derivatives: structures and properties. Coord Chem Rev. 2017;352(Suppl C):151–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2017.09.004.
Kostyukevych KV, Khristosenko RV, Pavluchenko AS, Vakhula AA, Kazantseva ZI, Koshets IA, et al. A nanostructural model of ethanol adsorption in thin calixarene films. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2016;223:470–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.09.123.
Nikoleli G-P, Nikolelis DP, Evtugyn G, Hianik T. Advances in lipid film based biosensors. Trends Anal Chem. 2016;79:210–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2016.01.021.
Temel F, Özçelik E, Türe AG, Tabakcı M. Sensing abilities of functionalized calix[4]arene coated QCM sensors towards volatile organic compounds in aqueous media. Appl Surf Sci. 2017;412:238–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.03.258.
Su WC, Zhang WG, Zhang S, Fan J, Yin X, Luo ML, et al. A novel strategy for rapid real-time chiral discrimination of enantiomers using serum albumin functionalized QCM biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron. 2009;25(2):488–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2009.06.040.
Temel F, Tabakcı M. Calix[4]arene coated QCM sensors for detection of VOC emissions: methylene chloride sensing studies. Talanta. 2016;153:221–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.03.026.
Long GL, Winefordner JD. Limit of detection a closer look at the IUPAC definition. Anal Chem. 1983;55(7):712A–24A. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00258a724.
Koshets IA, Kazantseva ZI, Belyaev AE, Kalchenko VI. Sensitivity of resorcinarene films towards aliphatic alcohols. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2009;140(1):104–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2009.04.014.
Fu Y, Finklea HO. Quartz crystal microbalance sensor for organic vapor detection based on molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal Chem. 2003;75(20):5387–93. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac034523b.
Grate JW, Snow A, Ballantine DS, Wohltjen H, Abraham MH, McGill RA, et al. Determination of partition coefficients from surface acoustic wave vapor sensor responses and correlation with gas-liquid chromatographic partition coefficients. Anal Chem. 1988;60(9):869–75. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00160a010.
Meng R, Kang J. Determination of the stereoisomeric impurities of sitafloxacin by capillary electrophoresis with dual chiral additives. J Chromatogr A. 2017;1506:120–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.05.010.
Li Z-T, Ji G-Z, Zhao C-X, Yuan S-D, Ding H, Huang C, et al. Self-assembling calix[4]arene [2]catenanes. Preorganization, conformation, selectivity, and efficiency. J Org Chem. 1999;64(10):3572–84. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo9824100.
Jeong H, Park K, Yoo J-C, Hong J. Structural heterogeneity in polymeric nitric oxide donor nanoblended coatings for controlled release behaviors. RSC Adv. 2018;8(68):38792–800. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA07707J.
Häkkinen H. The gold–sulfur interface at the nanoscale. Nat Chem. 2012;4:443. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.1352.
Zhang X, Yu Q, Lu W, Chen S, Dai Z. Synthesis of new chiral fluorescent sensors and their applications in enantioselective discrimination. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017;58(41):3924–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2017.08.077.
Memon FN, Memon S. Sorption and desorption of basic dyes from industrial wastewater using calix[4]arene based impregnated material. Sep Sci Technol. 2014;50(8):1135–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2014.965831.
Mutihac L, Lee JH, Kim JS, Vicens J. Recognition of amino acids by functionalized calixarenes. Chem Soc Rev. 2011;40(5):2777–96. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CS00005A.
Yuan Y, Lee TR. Contact angle and wetting properties. In: Bracco G, Holst B, editors. Surface science techniques. Berlin: Springer; 2013. p. 3–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-34243-1_1.
Mannan S, Fakhru'l-Razi A, Alam MZ. Optimization of process parameters for the bioconversion of activated sludge by Penicillium corylophilum, using response surface methodology. J Environ Sci. 2007;19(1):23–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(07)60004-7.
Noordin MY, Venkatesh VC, Sharif S, Elting S, Abdullah A. Application of response surface methodology in describing the performance of coated carbide tools when turning AISI 1045 steel. J Mater Process Technol. 2004;145(1):46–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00861-6.
Körbahti BK, Tanyolaç A. Electrochemical treatment of simulated textile wastewater with industrial components and Levafix Blue CA reactive dye: optimization through response surface methodology. J Hazard Mater. 2008;151(2–3):422–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.06.010.
Amini M, Younesi H, Bahramifar N, Lorestani AAZ, Ghorbani F, Daneshi A, et al. Application of response surface methodology for optimization of lead biosorption in an aqueous solution by Aspergillus niger. J Hazard Mater. 2008;154(1):694–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.10.114.
Silva JP, Sousa S, Gonçalves I, Porter JJ, Ferreira-Dias S. Modelling adsorption of acid orange 7 dye in aqueous solutions to spent brewery grains. Sep Purif Technol. 2004;40(2):163–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2004.02.006.
Lee K, Hamid S. Simple response surface methodology: investigation on advance photocatalytic oxidation of 4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid using UV-active ZnO photocatalyst. Materials. 2015;8(1):339–54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8010339.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Technical Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK grant number 115Z249) and the Research Foundation of Selçuk University (SUBAP grant number 16401003), Konya, Turkey, and for financial support of this work produced from FT’s Ph.D. thesis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1.17 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Temel, F., Erdemir, S., Tabakci, B. et al. Selective chiral recognition of alanine enantiomers by chiral calix[4]arene coated quartz crystal microbalance sensors. Anal Bioanal Chem 411, 2675–2685 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01705-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01705-5