Abstract
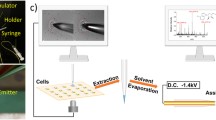
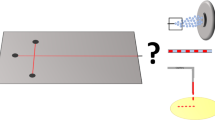
We present a lab-on-a-chip approach for the analysis of secondary metabolites produced in microfluidic droplets by simultaneous epifluorescence microscopy and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS). The approach includes encapsulation and long-term off-chip incubation of microbes in surfactant-stabilized droplets followed by a transfer of droplets into a microfluidic chip for subsequent analysis. Before the reinjected droplets are spaced and electrosprayed from an integrated emitter into a mass spectrometer, the presence of fluorescent marker molecules is monitored nearly simultaneously with a custom-made portable epifluorescence microscope. This combined fluorescence and MS-detection setup allows the analysis of metabolites and fluorescent labels in a complex biological matrix at a single droplet level. Using hyphae of Streptomyces griseus, encapsulated in microfluidic droplets of ~ 200 picoliter as a model system, we show the detection of in situ produced streptomycin by ESI-MS and the feasibility of detecting fluorophores inside droplets shortly before they are electrosprayed. The presented method expands the analytical toolbox for the discovery of bioactive metabolites such as novel antibiotics, produced by microorganisms.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Whitesides GM. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature. 2006;442:368–73.
Dittrich PS, Manz A. Lab-on-a-chip: microfluidics in drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:210–8.
Elvira KS, i Solvas XC, Wootton RCR, deMello AJ. The past, present and potential for microfluidic reactor technology in chemical synthesis. Nat Chem. 2013;5:905–15.
Fritzsche S, Ohla S, Glaser P, Giera DS, Sickert M, Schneider C, et al. Asymmetric organocatalysis and analysis on a single microfluidic nanospray chip. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2011;50:9467–70.
Shembekar N, Chaipan C, Utharala R, Merten CA. Droplet-based microfluidics in drug discovery, transcriptomics and high-throughput molecular genetics. Lab Chip. 2016;16:1314–31.
Thorsen T, Roberts RW, Arnold FH, Quake SR. Dynamic pattern formation in a vesicle-generating microfluidic device. Phys Rev Lett. 2001;86:4163–6.
Theberge AB, Courtois F, Schaerli Y, Fischlechner M, Abell C, Hollfelder F, et al. Microdroplets in microfluidics: an evolving platform for discoveries in chemistry and biology. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2010;49:5846–68.
Griffiths AD, Tawfik DS. Miniaturising the laboratory in emulsion droplets. Trends Biotechnol. 2006;24:395–402.
Song H, Chen DL, Ismagilov RF. Reactions in Droplets in Microfluidic Channels. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2006;45:7336–56.
Cao J, Köhler JM. Droplet-based microfluidics for microtoxicological studies. Eng Life Sci. 2015;15:306–17.
Cole RH, Tang S-Y, Siltanen CA, Shahi P, Zhang JQ, Poust S, et al. Printed droplet microfluidics for on demand dispensing of picoliter droplets and cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2017;114:8728–33.
Mazutis L, Baret J-C, Treacy P, Skhiri Y, Araghi AF, Ryckelynck M, et al. Multi-step microfluidic droplet processing: kinetic analysis of an in vitro translated enzyme. Lab Chip. 2009;9:2902–8.
Theberge A, Mayot E, Harrak AE, Kleinschmidt F, Huck WTS, Griffiths AD. Microfluidic platform for combinatorial synthesis in picolitre droplets. Lab Chip. 2012;12:1320–6.
Shang L, Cheng Y, Zhao Y. Emerging droplet microfluidics. Chem Rev. 2017;117:7964–8040.
Chiu Y-L, Chan HF, Phua, Zhang Y, Juul S, Knudsen BR, et al. Synthesis of fluorosurfactants for emulsion-based biological applications. ACS Nano. 2014;8:3913–20.
Baret J-C. Surfactants in droplet-based microfluidics. Lab Chip. 2012;12:422–33.
Holtze C, Rowat AC, Agresti JJ, Hutchison JB, Angilè FE, Schmitz CHJ, et al. Biocompatible surfactants for water-in-fluorocarbon emulsions. Lab Chip. 2008;8:1632–9.
Wagner O, Thiele J, Weinhart M, Mazutis L, Weitz DA, Huck WTS, et al. Biocompatible fluorinated polyglycerols for droplet microfluidics as an alternative to PEG-based copolymer surfactants. Lab Chip. 2015;16:65–9.
Brouzes E, Medkova M, Savenelli N, Marran D, Twardowski M, Hutchison JB, et al. Droplet microfluidic technology for single-cell high-throughput screening. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2009;106:14195–200.
Baret J-C, Miller OJ, Taly V, Ryckelynck M, El-Harrak A, Frenz L, et al. Fluorescence-activated droplet sorting (FADS): efficient microfluidic cell sorting based on enzymatic activity. Lab Chip. 2009;9:1850.
Debs BE, Utharala R, Balyasnikova IV, Griffiths AD, Merten CA. Functional single-cell hybridoma screening using droplet-based microfluidics. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2012;109:11570–5.
Clausell-Tormos J, Lieber D, Baret J-C, El-Harrak A, Miller OJ, Frenz L, et al. Droplet-based microfluidic platforms for the encapsulation and screening of mammalian cells and multicellular organisms. Chem Biol. 2008;15:427–37.
Price AK, Paegel BM. Discovery in droplets. Anal Chem. 2016;88:339–53.
Mair P, Gielen F, Hollfelder F. Exploring sequence space in search of functional enzymes using microfluidic droplets. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2017;37:137–44.
Guo F, Lapsley MI, Nawaz AA, Zhao Y, Lin S-CS, Chen Y, et al. A droplet-based, optofluidic device for high-throughput, quantitative bioanalysis. Anal Chem. 2012;84:10745–9.
Cole RH, de Lange N, Gartner ZJ, Abate AR. Compact and modular multicolour fluorescence detector for droplet microfluidics. Lab Chip. 2015;15:2754–8.
Pei J, Li Q, Lee MS, Valaskovic GA, Kennedy RT. Analysis of samples stored as individual plugs in a capillary by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2009;81:6558–61.
Pei J, Li Q, Kennedy RT. Rapid and label-free screening of enzyme inhibitors using segmented flow electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2010;21:1107–13.
Sun S, Slaney TR, Kennedy RT. Label free screening of enzyme inhibitors at femtomole scale using segmented flow electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2012;84:5794–800.
Diefenbach XW, Farasat I, Guetschow ED, Welch CJ, Kennedy RT, Sun S, et al. Enabling biocatalysis by high-throughput protein engineering using droplet microfluidics coupled to mass spectrometry. ACS Omega. 2018;3:1498–508.
Fidalgo LM, Whyte G, Bratton D, Kaminski CF, Abell C, Huck WTS. From microdroplets to microfluidics: selective emulsion separation in microfluidic devices. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2008;47:2042–5.
Fidalgo LM, Whyte G, Ruotolo BT, Benesch JLP, Stengel F, Abell C, et al. Coupling microdroplet microreactors with mass spectrometry: reading the contents of single droplets online. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2009;48:3665–8.
Kelly RT, Page JS, Marginean I, Tang K, Smith RD. Dilution-free analysis from picoliter droplets by nano-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2009;48:6832–5.
Zhu Y, Fang Q. Integrated droplet analysis system with electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry using a hydrophilic tongue-based droplet extraction interface. Anal Chem. 2010;82:8361–6.
Beulig JR, Warias R, Heiland JJ, Ohla S, Zeitler K, Belder D. A droplet-chip/mass spectrometry approach to study organic synthesis at nanoliter scale. Lab Chip. 2017;17:1996–2002.
Ji J, Nie L, Qiao L, Li Y, Guo L, Liu B, et al. Proteolysis in microfluidic droplets: an approach to interface protein separation and peptide mass spectrometry. Lab Chip. 2012;12:2625–9.
Wang X-L, Zhu Y, Fang Q. Coupling liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry detection with microfluidic droplet array for label-free enzyme inhibition assay. Analyst. 2013;139:191–7.
Sun X, Tang K, Smith RD, Kelly RT. Controlled dispensing and mixing of pico- to nanoliter volumes using on-demand droplet-based microfluidics. Microfluid Nanofluid. 2013;15:117–26.
Gasilova N, Yu Q, Qiao L, Girault HH. On-chip spyhole mass spectrometry for droplet-based microfluidics. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2014;53:4408–12.
Pereira F, Niu X, deMello AJ. A nano LC-MALDI mass spectrometry droplet interface for the analysis of complex protein samples. PLOS ONE. 2013;8:e63087.
Kuester SK, Fagerer SR, Verboket PE, Eyer K, Jefimovs K, Zenobi R, et al. Interfacing droplet microfluidics with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry: label-free content analysis of single droplets. Anal Chem. 2013;85:1285–9.
Gong X, Zhao Y, Cai S, Fu S, Yang C, Zhang S, et al. Single cell analysis with probe ESI-mass spectrometry: detection of metabolites at cellular and subcellular levels. Anal Chem. 2014;86:3809–16.
Wei Z, Han S, Gong X, Zhao Y, Yang C, Zhang S, et al. Rapid removal of matrices from small-volume samples by step-voltage nanoelectrospray. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2013;52:11025–8.
Zhu Y, Clair G, Chrisler WB, Shen Y, Zhao R, Shukla AK, et al. Proteomic analysis of single mammalian cells enabled by microfluidic nanodroplet sample preparation and ultrasensitive nanoLC-MS. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2018;57:1–6.
Smith CA, Li X, Mize TH, Sharpe TD, Graziani EI, Abell C, et al. Sensitive, high throughput detection of proteins in individual, surfactant-stabilized picoliter droplets using nanoelectrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2013;85:3812–6.
Mahler L, Wink K, Beulig RJ, Scherlach K, Tovar M, Zang E, et al. Detection of antibiotics synthetized in microfluidic picolitre-droplets by various actinobacteria. Sci Rep. 2018;8:13087.
Nichols D, Cahoon N, Trakhtenberg EM, Pham L, Mehta A, Belanger A, et al. Use of ichip for high-throughput in situ cultivation of “uncultivable” microbial species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010;76:2445–50.
Wohlleben W, Mast Y, Evi S, Nadine Z. Antibiotic drug discovery. Microb Biotechnol. 2016;9:541–8.
Scanlon TC, Dostal SM, Griswold KE. A high-throughput screen for antibiotic drug discovery. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2014;111:232–43.
Liu Z, Banaei N, Ren K. Microfluidics for combating antimicrobial resistance. Trends Biotechnol. 2017;35:1129–39.
Mahler L, Tovar M, Weber T, Brandes S, Michael Rudolph M, Ehgartner J, et al. Enhanced and homogeneous oxygen availability during incubation of microfluidic droplets. RSC Adv. 2015;5:101871–8.
Sun S, Kennedy RT. Droplet electrospray ionization mass spectrometry for high throughput screening for enzyme inhibitors. Anal Chem. 2014;86:9309–14.
Funding
This work was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation)—FOR 2177—project number 275564491.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 771 kb)
(MP4 3081 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wink, K., Mahler, L., Beulig, J.R. et al. An integrated chip-mass spectrometry and epifluorescence approach for online monitoring of bioactive metabolites from incubated Actinobacteria in picoliter droplets. Anal Bioanal Chem 410, 7679–7687 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1383-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1383-1