Abstract
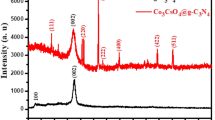
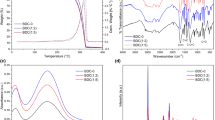
In this work, cobalt magnetic nanoporous carbon (Co-MNPC) is employed as an alternative to intensively used Fe3O4 cores for the preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers (Co-MNPC@MIPs) for the first time. Co-MNPC was prepared by one-step carbonization of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-67 (ZIF-67). Compared with the traditional Fe3O4 core, Co-MNPC showed a high specific surface area and large pore volumes. The prepared adsorbents, which could be rapidly collected from a matrix by external magnetic field, were applied for solid-phase extraction of phthalate plasticizers in edible oil. Several requisite extraction parameters were optimized to achieve desired extraction performance. Under the optimum extraction conditions, Co-MNPC@MIPs displayed better performance than commercialized columns. An analysis method based on Co-MNPC@MIPs coupled with gas chromatography (GC) was established. The linear range was 1–150 μg mL−1, and the detection limit range was 0.010–0.025 μg mL−1. The spiked recovery rate of the five phthalate plasticizers was 81.6–102.2%, with a relative standard deviation of 3.25–12.02%. Finally, the proposed method showed good feasibility for phthalate plasticizer extraction from edible oil.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farajzadeh MA, Sorouraddin SM, Mogaddam MRA. Microextraction methods for the determination of phthalate esters in liquid samples: a review. J Sep Sci. 2015;38(14):2470–87.
Pivnenko K, Eriksen MK, Martín-Fernández JA, Eriksson E, Astrup TF. Recycling of plastic waste: presence of phthalates in plastics from households and industry. Waste Manag. 2016;54:44–52.
Bornehag CG, Nanberg E. Phthalate exposure and asthma in children. Int J Androl. 2010;33(2):333–45.
Yen TH, Lin-Tan DT, Lin JL. Food safety involving ingestion of foods and beverages prepared with phthalate-plasticizer-containing clouding agents. J Formos Med Assoc. 2011;110(11):671–84.
Makkliang F, Kanatharana P, Thavarungkul P, Thammakhet C. Development of magnetic micro-solid phase extraction for analysis of phthalate esters in packaged food. Food Chem. 2015;166:275–82.
Barciela-Alonso MC, Otero-Lavandeira N, Bermejo-Barrera P. Solid phase extraction using molecular imprinted polymers for phthalate determination in water and wine samples by HPLC-ESI-MS. Microchem J. 2017;132:233–7.
Yang R, Liu Y, Yan X, Liu S. Simultaneous extraction and determination of phthalate esters in aqueous solution by yolk-shell magnetic mesoporous carbon-molecularly imprinted composites based on solid-phase extraction coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Talanta. 2016;161:114–21.
Hennion M-C. Solid-phase extraction: method development, sorbents, and coupling with liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 1999;856(1–2):3–54.
Behbahani M, Hassanlou PG, Amini MM, Moazami HR, Abandansari HS, Bagheri A, et al. Selective solid-phase extraction and trace monitoring of lead ions in food and water samples using new lead-imprinted polymer nanoparticles. Food Anal Method. 2015;8(3):558–68.
Wulff G, Sarhan A. Über die Anwendung von enzymanalog gebauten Polymeren zur Racemattrennung. Angew Chem. 1972;84(8):364.
Vlatakis G, Andersson LI, Muller R, Mosbach K. Drug assay using antibody mimics made by molecular imprinting. Nature. 1993;361(6413):645–7.
Lai S, Ouyang X, Cai C, Xu W, Chen C, Chen X. Surface-imprinted microspheres prepared by a template-oriented method for the chiral separation of amlodipine. J Sep Sci. 2017;40(9):1869–76.
Boulanouar S, Mezzache S, Combès A, Pichon V. Molecularly imprinted polymers for the determination of organophosphorus pesticides in complex samples. Talanta. 2018;176(Supplement C):465–78.
Wang Z, Qian Y, Wei X, Zhang Y, Wu G, Lu X. An “on-off” electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer and recycling amplifications for determination of dopamine. Electrochim Acta. 2017;250(Supplement C):309–19.
Mirata F, Resmini M. Molecularly imprinted polymers for catalysis and synthesis. In: Mattiasson B, Ye L, editors. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Biotechnology. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol, 2015. p. 107–129.
Li L, Chen L, Zhang H, Yang Y, Liu X, Chen Y. Temperature and magnetism bi-responsive molecularly imprinted polymers: preparation, adsorption mechanism and properties as drug delivery system for sustained release of 5-fluorouracil. Mater Sci Eng: C. 2016;61(Supplement C):158–68.
Tamayo FG, Turiel E, Martin-Esteban A. Molecularly imprinted polymers for solid-phase extraction and solid-phase microextraction: recent developments and future trends. J Chromatogr A. 2007;1152(1–2):32–40.
Tsukagoshi K, Murata M, Maeda M. In molecularly imprinted polymers: man-made mimics of antibodies and their applications in analytical chemistry. Tech Instrum Anal Chem. 2001;23:245–69.
Komiyama M, Takeuchi T, Mukawa T, Asanuma H. Molecular imprinting: from fundamentals to applications. Wiley Online Library; 2003.
Luo X, Zhan Y, Huang Y, Yang L, Tu X, Luo S. Removal of water-soluble acid dyes from water environment using a novel magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer. J Hazard Mater. 2011;187(1):274–82.
Anirudhan TS, Christa J, Deepa JR. Extraction of melamine from milk using a magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer. Food Chem. 2017;227(Supplement C):85–92.
Ben Aissa A, Herrera-Chacon A, Pupin RR, Sotomayor MDPT, Pividori MI. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for the isolation and detection of biotin and biotinylated biomolecules. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;88(Supplement C):101–8.
Ashley J, Wu K, Hansen MF, Schmidt MS, Boisen A, Sun Y. Quantitative detection of trace level cloxacillin in food samples using magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer extraction and surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy nanopillars. Anal Chem. 2017;89(21):11484–90.
Huang S, Xu J, Zheng J, Zhu F, Xie L, Ouyang G. Synthesis and application of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers in sample preparation. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018.
Kong X-J, Zheng C, Lan Y-H, Chi S-S, Dong Q, Liu H-L, et al. Synthesis of multirecognition magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer by atom transfer radical polymerization and its application in magnetic solid-phase extraction. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018;410(1):247–57.
Moura SL, Fajardo LM, Cunha LDA, Sotomayor MDPT, Machado FBC, Ferrão L, et al. Theoretical and experimental study for the biomimetic recognition of levothyroxine hormone on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;107:203–10.
Yu L, Chen J, Liang Z, Xu W, Chen L, Ye D. Degradation of phenol using Fe3O4-GO nanocomposite as a heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst. Sep Purif Technol. 2016;171:80–7.
Du D, Shi W, Wang L, Zhang J. Yolk-shell structured Fe3O4@void@TiO2 as a photo-Fenton-like catalyst for the extremely efficient elimination of tetracycline. Appl Catal B Environ. 2017;200:484–92.
Furukawa H, Cordova KE, O'Keeffe M, Yaghi OM. The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks. Science. 2013;341(6149):1230444.
Li H, Eddaoudi M, O'Keeffe M, Yaghi OM. Design and synthesis of an exceptionally stable and highly porous metal-organic framework. Nature. 1999;402:276. https://doi.org/10.1038/46248.
Hu Y, Huang Z, Liao J, Li G. Chemical bonding approach for fabrication of hybrid magnetic metal–organic framework-5: high efficient adsorbents for magnetic enrichment of trace analytes. Anal Chem. 2013;85(14):6885–93.
Jia Y, Su H, Wang Z, Wong Y-LE, Chen X, Wang M, et al. Metal–organic framework@microporous organic network as adsorbent for solid-phase microextraction. Anal Chem. 2016;88(19):9364–7.
Zhang X, Liang Q, Han Q, Wan W, Ding M. Metal–organic frameworks@ graphene hybrid aerogels for solid-phase extraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and selective enrichment of proteins. Analyst. 2016;141(13):4219–26.
Li Z-Q, Wang A, Guo C-Y, Tai Y-F, Qiu L-G. One-pot synthesis of metal–organic framework@SiO 2 core–shell nanoparticles with enhanced visible-light photoactivity. Dalton T. 2013;42(38):13948–54.
Qian J, Sun F, Qin L. Hydrothermal synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 (ZIF-67) nanocrystals. Mater Lett. 2012;82:220–3.
Banerjee R, Phan A, Wang B, Knobler C, Furukawa H, O'keeffe M, et al. High-throughput synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks and application to CO2 capture. Science. 2008;319(5865):939–43.
Sun N, Zhang X, Deng C. Designed synthesis of MOF-derived magnetic nanoporous carbon materials for selective enrichment of glycans for glycomics analysis. Nanoscale. 2015;7(15):6487–91.
Liu X, Wang C, Wu Q, Wang Z. Metal-organic framework-templated synthesis of magnetic nanoporous carbon as an efficient absorbent for enrichment of phenylurea herbicides. Anal Chim Acta. 2015;870:67–74.
Li X, Zeng C, Jiang J, Ai L. Magnetic cobalt nanoparticles embedded in hierarchically porous nitrogen-doped carbon frameworks for highly efficient and well-recyclable catalysis. J Mater Chem A. 2016;4(19):7476–82.
Min HY, Fow KL, Chen GZ. Synthesis and applications of MOF - derived porous nanostructures. Green Energ Environ. 2017.
Andrew Lin K-Y, Lee W-D. Self-assembled magnetic graphene supported ZIF-67 as a recoverable and efficient adsorbent for benzotriazole. Chem Eng J. 2016;284:1017–27.
Lin K-YA, Chang H-A. Ultra-high adsorption capacity of zeolitic imidazole framework-67 (ZIF-67) for removal of malachite green from water. Chemosphere. 2015;139:624–31.
Liu X, Wang C, Wang Z, Wu Q, Wang Z. Nanoporous carbon derived from a metal organic framework as a new kind of adsorbent for dispersive solid phase extraction of benzoylurea insecticides. Microchim Acta. 2015;182(11):1903–10.
Zeng Y, Zhou Y, Kong L, Zhou T, Shi G. A novel composite of SiO2-coated graphene oxide and molecularly imprinted polymers for electrochemical sensing dopamine. Biosens Bioelectron. 2013;45:25–33.
Su X, Li X, Li J, Liu M, Lei F, Tan X, et al. Synthesis and characterization of core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for solid-phase extraction and determination of Rhodamine B in food. Food Chem. 2015;171:292–7.
Li W-k, Chen J, Zhang H-x, Shi Y-p. Selective determination of aromatic acids by new magnetic hydroxylated MWCNTs and MOFs based composite. Talanta. 2017;168:136–45.
Frizzarin RM, Palomino Cabello C, Bauzà MdM, Portugal LA, Maya F, Cerdà V et al. Submicrometric magnetic Nanoporous carbons derived from metal–organic frameworks enabling automated electromagnet-assisted online solid-phase extraction. Anal Chem 2016;88(14):6990–6995. doi:https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b02065.
Prokůpková G, Holadová K, Poustka J, Hajšlová J. Development of a solid-phase microextraction method for the determination of phthalic acid esters in water. Anal Chim Acta. 2002;457(2):211–23.
Li C, Ma X, Zhang X, Wang R, Chen Y, Li Z. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles-based solid-phase extraction coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry for selective determination of trace di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in water samples. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016;408(27):7857–64.
Liu X, Sun Z, Chen G, Zhang W, Cai Y, Kong R, et al. Determination of phthalate esters in environmental water by magnetic Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 solid-phase extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2015;1409:46–52.
Xu M, Liu M, Sun M, Chen K, Cao X, Hu Y. Magnetic solid-phase extraction of phthalate esters (PAEs) in apparel textile by core-shell structured Fe3O4@silica@triblock-copolymer magnetic microspheres. Talanta. 2016;150:125–34
Wu W, Hu J, Wang J, Chen X, Yao N, Tao J et al. Analysis of phthalate esters in soils near an electronics manufacturing facility and from a non-industrialized area by gas purge microsyringe extraction and gas chromatography. Sci Total Environ. 2015;508:445–51
Lv YK, Zhang W, Guo MM, Zhao FF, Du XX. Centrifugal microextraction tube - cloud point extraction coupled with gas chromatography for simultaneous determination of six phthalate esters in mineral water. Anal Methods. 2015;7(2):560–5
Feng C-H, Jiang S-R. Micro-scale quantitation of ten phthalate esters in water samples and cosmetics using capillary liquid chromatography coupled to UV detection: effective strategies to reduce the production of organic waste. Microchim Acta. 2012;177(1-2):167–75
Qiao J, Wang M, Yan H, Yang G. Dispersive solid-phase extraction based on magnetic dummy molecularly imprinted microspheres for selective screening of phthalates in plastic bottled beverages. J Agric Food Chem. 2014;62(13):2782–9
Yan H, Cheng X, Yang G. Dummy Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction for Selective Determination of Five Phthalate Esters in Plastic Bottled Functional Beverages. J Agric Food Chem. 2012;60(22):5524–31
He J, Lv R, Zhu J, Lu K. Selective solid-phase extraction of dibutyl phthalate from soybean milk using molecular imprinted polymers. Anal Chim Acta. 2010;661(2):215
Funding
This study received financial support from the following research funds: National Natural Science Foundation of China (21575034, 51502079, 21577031, 21775140), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Henan Provincial Colleges and Universities in Henan University of Technology (2017RCJH10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 178 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, C., He, J., Chen, N. et al. Synthesis of cobalt-based magnetic nanoporous carbon core-shell molecularly imprinted polymers for the solid-phase extraction of phthalate plasticizers in edible oil. Anal Bioanal Chem 410, 6943–6954 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1299-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1299-9