Abstract
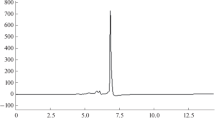
In the study presented, a simple analytical method for the direct determination of glycine in immunoglobulins by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography was developed. The HPLC separation was performed using a SeQuant ZIC-HILIC column (250 mm × 4.6 mm i.d, 5 μm) with the isocratic mobile phase consisting of ammonium formate (20 mM) and acetonitrile (30:70, v/v), and the flow rate set at 0.8 mL/min. UV detection was carried out at a wavelength of 210 nm. The procedure was validated for specificity, precision, linearity, accuracy, limit of detection, limit of quantitation, and robustness. The calibration curve was found to be linear within the concentration range of 1.2–3.6 mg/mL. RSD values for intra-day and inter-day precision were in the range of 0.66 to 1.84%. The limit of quantification and limit of detection were 0.10 mg/mL and 0.03 mg/mL, respectively. The developed chromatographic method was applied for the glycine analysis in various immunoglobulins.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HILIC:
-
Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography
- IgG:
-
Immunoglobulin G
References
Orange J, Hossny E, Weiler C, Ballow M, Berger M, Bonilla F, et al. Use of intravenous immunoglobulin in human disease: a review of evidence by members of the Primary Immunodeficiency Committee of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117(4):S525–53.
European Pharmacopoeia, 9.0, European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines and Health Care. Human normal immunoglobulin for intravenous administration. Strasbourg 2016; monograph 0918, 2687–9.
Dantal J. Intravenous immunoglobulins: in-depth review of excipients and acute kidney injury risk. Am J Nephrol. 2013;38(4):275–84. https://doi.org/10.1159/000354893.
Chapman S, Gilkerson K, Davin T, Pritzker M. Acute renal failure and intravenous immune globulin: occurs with sucrose-stabilized, but not with D-sorbitol-stabilized formulation. Ann Pharmacother. 2004;38(12):2059–67. https://doi.org/10.1345/aph.1E040.
Fekkes D, van Dalen A, Edelman M, Voskuilen A. Validation of the determination of amino acids in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography using automated pre-column derivatization with o-phtaldialdehyde. J Chromatogr B Biomed Appl. 1995;669:177–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-4347(95)00111-U.
Fekkes D. State-of-the-art of high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of amino acids in physiological samples. J Chromatogr B Biomed Appl. 1996;682:3–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-4347(96)00057-6.
Bosch L, Alegría A, Farré R. Application of the 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysccinimidyl carbamate (AQC) reagent to the RP-HPLC determination of amino acids in infant foods. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2006;831:176–83.
Cohen SA. Amino acid analysis using precolumn derivatization with 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate. Methods Mol Biol. 2000;159:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-047-0:039.
Marrubini G, Caccialanza G, Massolini G. Determination of glycine and threonine in topical dermatological preparations. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008;47(4–5):716–22.
Dolowy M, Pyka A. Application of TLC, HPLC and GC methods to the study of amino acid and peptide enantiomers. Biomed Chromatogr. 2008;28:84–101.
Zhong Q, Huang Q, Li S, Yang M, Rao B. Simultaneous determination of glutamate, glycine, and alanine in human plasma using precolumn derivatization with 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate and high-performance liquid chromatography. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012;16(5):355–60.
Groselj U, Murko S, Zerjav Tansek M, Kovac J, Trampus Bakija A, Repic Lampret B, et al. Comparison of tandem mass spectrometry and amino acid analyzer for phenylalanine and tyrosine monitoring - implications for clinical management of patients with hyperphenylalaninemia. Clin Biochem. 2015;48(1–2):14–8.
Periat A, Krull I, Guillarme D. Applications of hydrophilic interaction chromatography to amino acids, peptides, and proteins. J Sep Sci. 2015;38(3):357–67. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201400969.
Socia A, Foley J. Direct determination of amino acids by hydrophilic interaction chromatography with charged aerosol detection. J Chromatogr A. 2016;1446:41–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.03.042.
Kato M, Kato H, Evama S, Takatsu A. Application of amino acids analysis using hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled with isotope dilution mass spectrometry for peptide and protein quantification. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2009;877(27):3059–64.
Dell’mour M, Jaitz L, Oburger E, Puschenreiter M, Koellensperger G, Hann S. Hydrophilic interaction LC combined with electrospray MS for highly sensitive analysis of underivatized amino acids in rhizosphere research. J Sep Sci. 2010;33(6–7):911–22.
Iwasaki Y, Sawada T, Hatayama K, Ohyagi A, Tsukuda Y, Namekawa K, et al. Separation technique for the determination of highly polar metabolites in biological samples. Meta. 2012;2:496–515.
Reviewer guidance: validation of chromatographic methods, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), Washington. 1994, https://doi.org/10.17226/4757.
Jandera P. Stationary and mobile phases in hydrophilic interaction chromatography: a review. Anal Chim Acta. 2011;692(1–2):1–25.
Ruta J, Rudaz S, McCalley DV, Veuthey JL, Guillarme D. A systematic investigation of the effect of sample diluent on peak shape in hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2010;1217(52):8230–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2010.10.106.
Heaton JC, McCalley DV. Some factors that can lead to poor peak shape in hydrophilic interaction chromatography, and possibilities for their remediation. J Chromatogr A. 2016;1427:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.10.056.
McCalley D. Study of the selectivity, retention mechanisms and performance of alternative silica-based stationary phases for separation of ionised solutes in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2010;1217(20):3408–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2010.03.011.
Guo Y, Gaiki S. Retention and selectivity of stationary phases for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2011;1218(35):5920–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2011.06.052.
Guo Y, Gaiki S. Retention behavior of small polar compounds on polar stationary phases in hydrophilic interaction chromatograph. J Chromatogr A. 2005;1074(1–2):71–80.
Hao Z, Xiao B, Weng N. Impact of column temperature and mobile phase components on selectivity of hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC). J Sep Sci. 2008;31(9):1449–64. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200700624.
Johnsen E, Wilson SR, Odsbu I, Krapp A, Malerod H, Skarstad K, et al. Hydrophilic interaction chromatography of nucleoside triphosphates with temperature as a separation parameter. J Chromatogr A. 2011;1218(35):5981–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2011.01.066.
Kumar A, Heaton JC, McCalley DV. Practical investigation of the factors that affect the selectivity in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1276:33–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2012.12.037.
ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline, Validation of analytical procedures: text and methodology Q2(R1). International conference on harmonisation of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use. 2005.
Green JM. A practical guide to analytical method validation, analytical chemistry news and features. 1996;305A-9A.
Shabir GA. Validation of high-performance liquid chromatography methods for pharmaceutical analysis. Understanding the differences and similarities between validation requirements of the US Food and Drug Administration, the US Pharmacopeia and the International Conference on Harmonization. J Chromatogr A. 2003;987(1–2):57–66.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Informed consent
Informed consent was not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rounova, O., Demin, P., Korotkov, M. et al. Development of a hydrophilic interaction high-performance liquid chromatography method for the determination of glycine in formulations of therapeutic immunoglobulins. Anal Bioanal Chem 410, 6935–6942 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1297-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1297-y