Abstract
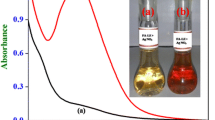
We have developed a green approach to prepare DNA-templated silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) from the direct reaction between Ag+ and ascorbic acid in the presence of DNA and sodium hydroxide. The Ag-NPs showed strong resonance light scattering (RLS) intensity property. Then, the interaction between hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and Ag-NPs was studied by measuring their RLS spectra. The results showed that there is a strong interaction between Ag-NPs and H2S, which resulted in a decrease in the size of Ag-NPs and a decrease in the RLS intensity of the Ag-NPs solution at the wavelength of 467 nm. The results demonstrated that the RLS technique offers a sensitive and simple tool for investigating the interaction between Ag-NPs and H2S, which can be applied to detect H2S with high sensitivity and selectivity without complex readout equipment. The linear range for H2S determination was found to be the range from 5.0 × 10−9 to 1.0 × 10−7 mol L−1, and the detection limit (3σ/k) was 2.8 × 10−9 mol L−1. Moreover, the proposed method was applied for the determination of H2S in natural water samples with satisfactory results.

The application of Ag-NPs in H2S detection






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haggard HW, Henderson Y. The influence of hydrogen sulphide upon respiration. Am J Phys. 1922;61(2):289–97.
Haggard HW. The fate of sulfides in the blood. J Biol Chem. 1921;49(2):519–29.
Calvert JW, Elston M, Nicholson CK, Gundewar S, Jha S, Elrod JW, Ramachandran A, Lefer DJ. Genetic and pharmacologic hydrogen sulfide therapy attenuates ischemia-induced heart failure in mice. Circulation. 2010;122(1):11–9.
Elrod JW, Calvert JW, Morrison J, Doeller JE, Kraus DW, Tao L, Jiao X, Scalia R, Kiss L, Szabo C. Hydrogen sulfide attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by preservation of mitochondrial function. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2007;104(39):15560–5.
Calvert JW, Jha S, Gundewar S, Elrod JW, Ramachandran A, Pattillo CB, Kevil CG, Lefer DJ. Hydrogen sulfide mediates cardioprotection through Nrf2 signaling. Circ Res. 2009;105(4):365–74.
Abe K, Kimura H. The possible role of hydrogen sulfide as an endogenous neuromodulator. J Neurosci. 1996;16(3):1066–71.
Boehning D, Snyder SH. Novel neural modulators. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2003;26(1):105–31.
Kimura H. Hydrogen sulfide as a neuromodulator. Mol Neurobiol. 2002;26(1):13–9.
Martelli A, Testai L, Breschi MC, Blandizzi C, Virdis A, Taddei S, Calderone V. Hydrogen sulphide: novel opportunity for drug discovery. Med Res Rev. 2012;32(6):1093–130.
Kamoun P, Belardinelli MC, Chabli A, Lallouchi K, Chadefaux VB. Endogenous hydrogen sulfide overproduction in Down syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2003;116(3):310–1.
Eto K, Asada T, Arima K, Makifuchi T, Kimura H. Brain hydrogen sulfide is severely decreased in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;293(5):1485–8.
Giovanelli D, Lawrence NS, Jiang L, Jones TGJ, Compton RG. Electrochemical determination of sulphide at nickel electrodes in alkaline media: a new electrochemical sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2003;88(3):320–8.
Doeller JE, Isbell TS, Benavides G, Koenitzer J, Patel H, Patel RP, Lancaster Jr JR, Darley-Usmar VM, Kraus DW. Polarographic measurement of hydrogen sulfide production and consumption by mammalian tissues. Anal Biochem. 2005;341(1):40–51.
Colon M, Todolí JL, Hidalgo M, Iglesias M. Development of novel and sensitive methods for the determination of sulfide in aqueous samples by hydrogen sulfide generation-inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy. Anal Chim Acta. 2008;609(2):160–8.
Ubuka T, Abe T, Kajikawa R, Morino K. Determination of hydrogen sulfide and acid-labile sulfur in animal tissues by gas chromatography and ion chromatography. J Chromatogr B. 2001;757(1):31–7.
Huang R, Zheng X, Qu Y. Highly selective electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) for sulfide ion determination at multi-wall carbon nanotubes-modified graphite electrode. Anal Chim Acta. 2007;582(2):267–74.
Shanmugaraj K, Ilanchelian M. Colorimetric determination of sulfide using chitosan-capped silver nanoparticles. Microchim Acta. 2016;183(5):1721–8.
Okumura M, Yano N, Fujinaga K, Seike Y, Matsuo S. In situ preconcentration method for trace dissolved sulfide in environmental water samples using solid-phase extraction followed by spectrophotometric determination. Anal Sci. 1999;15(5):427–31.
Pasternack RF, Bustamante C, Collings PJ, Giannetto A, Gibbs EJ. Porphyrin assemblies on DNA as studied by a resonance light-scattering technique. J Am Chem Soc. 1993;115(13):5393–9.
Zhao Y, Cao Q-E, Hu Z, Xu Q. Synthesis of a new triazene reagent and its application for the determination of silver(I) by the Rayleigh light-scattering. Anal Chim Acta. 1999;388(1–2):45–50.
Chen Z, Ding W, Ren F, Liu J, Liang Y. A simple and sensitive assay of nucleic acids based on the enhanced resonance light scattering of zwitterionics. Anal Chim Acta. 2005;550(1):204–9.
Huang CZ, Li YF, Feng P. Determination of proteins with α, β, γ, δ-tetrakis (4-sulfophenyl) porphine by measuring the enhanced resonance light scattering at the air/liquid interface. Anal Chim Acta. 2001;443(1):73–80.
Yao G, Li KA, Tong SY. Study on the interaction of protein with sulfonazo III by Rayleigh light scattering technique and its application. Anal Chim Acta. 1999;398(2):319–27.
Liu S, Luo H, Li N, Liu Z, Zheng W. Resonance Rayleigh scattering study of the interaction of heparin with some basic diphenyl naphthylmethane dyes. Anal Chem. 2001;73(16):3907–14.
Ling J, Huang CZ, Li YF, Long YF, Liao QG. Recent developments of the resonance light scattering technique: technical evolution, new probes and applications. Appl Spectrosc Rev. 2007;42(2):177–201.
Feng P, Shu WQ, Huang CZ, Li YF. Total internal reflected resonance light scattering determination of chlortetracycline in body fluid with the complex cation of chlortetracycline−europium−trioctyl phosphine oxide at the water/tetrachloromethane interface. Anal Chem. 2001;73(17):4307–12.
Wang YH, Guo HP, Tan KJ, Huang CZ. Backscattering light detection of nucleic acids with tetraphenylporphyrin–Al(III)–nucleic acids at liquid/liquid interface. Anal Chim Acta. 2004;521(1):109–15.
Liu X, Atwater M, Wang J, Huo Q. Extinction coefficient of gold nanoparticles with different sizes and different capping ligands. Colloid Surface B. 2007;58(1):3–7.
Liang S, Kuang Y, Ma F, Chen S, Long Y. A sensitive spectrofluorometric method for detection of berberine hydrochloride using Ag nanoclusters directed by natural fish sperm DNA. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;85:758–63.
Slocik JM, Wright DW. Biomimetic mineralization of noble metal nanoclusters. Biomacromolecules. 2003;4(5):1135–41.
Harris DC. Quantitative chemical analysis, 6th Ed. W.H. Freeman, 2010.
Hatamie A, Zargar B, Jalali A. Copper nanoparticles: a new colorimetric probe for quick, naked-eye detection of sulfide ions in water samples. Talanta. 2014;121:234–8.
Akins D, Zhu H, Guo C. Absorption and Raman scattering by aggregated meso-tetrakis (p-sulfonatophenyl) porphine. J Phys Chem. 1994;98(14):3612–8.
Miller GA. Fluctuation theory of the resonance enhancement of Rayleigh scattering in absorbing media. J Phys Chem. 1978;82(5):616–8.
Long YF, Huang CZ, He RX, Li YF. Selectively light scattering spectrometric detection of copper(II) based on a new synthesized oxamide ligand. Anal Chim Acta. 2008;624(1):128–32.
Zhang SZ, Zhao FL, Li KA, Tong SY. A study on the interaction between concanavalin A and glycogen by light scattering technique and its analytical application. Talanta. 2001;54(2):333–42.
Yu N, Peng H, Xiong H, Wu X, Wang X, Li Y, Chen L. Graphene quantum dots combined with copper(II) ions as a fluorescent probe for turn-on detection of sulfide ions. Microchim Acta. 2015;182(13):1–8.
Jin Y, Wu H, Tian Y, Chen L, Cheng J, Bi S. Indirect determination of sulfide at ultratrace levels in natural waters by flow injection on-line sorption in a knotted reactor coupled with hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2007;79(18):7176–81.
Acknowledgments
This work has been gotten the supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21275047 to YL, No. 21445008 to SC), supported by Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 2016JJ5005 to YL), and Doctor Science Foundation of Hunan University of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 174 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuang, Y., Chen, S. & Long, Y. Highly sensitive and selective determination of hydrogen sulfide by resonance light scattering technique based on silver nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem 409, 4001–4008 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0343-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0343-5