Abstract
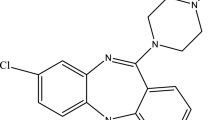
An efficient and inexpensive method using vortex-assisted surfactant-enhanced emulsification microextraction (VASEME) based on solidification of floating organic droplet coupled with ultraperformance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry is proposed for the analysis of glucocorticoids in water samples (river water and hospital wastewater). VASEME was optimized by the experimental validation of Plackett–Burman design and central composite design, which has been co-related to experimental design. Plackett–Burman design showed that factors such as vortex time, surfactant concentration, and pH significantly affect the extraction efficiency of the method. Method validation was characterized by an acceptable calibration range of 1–1000 ng L−1, and the limit of detection was in the range from 2.20 to 8.12 ng L−1 for glucocorticoids. The proposed method was applied to determine glucocorticoids in river water and hospital wastewater in Lucknow, India. It is reliable and rapid and has potential application for analysis of glucocorticoids in environmental aqueous samples.

Low density based extraction of gluococorticoids by using design of experiment






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim S-C, Carlson K. Occurrence of ionophore antibiotics in water and sediments of a mixed-landscape watershed. Water Res. 2006;40(13):2549–60.
Samanidou VF, Karageorgou EG, Papadoyannis IN. Simultaneous determination of testosterone and its major metabolite epitestosterone in biological fluids by HPLC. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol. 2007;30(9-10):1317–31.
Chiesa L, Nobile M, Panseri S, Vigo D, Pavlovic R, Arioli F. Suitability of bovine bile compared to urine for detection of free, sulfate and glucuronate boldenone, androstadienedione, cortisol, cortisone, prednisolone, prednisone and dexamethasone by LC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2015;188:473–80.
Chang H, Wan Y, Hu J. Determination and source apportionment of five classes of steroid hormones in urban rivers. Environ Sci Technol. 2009;43(20):7691–8.
Vieno NM, Tuhkanen T, Kronberg L. Seasonal variation in the occurrence of pharmaceuticals in effluents from a sewage treatment plant and in the recipient water. Environ Sci Technol. 2005;39(21):8220–6.
Arditsoglou A, Voutsa D. Determination of phenolic and steroid endocrine disrupting compounds in environmental matrices. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2008;15(3):228–36.
Crain A, GuilletteJr LJ. Environmental endocrine disruptors: an evolutionary perspective: CRC Press; 2000.
Richardson SD. Water analysis: emerging contaminants and current issues. Anal Chem. 2009;81(12):4645–77.
Stumpf M, Ternes TA, Wilken R-D, Rodrigues SV, Baumann W. Polar drug residues in sewage and natural waters in the state of Rio de Janeiro. Brazil Sci Total Environ. 1999;225(1):135–41.
Sun H, Kang Z, Li H, Zhang J, Lv Y. Quantitative determination and confirmation of five synthetic glucocorticoid residues in milk powder by gel permeation chromatography–liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Food Anal Methods. 2012;5(4):643–50.
Callejas SL, Biddlecombe RA, Jones AE, Joyce KB, Pereira AI, Pleasance S. Determination of the glucocorticoid fluticasone propionate in plasma by automated solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B. 1998;718(2):243–50.
Volmer DA, Hui JP. Rapid determination of corticosteroids in urine by combined solid phase microextraction/liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1997;11(17):1926–34.
Amendola L, Garribba F, Botrè F. Determination of endogenous and synthetic glucocorticoids in human urine by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry following microwave-assisted derivatization. Anal Chim Acta. 2003;489(2):233–43.
Krone N, Hughes BA, Lavery GG, Stewart PM, Arlt W, Shackleton CH. Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) remains a pre-eminent discovery tool in clinical steroid investigations even in the era of fast liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2010;121(3):496–504.
Liu R, Zhou JL, Wilding A. Simultaneous determination of endocrine disrupting phenolic compounds and steroids in water by solid-phase extraction gas chromatography mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2004;1022(1):179–89.
Kelly C. Analysis of steroids in environmental water samples using solid-phase extraction and ion-trap gas chromatography mass spectrometry and gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2000;872(1):309–14.
Yang L, Luan T, Lan C. Solid-phase microextraction with on-fiber silylation for simultaneous determinations of endocrine disrupting chemicals and steroid hormones by gas chromatography mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2006;1104(1):23–32.
Walker CJ, Cowan DA, Taylor NF, Kicman AT. Determination of xenobiotic glucocorticoids by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for clinical purposes. Endoc Abstr. 2006;12:119.
Cui X, Shao B, Zhao R, Yang Y, Hu J, Tu X. Simultaneous determination of seventeen glucocorticoids residues in milk and eggs by ultra-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2006;20(15):2355–64.
Almeida C, Nogueira JMF. Determination of steroid sex hormones in water and urine matrices by stir bar sorptive extraction and liquid chromatography with diode array detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2006;41(4):1303–11.
Herrero P, Borrull F, Pocurull E, Marce RM. Determination of glucocorticoids in sewage and river waters by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2012;1224:19–26.
Qin H, Li B, Liu MS, Yang YL. Separation and pre-concentration of glucocorticoids in water samples by ionic liquid supported vortex assisted synergic microextraction and HPLC determination. J Sep Sci. 2013;36(8):1463–9.
Sniecinska-Cooper AM, Shah AJ, Dimitriou D, Iles RK, Butler SA, Bayford R. Determination of urinary cortisol, cortisone and 6-sulfatoxymelatonin using dilute and shoot ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B. 2015;978:18–23.
Chen D, Tao Y, Liu Z, Zhang H, Liu Z, Wang Y, et al. Development of a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with pressurized liquid extraction for determination of glucocorticoid residues in edible tissues. J Chromatogr B. 2011;879(2):174–80.
De Clercq N, Bussche JV, Croubels S, Delahaut P, Vanhaecke L. Development and validation of a high-resolution mass-spectrometry based method to study the long-term stability of natural and synthetic glucocorticoids in faeces. J Chromatogr A. 2014;1336:76–86.
DiFrancesco R, Frerichs V, Donnelly J, Hagler C, Hochreiter J, Tornatore KM. Simultaneous determination of cortisol, dexamethasone, methylprednisolone, prednisone, prednisolone, mycophenolic acid and mycophenolic acid glucuronide in human plasma utilizing liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B. 2007;859(1):42–51.
Frerichs VA, Tornatore KM. Determination of the glucocorticoids prednisone, prednisolone, dexamethasone, and cortisol in human serum using liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B. 2004;802(2):329–38.
Vonaparti A, Lyris E, Panderi I, Koupparis M, Georgakopoulos C. Direct injection LC/ESI/MS horse urine analysis for the quantification and identification of threshold substances for doping control. I. determination of hydrocortisone. J Mass Spectrom. 2008;43(9):1255–64.
Xue X, Zheng C, Jifeng L, Jing Z, Huihua D, Zuhong L. Study on dissolution mechanism of cortisol and cortisone from hair matrix with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chim Acta. 2013;421:62–72.
Fiori J, Andrisano V. LC-MS method for the simultaneous determination of six glucocorticoids in pharmaceutical formulations and counterfeit cosmetic products. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014;91:185–92.
Shou M, Galinada WA, Wei Y-C, Tang Q, Markovich RJ, Rustum AM. Development and validation of a stability-indicating HPLC method for simultaneous determination of salicylic acid, betamethasone dipropionate and their related compounds in Diprosalic Lotion®. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2009;50(3):356–61.
Ho EN, Leung DK, Wan TS, Nola HY. Comprehensive screening of anabolic steroids, corticosteroids, and acidic drugs in horse urine by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2006;1120(1):38–53.
Andersen JH, Hansen LG, Pedersen M. Optimization of solid phase extraction clean up and validation of quantitative determination of corticosteroids in urine by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta. 2008;617(1):216–24.
Kumazawa T, Lee X-P, Sato K, Suzuki O. Solid-phase microextraction and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry in drug analysis. Anal Chim Acta. 2003;492(1):49–67.
Draisci R, Palleschi L, Ferretti E, Marchiafava C, Lucentini L, Cammarata P. Quantification of 17β-estradiol residues in bovine serum by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization. Analyst. 1998;123(12):2605–9.
Carabias-Martínez R, Rodríguez-Gonzalo E, Revilla-Ruiz P, Hernández-Méndez J. Pressurized liquid extraction in the analysis of food and biological samples. J Chromatogr A. 2005;1089(1):1–17.
Rezaee M, Assadi Y, Hosseini M-RM, Aghaee E, Ahmadi F, Berijani S. Determination of organic compounds in water using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. J Chromatogr A. 2006;1116(1):1–9.
Wu Q, Chang Q, Wu C, Rao H, Zeng X, Wang C, et al. Ultrasound-assisted surfactant-enhanced emulsification microextraction for the determination of carbamate pesticides in water samples by high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2010;1217(11):1773–8.
Shamsipur M, Jouybari TA, Barati A, Mahmoudi M, Amin N, Pashabadi A. A manual shaking-enhanced, ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the determination of betamethasone and dexamethasone: optimization using Response surface methodology. Anal Methods. 2014;6(13):4542–50.
Yiantzi E, Psillakis E, Tyrovola K, Kalogerakis N. Vortex-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction of octylphenol, nonylphenol and bisphenol-A. Talanta. 2010;80(5):2057–62.
Zgoła-Grześkowiak A, Grześkowiak T. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. Trends Anal Chem. 2011;30(9):1382–99.
Ghorbani M, Chamsaz M, Rounaghi GH, Aghamohammadhasani M, Seyedin O, Lahoori NA. Development of a novel ultrasonic-assisted magnetic dispersive solid-phase microextraction method coupled with high performance liquid chromatography for determination of mirtazapine and its metabolites in human urine and water samples employing experimental design. J Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016;408(27):7719–29.
Abilasha R, Kumar PV, Jen J-F. Low density extractant based ultrasound-assisted surfactant-enhanced emulsification microextraction for the determination of aniline and its chlorinated derivatives in water samples by HPLC-UV. http://research.nchu.edu.tw/upfiles/ADUpload/oc_downmul1408321695.pdf.
Ezoddin M, Taghizadeh T, Majidi B. Ultrasound-assisted surfactant-enhanced emulsification microextraction for the determination of Cd and Ni in tea and water samples. Environ Technol. 2014;35(19):2401–9.
Anjum F, Shahid M, Bukhari S, Potgieter JH. Combined ultrasonic and bioleaching treatment of hospital waste incinerator bottom ash with simultaneous extraction of selected metals. Environ Technol. 2014;35(3):262–70.
Abdelhamid HN, Bhaisare ML, Wu H-F. Ceria nanocubic-ultrasonication assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled with matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry for pathogenic bacteria analysis. Talanta. 2014;120:208–17.
Khodadoust S, Hadjmohammadi M. Determination of N-methylcarbamate insecticides in water samples using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and HPLC with the aid of experimental design and desirability function. Anal Chim Acta. 2011;699(1):113–9.
Bezerra MA, Santelli RE, Oliveira EP, Villar LS, Escaleira LA. Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta. 2008;76(5):965–77.
Khodadoust S, Ghaedi M. Optimization of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction with central composite design for preconcentration of chlordiazepoxide drug and its determination by HPLC–UV. J Sep Sci. 2013;36(11):1734–42.
Sereshti H, Karimi M, Samadi S. Application of response surface method for optimization of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of water-soluble components of Rosa damascena Mill. essential oil. J Chromatogr A. 2009;1216(2):198–204.
Masson P. Quality control techniques for routine analysis with liquid chromatography in laboratories. J Chromatogr A. 2007;1158(1):168–73.
Konieczka P, Namieśnik J. Estimating uncertainty in analytical procedures based on chromatographic techniques. J Chromatogr A. 2010;1217(6):882–91.
Whitmire M, Ammerman J, de Lisio P, Killmer J, Kyle D, Mainstone E, et al. LC-MS/MS bioanalysis method development, validation, and sample analysis: points to consider when conducting nonclinical and clinical studies in accordance with current regulatory guidances. J Anal Bioanal Tech. 2013; 2011.
Hall TG, Smukste I, Bresciano KR, Wang Y, McKearn D, Savage RE. Identifying and overcoming matrix effects in drug discovery and development. In: Prasain J, editor. Tandem mass spectrometry - applications and principles. InTech; 2012. doi:10.5772/32108
Stokvis E, Rosing H, Beijnen JH. Stable isotopically labeled internal standards in quantitative bioanalysis using liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry: necessity or not? Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2005;19(3):401–7.
Wieling J. LC-MS-MS experiences with internal standards. Chromatographia. 2002;55(1):S107–13.
Matuszewski B, Constanzer M, Chavez-Eng C. Strategies for the assessment of matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLC-MS/MS. Anal Chem. 2003;75(13):3019–30.
Kumari R, Patel DK, Panchal S, Jha RR, Satyanarayana G, Asati A, et al. Fast agitated directly suspended droplet microextraction technique for the rapid analysis of eighteen organophosphorus pesticides in human blood. J Chromatogr A. 2015;1377:27–34.
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to the Director, CSIR-Indian Institute of Toxicology Research, Lucknow, India, for providing the necessary facilities for this research study. The authors also thank the University Grant Commission, GAP project-155, New Delhi, India, and the CSIR-INDEPTH project for financial assistance. We are also thankful to B.D. Bhattacharji for support in terms of manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Humans or animals study
This study does not involve any experiments on humans or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This is CSIR-IITR institutional communication no. 3448.
Ankita Asati and G. N. V. Satyanarayana contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 107 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asati, A., Satyanarayana, G.N.V. & Patel, D.K. Vortex-assisted surfactant-enhanced emulsification microextraction combined with LC–MS/MS for the determination of glucocorticoids in water with the aid of experimental design. Anal Bioanal Chem 409, 2905–2918 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0236-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0236-7