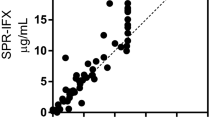
Abstract
Adalimumab (ADA) is a TNF-α blocker drug antibody fully humanized and thus indistinguishable in structure and function from natural human IgG1, used in the juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) treatment. Immunogenicity against the drug has been frequently detected in treated patients, and the presence of anti-ADA antibodies is correlated to treatment failure or lower clinical remission. Herein, we measured by surface plasmon resonance (SPR) both the binding and the affinity of anti-ADA antibodies to the ADA-immobilized biosensor. The binding of anti-ADA antibodies was evaluated by testing sera from ADA-treated patients (n = 30), untreated patients (n = 9), and healthy donors (n = 20) in the SPR biosensor. The optimal cut-off point was defined using the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC-curve) analysis with 79 % (60.28 to 92.01 %, 95 % CI) sensitivity, 99 % (88.06 to 100.0 %, 95 % CI) specificity, and a positive likelihood ratio of 23. The area under the curve was 0.9298 (p < 0.0001). The apparent affinity of anti-ADA antibodies from pediatric patients’ sera was measured, analyzing the interaction of anti-drug antibodies using whole sera, enriched IgG fractions, and isolated anti-ADA antibodies. The immobilized drug ADA interacted with purified antibodies at low affinities (10−6 M > K D > 10−9 M).

Adalimumab immobilized on the biosensor chip surface detects specific anti-drug antibodies in treated patients’ sera





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suryaprasad AG, Prindiville T (2003) The biology of TNF blockade. Autoimmun Rev 2:346–357
Armuzzi A, Lionetti P, Blandizzi C, Caporali R, Chimenti S, Cimino L, Gionchetti P, Girolomoni G, Lapadula G, Marchesoni A, Marcellusi A, Mennini FS, Salvarani C, Cimaz R (2014) Anti-TNF agents as therapeutic choice in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases: focus on adalimumab. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 27(1 Suppl):11–32
Ungar WJ, Costa V, Burnett HF, Feldman BM, Laxer RM (2013) The use of biologic response modifiers in polyarticular-course juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 42(6):597–618
Otten MH, Anink J, Spronk S, van Suijlekom-Smit LW (2013) Efficacy of biological agents in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a systematic review using indirect comparisons. Ann Rheum Dis 72(11):1806–12
Schmeling H, Minden K, Foeldvari I, Ganser G, Hospach T, Horneff G (2014) Efficacy and safety of adalimumab as the first and second biologic agent in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: the German biologics JIA registry. Arthritis Rheumatol 66(9):2580–2589
La Torre F, Cattalini M, Teruzzi B, Meini A, Moramarco F, Iannone F (2014) Efficacy of adalimumab in young children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis and chronic uveitis: a case series. BMC Res Notes 7:316
Lovell DJ, Ruperto N, Goodman S, Reiff A, Jung L, Jarosova K, Nemcova D, Mouy R, Sandborg C, Bohnsack J, Elewaut D, Foeldvari I, Gerloni V, Rovensky J, Minden K, Vehe RK, Weiner LW, Horneff G, Huppertz HI, Olson NY, Medich JR, Carcereri-De-Prati R, McIlraith MJ, Giannini EH, Martini A (2008) Adalimumab with or without methotrexate in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 359(8):810–820
Salfeld J, Kaymakcalan Z, Tracey D, Roberts A, Kamen R (1998) Generation of fully human anti-TNF antibody D2E7 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheum 41(9):S57
Vogelzang EH, Kneepkens EL, Nurmohamed MT, van Kuijk AW, Rispens T, Wolbink G, Krieckaert CL (2014) Anti-adalimumab antibodies and adalimumab concentrations in psoriatic arthritis: an association with disease activity at 28 and 52 weeks of follow-up. Ann Rheum Dis 73(12):2178–2182
Imaeda H, Takahashi K, Fujimoto T, Bamba S, Tsujikawa T, Sasaki M, Fujiyama Y, Andoh A (2014) Clinical utility of newly developed immunoassays for serum concentrations of adalimumab and anti-adalimumab antibodies in patients with Crohn’s disease. J Gastroenterol 49(1):100–109
vanKuijk AW, de Groot M, Stapel SO, Dijkmans BA, Wolbink GJ, Tak PP (2010) Relationship between the clinical response to adalimumab treatment and serum levels of adalimumab and anti-adalimumab antibodies in patients with psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 69(3):624–625, 13
Bartelds GM, Wijbrandts CA, Nurmohamed MT, Stapel S, Lems WF, Aarden L, Dijkmans BA, Tak PP, Wolbink GJ (2007) Clinical response to adalimumab: relationship to anti-adalimumab antibodies and serum adalimumab concentrations in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 66(7):921–926
Vincent FB, Morand EF, Murphy K, Mackay F, Mariette X, Marcelli C (2013) Antidrug antibodies (ADAb) to tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-specific neutralizing agents in chronic inflammatory diseases: a real issue, a clinical perspective. Ann Rheum Dis 72:165–178
Bloem K, van Leeuwen A, Verbeek G, Nurmohamed MT, Wolbink GJ, van der Kleij D, Rispens T (2015) Systematic comparison of drug-tolerant assays for anti-drug antibodies in a cohort of adalimumab-treated rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Immunol Methods 418:29–38
Bartelds GM, Krieckaert CLM, Nurmohamed MT, van Schouwenburg PA, Lems WF, Twisk JWR, Dijkmans BAC, Aarden L, Wolbink GJ (2011) Development of antidrug antibodies against adalimumab and association with disease activity and treatment failure during long term follow-up. JAMA 305(14):1460–1468
van Schouwenburg PA, van de Stadt LA, de Jong RN, van Buren EEL, Kruithof S, de Groot E, Hart M, van Ham SM, Rispens T, Aarden L, Wolbink GJ, Wouters D (2013) Adalimumab elicits a restricted anti-idiotypic antibody response in autoimmune patients resulting in functional neutralization. Ann Rheum Dis 72:104–109
vanSchie KA, Hart MH, de Groot ER, Kruithof S, Aarden LA, Wolbink GJ, Rispens T (2015) The antibody response against human and chimeric anti-TNF therapeutic antibodies primarily targets the TNF binding region. Ann Rheum Dis 74:311–314
Aarden L, Ruuls SR, Wolbink G (2008) Immunogenicity of anti-tumor necrosis factorantibodies-toward improved methods of anti-antibody measurement. Curr Opin Immunol 20(4):431–435
Patton A, Mullenix MC, Swanson SJ, Koren E (2005) An acid dissociation bridging ELISA for detection of antibodies directed against therapeutic proteins in the presence of antigen. J Immunol Methods 304:189–195
van Schouwenburg PA, Bartelds GM, Hart MH, Aarden L, Wolbink GJ, Wouters D (2010) A novel method for the detection of antibodies to adalimumab in the presence of drug reveals “hidden” immunogenicity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Immunol Methods 362(1–2):82–88
vanSchouwenburg PA, Krieckaert CL, Rispens T, Aarden L, Wolbink GJ, Wouters D (2013) Long-term measurement of anti-adalimumab using pH-shift-anti-idiotype antigen binding test shows predictive value and transient antibody formation. Ann Rheum Dis 72:1680–1686
Wang SL, Hauenstein S, Ohrmund L, Shringarpure R, Salbato J, Reddy R, McCowen K, Shah S, Lockton S, Chuang E, Singh S (2013) Monitoring of adalimumab and antibodies-to-adalimumab levels in patient serum by the homogeneous mobility shift assay. J Pharm Biomed Anal 78–79:39–44
Lofgren JA, Dhandapani S, Pennucci JJ, Abbott CM, Mytych DT, Kaliyaperumal A, Swanson SJ, Mullenix MC (2007) Comparing ELISA and surface plasmon resonante for assesing clinical immunogenicity of panitumumab. J Immunol 178:7467–7472
Stubenrauch K, Wessels U, Vogel R, Schleypen J (2009) Evaluation of a biosensor immunoassay for simultaneous characterization of isotype and binding region of human antitocilizumab antibodies with control surrogate standards. Anal Biochem 390:189–196
Weeraratne DK, Lofgren J, Dinnogen S, Swanson SJ, Zhong ZD (2013) Development of a biosensor-based immunogenicity assay capable of blocking soluble drug target interference. J Immunol Methods 396:44–55
Kaymakcalan Z, Sakorafas P, Bose S, Scesney S, Xiong L, Hanzatian DK, Salfeld J, Sasso EH (2009) Comparisons of affinities, avidities, and complement activation of adalimumab, infliximab, and etanercept in binding to soluble and membrane tumor necrosis factor. Clin Immunol 131:308–316
Arvinte T, Palais C, Green-Trexler E, Gregory S, Mach H, Narasimhan C, Shameem M (2013) Aggregation of biopharmaceuticals in human plasma and human serum. mAbs 5(3):491–500
Kosmač M, Avčin T, Toplak N, Simonini G, Cimaz R, Šerbec VC (2011) Exploring the binding sites of anti-infliximab antibodies in pediatric patients with rheumatic diseases treated with infliximab. Pediatr Res 69(3):243–248, 14
Real Fernández F, Di Pisa M, Rossi G, Auberger N, Lequin O, Larregola M, Benchohra A, Mansuy C, Chassaing G, Lolli F, Hayek J, Lavielle S, Rovero P, Mallet JM, Papini AM (2015) Antibody recognition in multiple sclerosis and Rett syndrome using a collection of linear and cyclic N-glucosylated antigenic probes. Biopolymers (Pept Sci). doi:10.1002/bip.22677
Johnstone A, Thorpe (1988) Immunochemistry in practice, 3rd edn. Wiley-Blackwell, New York
Habbema JDF, Eijkmans R, Krijnen P, Knottnerus JA (2002) Analysis of data on the accuracy of diagnostic tests. In: Knottnerus JA (ed) The evidence base of clinical diagnosis: how to do diagnostic research. BMJ Books, London, pp 117–143
Imagawa T, Takei S, Umebayashi H, Yamaguchi K, Itoh Y, Kawai T, Iwata N, Murata T, Okafuji I, Miyoshi M, Onoe Y, Kawano Y, Kinjo N, Mori M, Mozaffarian N, Kupper H, Santra S, Patel G, Kawai S, Yokota S (2012) Efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and safety of adalimumab in pediatric patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis in Japan. Clin Rheumatol 31(12):1713–1721
Murias S, Alcobendas R, Pascual-Salcedo D, Remesal A, Peralta J, Merino R (2014) Antiadalimumab antibodies in pediatric rheumatology patients: a pilot experience. Rheumatology 53:2124–2126
Barbosa MDFS, Gokemeijer J, Martin AD, Bush A (2013) Altering drug tolerance of surface plasmon resonance assays for the detection of anti-drug antibodies. Anal Biochem 441:174–179
Cimitan S, Lindgren MT, Bertucci C, Danielson UH (2005) Early absorption and distribution analysis of antitumor and anti-AIDS drugs: lipid membrane and plasma protein interactions. J Med Chem 48:3536–3546
van Schouwenburg PA, Kruithof S, Votsmeier C, van Schie K, Hart MH, de Jong RN, van Buren EEL, van Ham M, Aarden L, Wolbink G, Wouters D, Rispens T (2014) Functional analysis of the anti-adalimumab response using patient-derived monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem 289(50):34482–34488
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge Ente Cassa di Risparmio di Firenze for the financial support and Dr. Tadej Avcin, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia, for kindly providing positive samples.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Real-Fernández, F., Cimaz, R., Rossi, G. et al. Surface plasmon resonance-based methodology for anti-adalimumab antibody identification and kinetic characterization. Anal Bioanal Chem 407, 7477–7485 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8915-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8915-8