Abstract
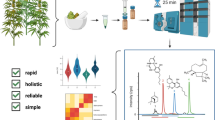
NMR-based metabolite profiling of urine is a fast and reproducible method for detection of numerous metabolites with diverse chemical properties. However, signal overlap in the 1H NMR profiles of human urine may hamper quantification and identification of metabolites. Therefore, a new method has been developed using automated solid-phase extraction (SPE) combined with NMR metabolite profiling. SPE–NMR of urine resulted in three fractions with complementary and reproducible sub-profiles. The sub-profile from the wash fraction (100 % water) contained polar metabolites; that from the first eluted fraction (10 % methanol–90 % water) semi-polar metabolites; and that from the second eluted fraction (100 % methanol) aromatic metabolites. The method was validated by analysis of urine samples collected from a crossover human nutritional intervention trial in which healthy volunteers consumed capsules containing a polyphenol-rich mixture of red wine and grape juice extract (WGM), the same polyphenol mixture dissolved in a soy drink (WGM_Soy), or a placebo (PLA), over a period of five days. Consumption of WGM clearly increased urinary excretion of 4-hydroxyhippuric acid, hippuric acid, 3-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, homovanillic acid, and 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-3-hydroxypropionic acid. However, there was no difference between the excreted amounts of these metabolites after consumption of WGM or WGM_Soy, indicating that the soy drink is a suitable carrier for WGM polyphenols. Interestingly, WGM_Soy induced a significant increase in excretion of cis-aconitate compared with WGM and PLA, suggesting a higher demand on the tricarboxylic acid cycle. In conclusion, SPE–NMR metabolite sub-profiling is a reliable and improved method for quantification and identification of metabolites in urine to discover dietary effects and markers of phytochemical exposure.

SPE-NMR sub-profiles of urine compared to reconstructed (blue) and non-fractionated (reference) profile





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brennan L (2008) Session 2: Personalised nutrition. Metabolomic applications in nutritional research. Proc Nutr Soc 67:404–408
Rhee EP, Gerszten RE (2012) Metabolomics and cardiovascular biomarker discovery. Clin Chem 58:139–147
van Ravenzwaay B, Cunha GC, Leibold E, Looser R, Mellert W, Prokoudine A, Walk T, Wiemer J (2007) The use of metabolomics for the discovery of new biomarkers of effect. Toxicol Lett 172:21–28
Holmes E, Loo RL, Stamler J, Bictash M, Yap IK, Chan Q, Ebbels T, De Iorio M, Brown IJ, Veselkov KA, Daviglus ML, Kesteloot H, Ueshima H, Zhao L, Nicholson JK, Elliott P (2008) Human metabolic phenotype diversity and its association with diet and blood pressure. Nature 453:396–400
Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Wilson ID (2005) Gut microorganisms, mammalian metabolism and personalized health care. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:431–438
Ryan D, Robards K, Prenzler PD, Kendall M (2011) Recent and potential developments in the analysis of urine: a review. Anal Chim Acta 684:8–20
Lloyd AJ, Fave G, Beckmann M, Lin W, Tailliart K, Xie L, Mathers JC, Draper J (2011) Use of mass spectrometry fingerprinting to identify urinary metabolites after consumption of specific foods. Am J Clin Nutr 94:981–991
Rasmussen LG, Winning H, Savorani F, Ritz C, Engelsen SB, Astrup A, Larsen TM, Dragsted LO (2012) Assessment of dietary exposure related to dietary GI and fibre intake in a nutritional metabolomic study of human urine. Genes Nutr 7:281–293
van Duynhoven J, Vaughan EE, Jacobs DM, Kemperman RA, van Velzen EJ, Gross G, Roger LC, Possemiers S, Smilde AK, Dore J, Westerhuis JA, van de Wiele T (2011) Metabolic fate of polyphenols in the human superorganism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(Suppl 1):4531–4538
Zheng X, Xie G, Zhao A, Zhao L, Yao C, Chiu NH, Zhou Z, Bao Y, Jia W, Nicholson JK, Jia W (2011) The footprints of gut microbial-mammalian co-metabolism. J Proteome Res 10:5512–5522
Keun HC, Athersuch TJ (2011) Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)-based metabolomics. Methods Mol Biol 708:321–334
Lenz EM (2011) Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)-based drug metabolite profiling. Methods Mol Biol 708:299–319
Psychogios N, Hau DD, Peng J, Guo AC, Mandal R, Bouatra S, Sinelnikov I, Krishnamurthy R, Eisner R, Gautam B, Young N, Xia J, Knox C, Dong E, Huang P, Hollander Z, Pedersen TL, Smith SR, Bamforth F, Greiner R, McManus B, Newman JW, Goodfriend T, Wishart DS (2011) The human serum metabolome. PLoS One 6:e16957
Xu EY, Schaefer WH, Xu Q (2009) Metabolomics in pharmaceutical research and development: metabolites, mechanisms and pathways. Curr Opin Drug Discov Dev 12:40–52
Zhang S, Nagana Gowda GA, Ye T, Raftery D (2010) Advances in NMR-based biofluid analysis and metabolite profiling. Analyst 135:1490–1498
Savorani F, Tomasi G, Engelsen SB (2010) icoshift: a versatile tool for the rapid alignment of 1D NMR spectra. J Magn Reson 202:190–202
van Velzen EJ, Westerhuis JA, van Duynhoven JP, van Dorsten FA, Hoefsloot HC, Jacobs DM, Smit S, Draijer R, Kroner CI, Smilde AK (2008) Multilevel data analysis of a crossover designed human nutritional intervention study. J Proteome Res 7:4483–4491
Tulpan D, Leger S, Belliveau L, Culf A, Cuperlovic-Culf M (2011) MetaboHunter: an automatic approach for identification of metabolites from 1H NMR spectra of complex mixtures. BMC Bioinforma 12:400
Wishart DS, Tzur D, Knox C, Eisner R, Guo AC, Young N, Cheng D, Jewell K, Arndt D, Sawhney S, Fung C, Nikolai L, Lewis M, Coutouly MA, Forsythe I, Tang P, Shrivastava S, Jeroncic K, Stothard P, Amegbey G, Block D, Hau DD, Wagner J, Miniaci J, Clements M, Gebremedhin M, Guo N, Zhang Y, Duggan GE, Macinnis GD, Weljie AM, Dowlatabadi R, Bamforth F, Clive D, Greiner R, Li L, Marrie T, Sykes BD, Vogel HJ, Querengesser L (2007) HMDB: the Human Metabolome Database. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D521–D526
Adosraku RK, Choi GT, Constantinou-Kokotos V, Anderson MM, Gibbons WA (1994) NMR lipid profiles of cells, tissues, and body fluids: proton NMR analysis of human erythrocyte lipids. J Lipid Res 35:1925–1931
Akira K, Mitome H, Imachi M, Shida Y, Miyaoka H, Hashimoto T (2010) LC–NMR identification of a novel taurine-related metabolite observed in (1)H NMR-based metabonomics of genetically hypertensive rats. J Pharm Biomed Anal 51:1091–1096
Godejohann M, Tseng LH, Braumann U, Fuchser J, Spraul M (2004) Characterization of a paracetamol metabolite using on-line LC–SPE–NMR–MS and a cryogenic NMR probe. J Chromatogr A 1058:191–196
Djukovic D, Appiah-Amponsah E, Shanaiah N, Gowda GA, Henry I, Everly M, Tobias B, Raftery D (2008) Ibuprofen metabolite profiling using a combination of SPE/column-trapping and HPLC-micro-coil NMR. J Pharm Biomed Anal 47:328–334
Rezzi S, Vera FA, Martin FP, Wang S, Lawler D, Kochhar S (2008) Automated SPE–RP-HPLC fractionation of biofluids combined to off-line NMR spectroscopy for biomarker identification in metabonomics. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 871:271–278
Chylla RA, Hu K, Ellinger JJ, Markley JL (2011) Deconvolution of two-dimensional NMR spectra by fast maximum likelihood reconstruction: application to quantitative metabolomics. Anal Chem 83:4871–4880
Gronwald W, Klein MS, Kaspar H, Fagerer SR, Nurnberger N, Dettmer K, Bertsch T, Oefner PJ (2008) Urinary metabolite quantification employing 2D NMR spectroscopy. Anal Chem 80:9288–9297
Rai RK, Tripathi P, Sinha N (2009) Quantification of metabolites from two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: application to human urine samples. Anal Chem 81:10232–10238
Bollard ME, Stanley EG, Lindon JC, Nicholson JK, Holmes E (2005) NMR-based metabonomic approaches for evaluating physiological influences on biofluid composition. NMR Biomed 18:143–162
Savage AK, van Duynhoven JP, Tucker G, Daykin CA (2011) Enhanced NMR-based profiling of polyphenols in commercially available grape juices using solid-phase extraction. Magn Reson Chem 49(Suppl 1):S27–S36
Jacobs DM, Fuhrmann JC, van Dorsten FA, Rein D, Peters S, van Velzen EJ, Hollebrands B, Draijer R, van Duynhoven J, Garczarek U (2012) Impact of short-term intake of red wine and grape polyphenol extract on the human metabolome. J Agric Food Chem 60:3078–3085
van Dorsten FA, Grun CH, van Velzen EJ, Jacobs DM, Draijer R, van Duynhoven JP (2010) The metabolic fate of red wine and grape juice polyphenols in humans assessed by metabolomics. Mol Nutr Food Res 54:897–908
Smilde AK, Jansen JJ, Hoefsloot HC, Lamers RJ, van der Greef J, Timmerman ME (2005) ANOVA-simultaneous component analysis (ASCA): a new tool for analyzing designed metabolomics data. Bioinformatics 21:3043–3048
Jacobs DM, Deltimple N, van Velzen E, van Dorsten FA, Bingham M, Vaughan EE, van Duynhoven J (2008) (1)H NMR metabolite profiling of feces as a tool to assess the impact of nutrition on the human microbiome. NMR Biomed 21:615–626
Manach C, Williamson G, Morand C, Scalbert A, Remesy C (2005) Bioavailability and bioefficacy of polyphenols in humans. I. Review of 97 bioavailability studies. Am J Clin Nutr 81:230S–242S
Monagas M, Urpi-Sarda M, Sanchez-Patan F, Llorach R, Garrido I, Gomez-Cordoves C, Andres-Lacueva C, Bartolome B (2010) Insights into the metabolism and microbial biotransformation of dietary flavan-3-ols and the bioactivity of their metabolites. Food Funct 1:233–253
Scalbert A, Morand C, Manach C, Remesy C (2002) Absorption and metabolism of polyphenols in the gut and impact on health. Biomed Pharmacother 56:276–282
Manach C, Hubert J, Llorach R, Scalbert A (2009) The complex links between dietary phytochemicals and human health deciphered by metabolomics. Mol Nutr Food Res 53:1303–1315
Spencer JP, Abd El Mohsen MM, Minihane AM, Mathers JC (2008) Biomarkers of the intake of dietary polyphenols: strengths, limitations and application in nutrition research. Br J Nutr 99:12–22
Gonthier MP, Cheynier V, Donovan JL, Manach C, Morand C, Mila I, Lapierre C, Remesy C, Scalbert A (2003) Microbial aromatic acid metabolites formed in the gut account for a major fraction of the polyphenols excreted in urine of rats fed red wine polyphenols. J Nutr 133:461–467
Requena T, Monagas M, Pozo-Bayón MA, Martín-Álvarez PJ, Bartolomé B, del Campo R, Ávila M, Martinéz-Cuesta MC, Peláez C, Moreno-Arribas MV (2010) Perspectives of the potential implications of wine polyphenols on human oral and gut microbiota. Trends Food Sci Technol 21:332–344
Daykin CA, van Duynhoven JP, Groenewegen A, Dachtler M, Van Amelsvoort JM, Mulder TP (2005) Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic based studies of the metabolism of black tea polyphenols in humans. J Agric Food Chem 53:1428–1434
Urpi-Sarda M, Llorach R, Khan N, Monagas M, Rotches-Ribalta M, Lamuela-Raventos R, Estruch R, Tinahones FJ, Andres-Lacueva C (2010) Effect of milk on the urinary excretion of microbial phenolic acids after cocoa powder consumption in humans. J Agric Food Chem 58:4706–4711
Llorach R, Urpi-Sarda M, Jauregui O, Monagas M, Andres-Lacueva C (2009) An LC-MS-based metabolomics approach for exploring urinary metabolome modifications after cocoa consumption. J Proteome Res 8:5060–5068
Schroeter H, Holt RR, Orozco TJ, Schmitz HH, Keen CL (2003) Nutrition: milk and absorption of dietary flavanols. Nature 426:787–788
Lampe JW (2003) Isoflavonoid and lignan phytoestrogens as dietary biomarkers. J Nutr 133(Suppl 3):956S–964S
Ogegbo OL, Dissanyake W, Crowder J, Asekun O, Familoni O, Branford-White CJ, Annie Bligh SW (2012) Urinary (1)H NMR metabonomics study on intervention effects of soya milk in Africans. Phytother Res 26:127–135
Solanky KS, Bailey NJ, Beckwith-Hall BM, Bingham S, Davis A, Holmes E, Nicholson JK, Cassidy A (2005) Biofluid 1H NMR-based metabonomic techniques in nutrition research - metabolic effects of dietary isoflavones in humans. J Nutr Biochem 16:236–244
Akira K, Hichiya H, Shuden M, Morita M, Mitome H (2012) Sample preparation method to minimize chemical shift variability for NMR-based urinary metabonomics of genetically hypertensive rats. J Pharm Biomed Anal 66:339–344
Acknowledgments
Part of this project was performed within the research program of the Netherlands Metabolomics Centre (NMC) which is part of the Netherlands Genomics Initiative/Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jacobs, D.M., Spiesser, L., Garnier, M. et al. SPE–NMR metabolite sub-profiling of urine. Anal Bioanal Chem 404, 2349–2361 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6339-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6339-2