Abstract
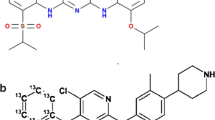
Imatinib is a first-line treatment for chronic myelogenous leukaemia (CML). The pharmacokinetics of imatinib in patients with CML are characterised by large interpatient variability. Concentration monitoring of imatinib and its active metabolite N-desmethyl imatinib (DMI) is considered necessary to enhance the safe and effective use of imatinib. A rapid, simple and sensitive liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry assay was developed for the simultaneous determination of imatinib and its metabolite DMI in human plasma. After proteins were precipitated with acetonitrile, imatinib, DMI and the internal standard D8-imatinib were resolved on a Gemini-NX 3 μm C18 column using gradient elution of 0.05 % formic acid and methanol. The three compounds were detected using electrospray ionisation in the positive mode. Standard curves of imatinib and DMI were adequately fitted by quadratic equations (r > 0.999) over the concentration range of 10 to 2,000 ng/mL which encompasses clinical concentrations. Bias was ≤±8.3 %, intra- and inter-day coefficients of variation (imprecision) were ≤8.0 % and the limit of quantification was 10 ng/mL for both imatinib and DMI. The assay is being used successfully in clinical practice to enhance the safe and effective use of imatinib.

Representative LC-MS/MS chromatogram of imatinib, N–desmethyl imatinib and the internal standard D8-imatinib in human plasma


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guilhot F (2004) Indications for imatinib mesylate therapy and clinical management. Oncologist 9:271–281
Mahon FX (2009) Pharmacologic monitoring and determinants of intracytoplasmic drug levels. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 22:381–386
Peng B, Lloyd P, Schran H (2005) Clinical pharmacokinetics of imatinib. Clin Pharmacokinet 44:879–894
Leveque D, Maloisel F (2005) Clinical pharmacokinetics of imatinib mesylate. In Vivo 19:77–84
Titter K, Picard S, Ducint D, Teilhet E, Moore N, Berthaud P, Mahon FX, Molimard M (2005) Quantification of imatinib in human plasma by high-perfomance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Ther Drug Monit 27:634–640
Haouala A, Zanolari B, Rochat B, Montemurro M, Zaman K, Duchosal MA, Ris HB, Leyvraz S, Widmer N, Decosterd LA (2009) Therapeutic drug monitoring of the new targeted anticancer agents imatinib, nilotinib, dasatinib, sunitinib, sorafenib and lapatinib by LC tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 877:1982–1996
Klawitter J, Zhang YL, Klawitter J, Anderson N, Serkova NJ, Christians U (2009) Development and validation of sensitive assay for the quantification of imatinib using LC-MS/MS in human whole blood and cell culture. Biomed Chromatogr 23:1251–1258
Mičová K, Friedecký D, Faber E, Polýnková A, Adam T (2010) Flow injection analysis vs. ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry for determination of imatinib in human plasma. Clin Chim Acta 411:1957–1962
Awidi A, Salem I, Najib N, Mefleh R, Tarawneh B (2010) Determination of imatinib plasma levels in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia by high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detection and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: methods' comparison. Leuk Res 34:714–717
Iqbal Z, Elliott M, Watson DG, Holyoake T, Jørgensen H (2011) Analysis of imatinib in bone marrow and plasma samples of chronic myeloid leukemia patients using solid phase extraction LC-ESI-MS. Pak J Pharm Sci 24:285–291
Parise RA, Ramanathan RK, Hayes MJ, Egorin MJ (2003) Liquid chromatographic-mass spectrometric assay for quantitation of imatinib and its main metabolite (CGP74588) in plasma. J Chromatogr B 791:39–44
Bakhtiar R, Lohne J, Ramos L, Khemani L, Hayes M, Tse F (2002) High-throughput quantification of anti-leukemia drug STI571 (Gleevec™) and its metabolite (CGP74588) in human plasma using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 768:325–340
Streit F, Binder L, Hafke A, Brandhorst G, Braulke F, Haase D, Armbrust T, Cameron S, Ramadori G, Oellerich M, Walson P (2011) Use of total and unbound imatinib and metabolite LC-MS/MS assay to understand individual responses in CML and GIST patients. Ther Drug Monit 33:632–643
Matuszewski BK, Constanzer ML, Chavez-Eng CM (2003) Strategies for the assessment of matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLC-MS/MS. Anal Chem 75:3019–3030
US Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) (2001) Guidance for industry, bioanalytical method validation
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Moore, G.A., Fernyhough, L.J. et al. Determination of imatinib and its active metabolite N-desmethyl imatinib in human plasma by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 404, 2091–2096 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6284-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6284-0