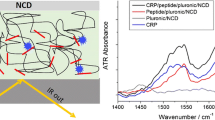
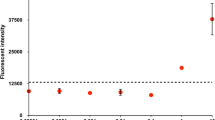
Abstract
A platform for diagnostic applications showing signal-to-noise ratios that by far surpass those of traditional bioanalytical test formats has been developed. It combines the properties of modified nanocrystalline diamond (NCD) surfaces and those of polyethylene oxide and polypropylene oxide based block copolymers for surface passivation and binder conjugation with a new class of synthetic binders for proteins. The NCD surfaces were fluorine-, hydrogen-, or oxygen-terminated prior to further biofunctionalization and the surface composition was characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. In a proof of principle demonstration targeting the C-reactive protein, an ELISA carried out using an F-terminated diamond surface showed a signal-to-noise ratio of 3,900 which compares well to the signal-to-noise of 89 obtained in an antibody-based ELISA on a polystyrene microtiter plate, a standard test format used in most life science laboratories today. The increase in signal-to-noise ratio is to a large extent the result of extremely efficient passivation of the diamond surface. The results suggest that significant improvements can be obtained in standardized test formats using new materials in combination with new types of chemical coatings and receptor molecules.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Härtl A, Schmich E, Garrido JA, Hernando J, Catharino SCR, Walter S, Feulner P, Kromka A, Steinmüller D, Stutzmann M (2004) Protein-modified nanocrystalline diamond thin films for biosensor applications. Nat Mater 3:736–742
Baltzer L (2012) Crossing borders to bind proteins—a new concept in protein recognition based on the conjugation of small organic molecules or short peptides to polypeptides from a designed set. Anal Bioanal Chem 400(6):1653–1664
Rifai N, Ridker PM (2001) High-sensitivity C-reactive protein: a novel and promising marker of coronary heart disease. Clin Chem 47:403–411
Pepys MB, Hirschfield GM (2003) C-reactive protein: a critical update. J Clin Invest 111:1805–1812
Tegler LT, Nonglaton G, Büttner F, Caldwell K, Christopeit T, Danielsson H, Fromell K, Gossas T, Larsson A, Longati P, Norberg T, Ramapanicker R, Rydberg J, Baltzer L (2011) Efficient protein binders for the C-reactive protein from a designed chemically modified peptide library—a new concept for biomolecular recognition. Angew Chem 50:1823–1827
Li JT, Carlsson J, Lin JN, Caldwell KD (1996) Chemical modification of surface active poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(propylene oxide) triblock copolymers. Bioconj Chem 7:592–599
Vivensang C, Turban G, Anger E, Giquel A (1994) Reactive ion etching of diamond and diamond-like carbon films. Diam Relat Mater 3:645–649
Shirafuji J, Sakamoto Y, Furukawa A, Shigeta H, Sugino T (1995) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis of plasma-treated surfaces of diamond films. Diam Relat Mater 4:984–988
Maier F, Graupner R, Hollering M, Hammer L, Ristein J, Ley L (1999) The hydrogenated and bare diamond (110) surface: a combined LEED-, XPS-, and ARPES study. Surf Sci 443:177–185
Francz G, Reinke P, Oelhafen P, Hänni W (1995) Photoelectron spectroscopy of ion-irradiated B-doped CVD diamond surfaces. Thin Solid Films 270:200–204
Steinmüller-Nethl D, Kloss FR, Najam-Ul-Haq M, Rainer M, Larsson K, Linsmeier C, Köhler G, Gassner R, Fehrer C, Lepperdinger G, Huck CW, Bonn G (2006) Strong physisorption of BMP-2 on nanocrystalline diamond retains bioactivity. Biomaterials 27:4547–4556
Petrini D, Larsson K (2007) A theoretical approach to the energetic stability and geometry of hydrogen and oxygen terminated diamond (100) surfaces. J Phys Chem C 111:795
Christopeit T, Gossas T, Danielson UH (2009) Characterization of Ca2+ and phosphocholine interactions with C-reactive protein using a surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Anal Biochem 391:39–44
Neff JA, Caldwell KD, Tresco PA (1998) A novel method for surface modification to promote cell attachment to hydrophobic substrates. J Biomed Mater Res 40:511–519
Karlsson M, Forsberg P, Nikolajeff F (2010) From hydrophilic to superhydrophobic: fabrication of micrometer-sized nail-head-shaped pillars in diamond. Langmuir 26:889–892
ter Veen R, Fromell K, Caldwell KD (2005) Shifts in polystyrene particle surface charge upon adsorption of the Pluronic F108 surfactant. J Colloids Interface Sci 288:124–128
Albrecht C, Fechner P, Honcharenko D, Baltzer L, Gauglitz G (2010) A new assay design for clinical diagnostics based on alternative recognition elements. Biosens Bioelectron 25:2302–2308
Acknowledgments
This work has enjoyed financial support from the Uppsala Berzelii Technology Centre for Neurodiagnostics and by The Swedish Diamond Centre. We also wish to thank Allvivo Inc. for supporting us with Pluronic F108-PDS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 69 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fromell, K., Forsberg, P., Karlsson, M. et al. Designed protein binders in combination with nanocrystalline diamond for use in high-sensitivity biosensors. Anal Bioanal Chem 404, 1643–1651 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6245-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6245-7