Abstract
In the present study, we synthesized dextran (MW = ca. 2,000 kDa)-based macromolecular probes containing multiple molecules of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) as a signal-trigger enzyme and of biotin as an assembly mediator. The ALP and biotin molecules were covalently attached into the dextran backbone after the formation of aldehyde groups into the macromolecule by periodate oxidation. The synthesized probes contained 27–31 molecules of ALP in their macromolecules when 50-fold molar ratio of ALP to the dextran was used for the synthesis. These probes provided 14–20 times stronger chemiluminescence (CL) than that of the equimolar free ALP adsorbed on a nylon membrane. The velocity of the CL reaction of ALP-catalyzed adamantlyl-1,2-dioxetane substrate was improved from a slower emission (glow type) of CL to a faster one (flash type). The CL signal integrated for 2 min under strongly alkaline conditions (pH 13.0) was about ten times greater than that obtained by the conventional conditions (pH 9.5). Therefore, the synthesized macromolecular probe could be successfully utilized for the high-throughput CL detection of biotin-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody with a lower detection limit of 880 amol per spot on the nylon membrane. This study provides analytical strategy for the rapid, convenient, and sensitive detection of target proteins in immunoassays.

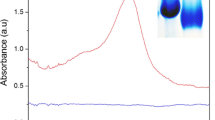
A Schematic principle for the chemiluminescence (CL) detection of biotin-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (b-Ab) on a solid-phase membrane by using a dextran (Dex)-biotin (Bio)-ALP probe, B CL-imaging detection of Dex-Bio-ALP probes and ALP adsorbed on a nylon membrane, and C CL-imaging detection of b-Ab on a nylon membrane using Dex-Bio120-ALP28 probe. Amounts (femtomole) of b-Ab per spot: a 1 = 0.32, a 2 = 0.63, a 3 = 1.25, a 4 = 2.5, a 5 = 5, and a 6 = 10








Similar content being viewed by others
References
García-Campaña AM, Baeyens WRG, Zhang X (2001) In: García-Campaña AM, Baeyens WRG (eds) Chemiluminescence in analytical chemistry. Marcel Dekker, New York
Roda A, Guardigli M, Pasini P, Mirasoli M (2003) Anal Bioanal Chem 377:826–833
Kricka LJ (2003) Anal Chim Acta 500:279–286
García-Campaña AM, Lara FJ (2007) Anal Bioanal Chem 387:165–169
Bi S, Yan Y, Yang X, Zhang S (2009) Chem Eur J 15:4704–4709
Zhu H, Snyder M (2003) Curr Opin Chem Biol 7:55–63
Lee Y, Lee EK, Cho YW, Matsui T, Kang IC, Kim TS, Han MH (2003) Proteomics 3:2289–2304
Bronstein I, Juo RR, Voyta JC, Edwards B (1991) In: Stanley PE, Kricka LJ (eds) Bioluminescence and chemiluminescence: current status. Chichester, Wiley
Olesen CEM, Mosier J, Voyta JC, Bronstein I (2000) Methods Enzymol 305:417–427
Zhang H, Smanmoo C, Kabashima T, Lu J, Kai M (2007) Angew Chem Int Ed 46:8226–8229
Zhang H, Shibata T, Krawczyk T, Kabashima T, Lu J, Myung K, Kai M (2009) Talanta 9:700–705
Penzol G, Armisen P, Fernandez-Lafuente R, Rodes L, Guisan JM (1998) Biotechnol Bioeng 60:518–523
Green NM (1970) Methods Enzymol 18:418–424
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants-in-aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and partly by the Global Center of Excellence Program of Nagasaki University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azam, M.G., Shibata, T., Kabashima, T. et al. Alkaline phosphatase-labeled macromolecular probe for sensitive chemiluminescence detection of proteins on a solid-phase membrane. Anal Bioanal Chem 401, 1211–1217 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5196-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5196-8