Abstract
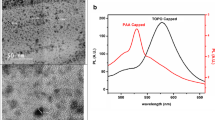
In this paper, a rapid, simple, and sensitive method was described for detection of the total bacterial count using SiO2-coated CdSe/ZnS quantum dots (QDs) as a fluorescence marker that covalently coupled with bacteria using glutaraldehyde as the crosslinker. Highly luminescent CdSe/ZnS were prepared by applying cadmium oxide and zinc stearate as precursors instead of pyrophoric organometallic precursors. A reverse-microemulsion technique was used to synthesize CdSe/ZnS/SiO2 composite nanoparticles with a SiO2 surface coating. Our results showed that CdSe/ZnS/SiO2 composite nanoparticles prepared with this method possessed highly luminescent, biologically functional, and monodispersive characteristics, and could successfully be covalently conjugated with the bacteria. As a demonstration, it was found that the method had higher sensitivity and could count bacteria in 3 × 102 CFU/mL, lower than the conventional plate counting and organic dye-based method. A linear relationship of the fluorescence peak intensity (Y) and the total bacterial count (X) was established in the range of 3 × 102–107 CFU/mL using the equation Y = 374.82X − 938.27 (R = 0.99574). The results of the determination for the total count of bacteria in seven real samples were identical with the conventional plate count method, and the standard deviation was satisfactory.

The synthesis and coupling process of CdSe/ZnS/SiO2 composite nanoparticles with bacterial cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kubitschek HE (1990) Cell volume increase in Escherichia coli after shifts to richer media. J Bacteriol 172:94–101
Rolhion N, Darfeuille-Michaud A (2007) Adherent-invasive Escherichia coli in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 13:1277–1283
Abdel-Hamid I, Ivnitski D, Atanasov P, Wilkins E (1999) Flow-through immunofiltration assay system for rapid detection of E. coli O157:H7. Biosens Bioelectron 14:309–316
Salinas F, Garrido D, Ganga A, Veliz G, Martinez C (2009) Taqman real-time PCR for the detection and enumeration of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in wine. Food Microbiol 26:328–332
Pavlova D, Wet CME, Grabow WOK, Ehlers MM (2004) Potentially pathogenic features of heterotrophic plate count bacteria isolated from treated and untreated drinking water. Int J Food Microbiol 92:275–287
Gunasekera ST, Attfield VP, Veal AD (2000) A flow cytometry method for rapid detection and enumeration of total bacteria in milk. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1228–1232
Johnson JL, Rose BE, Sharar AK, Ransom GM, Lattuada CP, McNamara AM (1995) Methods used for detection and recovery of Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with a food-borne disease outbreak. J Food Prot 58:597–603
Scolaro LM, Castriciano M, Romeo A, Patane S, Cefali E, Allegrini M (2002) Aggregation behavior of protoporphyrin IX in aqueous solutions: clear evidence of vesicle formation. J Phys Chem B 106:2453–2459
Santra S, Liesenfeld B, Bertolino C, Dutta D, Cao ZH, Tan WH, Moudgil BM, Mericle RA (2006) Fluorescence lifetime measurements to determine the core–shell nanostructure of FITC-doped silica nanoparticles: An optical approach to evaluate nanoparticle photostability. J Lumin 117:75–82
Luo J, Liu XH, Tian Q, Yue WW, Zeng J, Chen GQ, Cai XX (2009) Disposable bioluminescence-based biosensor for detection of bacterial count in food. Anal Biochem. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2009.05.021
Yamashoji S, Asakawa A, Kawasaki S, Kawamoto S (2004) Chemiluminescent assay for detection of viable microorganisms. Anal Biochem 333:303–308
Maruyama F, Yamaguchi N, Kenzaka T, Tani K, Nasu M (2004) Simplified sample preparation using frame spotting method for direct counting of total bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. J Microbiol Meth 59:427–431
Hobbie JE, Daley RJ, Jasper S (1977) Use of nuclepore filters for counting bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol 33:1225–1228
Bruchez JM, Moronne M, Gin P, Weiss S, Alivisatos AP (1998) Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 281:2013–2016
Chan WCW, Nie S (1998) Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science 281:2016–2018
Zhang Y, Deng ZT, Yue JC, Tang FQ, Wei Q (2007) Using cadmium telluride quantum dots as a proton flux sensor and applying to detect H9 avian influenza virus. Anal Biochem 364:122–127
Xue XH, Pana J, Xie HM, Wang JH, Zhang S (2009) Fluorescence detection of total count of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus on water-soluble CdSe quantum dots coupled with bacteria. Talanta 77:1808–1813
Su XL, Li YB (2004) Quantum dot biolabeling coupled with immunomagnetic separation for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Anal Chem 76:4806–4810
Son A, Dosev D, Nichkova M, Ma ZY, Kennedy LM, Scow KM, Hristova KR (2007) Quantitative DNA hybridization in solution using magnetic/luminescent core–shell nanoparticles. Anal Biochem 370:186–194
Sukhanova A, Devy J, Venteo L, Kaplan H, Artemyev M, Oleinikov V, Klinov D, Pluot M, Cohen JHM, Nabieva I (2004) Biocompatible fluorescent nanocrystals for immunolabeling of membrane proteins and cells. Anal Biochem 324:60–67
Santra S, Zhang P, Wang KM, Tapec R, Tan W (2001) Conjugation of biomolecules with luminophored silica nanoparticles for photostable biomarkers. Anal Chem 73:4988–4993
Wang L, Tan W (2006) Multicolor FRET silica nanoparticles by single wavelength excitation. Nano Lett 6:84–88
He XX, Chen JY, Wang KM, Qin DL, Tan WH (2007) Preparation of luminescent Cy5 doped core-shell SFNPs and its application as a near-infrared fluorescent marker. Talanta 72:1519–1526
Rossi LM, Shi L, Rosenzweig N, Rosenzweig Z (2006) Fluorescent silica nanospheres for digital counting bioassay of the breast cancer marker HER2/nue. Biosens Bioelectron 21:1900–1906
Hillard LR, Zhao X, Tan W (2002) Immobilization of oligonucleotides onto silica nanoparticles for DNA hybridization studies. Anal Chim Acta 470:51–56
Azioure A, Slimane AB, Hamou LA, Pleuvy A, Chehimi MM, Perruchot C, Armes SP (2004) Synthesis and characterization of active ester-functionalized polypyrrole-silica nanoparticles: application to the covalent attachment of proteins. Langmuir 20:3350–3356
Nakamura M, Ishimura K (2007) Synthesis and characterization of organosilica nanoparticles prepared from 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane as the single silica source. J Phys Chem C 111:18892–18898
Santra S, Wang K, Tapec R, Tan W (2001) Development of novel dye-doped silica nanoparticles for biomarker application. J Biomed Opt 6:160–166
Tapec R, Zhao XJ, Tan W (2002) Development of organic dye-doped silica nanoparticles for bioanalysis and biosensors. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 2:405–409
Wang C, Ma Q, Dou WC, Kanwal S, Wang GN, Yuan PF, Su XG (2009) Synthesis of aqueous CdTe quantum dots embedded silica nanoparticles and their applications as fluorescence probes. Talanta 77:1358–1364
Jin L, Yu DD, Liu Y, Zhao XL, Zhou JG (2008) The application of CdTe@SiO2 particles in immunoassay. Talanta 76:1053–1057
Reiss P, Bleuse J, Pron A (2002) Highly luminescent CdSe/ZnSe core/shell nanocrystals of low size dispersion. Nano Lett 2:781–784
Selvan ST, Tan TT, Ying JY (2005) Robust, non-cytotoxic, silica-coated CdSe quantum dots with efficient photoluminescence. Adv Mater 17:1620–1625
Yang Y, Gao MY (2005) Preparation of fluorescent SiO2 particles with single CdTe nanocrystal cores by the reverse microemulsion method. Adv Mater 17:2354–2357
Ye Z, Tan M, Wang G, Yuan J (2004) Preparation, characterization and time-resolved fluorometric application of silica-coated terbium(III) fluorescent nanoparticles. Anal Chem 76:513–518
Ye Z, Tan M, Wang G, Yuan J (2005) Development of functionalized terbium fluorescent nanoparticles for antibody labeling and time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay application. Talanta 65:206–210
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, X., Huang, K. & Liu, S. A rapid and universal bacteria-counting approach using CdSe/ZnS/SiO2 composite nanoparticles as fluorescence probe. Anal Bioanal Chem 396, 1397–1404 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3352-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3352-1