Abstract
The number of commercially available genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and therefore the diversity of possible target sequences for molecular detection techniques are constantly increasing. As a result, GMO laboratories and the food production industry currently are forced to apply many different methods to reliably test raw material and complex processed food products. Screening methods have become more and more relevant to minimize the analytical effort and to make a preselection for further analysis (e.g., specific identification or quantification of the GMO). A multiplex real-time PCR kit was developed to detect the 35S promoter of the cauliflower mosaic virus, the terminator of the nopaline synthase gene of Agrobacterium tumefaciens, the 35S promoter from the figwort mosaic virus, and the bar gene of the soil bacterium Streptomyces hygroscopicus as the most widely used sequences in GMOs. The kit contains a second assay for the detection of plant-derived DNA to control the quality of the often processed and refined sample material. Additionally, the plant-specific assay comprises a homologous internal amplification control for inhibition control. The determined limits of detection for the five assays were 10 target copies/reaction. No amplification products were observed with DNAs of 26 bacterial species, 25 yeasts, 13 molds, and 41 not genetically modified plants. The specificity of the assays was further demonstrated to be 100% by the specific amplification of DNA derived from reference material from 22 genetically modified crops. The applicability of the kit in routine laboratory use was verified by testing of 50 spiked and unspiked food products. The herein described kit represents a simple and sensitive GMO screening method for the reliable detection of multiple GMO-specific target sequences in a multiplex real-time PCR reaction.

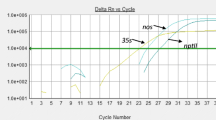
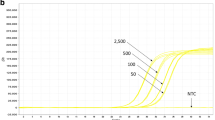
Real-time amplification curves for the event MON810 with 1,000, 100, 10, and 1 target copies/reaction of the 35S promoter of the cauliflower mosaic virus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anklam E, Gadani F, Heinze P, Pijnenburg H, Van den Eede G (2002) Eur Food Res Technol 214:3–26
Alexander TW, Reuter T, Aulrich K, Sharma R, Okine EK, Dixon WT, McAllister TA (2007) Anim Feed Sci Technol 133:31–62
Miraglia M, Berdal KG, Brera C, Corbisier P, Holst-Jensen A, Kok EJ, Marvin HJP, Schimmel H, Rentsch J, van Rie JPPF, Zagon J (2004) Food Chem Toxicol 42:1157–1180
Community Reference Laboratory, GM Food and Feed, Ispra. http://gmo-crl.jrc.ec.europa.eu/statusofdoss.htm
Holst-Jensen A, Rønning SB, Løvseth A, Berdal KG (2003) Anal Bioanal Chem 375:985–993
Wolf C, Scherzinger M, Wurz A, Pauli U, Hübner P, Lüthy J (2000) Eur Food Res Technol 210:367–372
Marmiroli N, Maestri E, Gullì M, Malcevschi A, Peano C, Bordoni R, de Bellis G (2008) Anal Bioanal Chem 392:369–384
James C (2008) ISAAA Brief 39
Michelini E, Simoni P, Cevenini L, Mezzanotte L, Roda A (2008) Anal Bioanal Chem 392:355–367
Waiblinger HU, Ernst B, Anderson A, Pietsch K (2008) Eur J Food Res Technol 226:1221–1228
Technische Regel BVL L 00.00-122 (2008)
Waiblinger HU, Boernsen B, Pietsch K (2008) Deut Lebensm-Rundsch 104:261–264
AGBIOS. http://www.agbios.com/main.php
Tengs T, Kristoffersen A, Berdal K, Thorstensen T, Butenko M, Nesvold H, Holst-Jensen A (2007) BMC Biotechnol 7:91
Bennett MD, Leitch IJ (1997) Ann Bot 80:169–196
Halpin C (2005) Plant Biotechnol 3:141–155
Akiyama H, Watanabe T, Wakabayashi K, Nakade S, Yasui S, Sakata K, Chiba R, Spiegelhalter F, Hino A, Maitani T (2005) Anal Chem 77:7421–7428
Xu W, Yuan Y, Luo Y, Bai W, Zhang C, Huang K (2009) J Agric Food Chem 57:395–402
Chaouachi M, Chupeau G, Berard A, McKhann H, Romaniuk M, Giancola S, Laval V, Bertheau Y, Brunel D (2008) J Agric Food Chem 56:11596–11606
Matsuoka T, Kuribara H, Akiyama H, Miura H, Goda Y, Kusakabe Y, Isshiki K, Toyoda M, Hino A (2001) J Food Hyg Soc Jpn 42:24–32
James D, Schmidt A-M, Wall E, Green M, Masri S (2003) J Agric Food Chem 51:5829–5834
Shrestha HK, Hwu K-K, Wang S-J, Liu L-F, Chang M-C (2008) J Agric Food Chem 56:8962–8968
Onishi M, Matsuoka T, Kodama T, Kashiwaba K, Futo S, Akiyama H, Maitani T, Furui S, Oguchi T, Hino A (2005) J Agric Food Chem 53:9713–9721
Germini A, Zanetti A, Salati C, Rossi S, Forre C, Schmid S, Marchelli R (2004) J Agric Food Chem 52:3275–3280
Hernandez M, Rodriguez-Lazaro D, Zhang D, Esteve T, Pla M, Prat S (2005) J Agric Food Chem 53:3333–3337
Gaudron T, Peters C, Boland E, Steinmetz A, Moris G (2009) Eur Food Res Technol 229:295–305
Xu J, Miao H, Wu H, Huang W, Tang R, Qiu M, Wen J, Zhu S, Li Y (2006) Biosens Bioelectron 22:71–77
Leimanis S, Hernández M, Fernández S, Boyer F, Burns M, Bruderer S, Glouden T, Harris N, Kaeppeli O, Philipp P, Pla M, Puigdomènech P, Vaitilingom M, Bertheau Y, Remacle J (2006) Plant Mol Biol 61:123–139
Rønning SB, Vaïtilingom M, Berdal KG, Holst-Jensen A (2003) Eur Food Res Technol 216:347–354
Huang C-C, Pan T-M (2005) J Agric Food Chem 53:3833–3839
Hemmer W (1997) Foods derived from genetically modified organisms and detection methods. BATS-Report 2/1997, Agency for Biosafety Research and Assessment of Technology Impacts of the Swiss Priority Program Biotechnology of the Swiss National Science Foundation, Basel, Switzerland
Salvi S, D’Orso F, Morelli G (2008) J Agric Food Chem 56:4320–4327
Holden MJ, Blasic JR, Bussjaeger L, Kao C, Shokere LA, Kendall DC (2003) J Agric Food Chem 51:2468–2474
Wilson IG (1997) Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3741–3751
Cazzola ML, Petruccelli S (2006) Electronic J Biotechnol 9:320–325
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dörries, HH., Remus, I., Grönewald, A. et al. Development of a qualitative, multiplex real-time PCR kit for screening of genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Anal Bioanal Chem 396, 2043–2054 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3149-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3149-2