Abstract
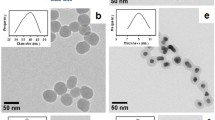
There is substantial interest in the development of near-infrared dye-doped nanoparticles (NPs) for a range of applications including immunocytochemistry, immunosorbent assays, flow cytometry, and DNA/protein microarray analysis. The main motivation for this work is the significant increase in NP fluorescence that may be obtained compared with a single dye label, for example Cy5. Dye-doped NPs were synthesised and a reduction in fluorescence as a function of dye concentration was correlated with the occurrence of homo-Förster resonance energy transfer (HFRET) in the NP. Using standard analytical expressions describing HFRET, we modelled the fluorescence of NPs as a function of dye loading. The results confirmed the occurrence of HFRET which arises from the small Stokes shift of near-infrared dyes and provided a simple method for predicting the optimum dye loading in NPs for maximum fluorescence. We used the inverse micelle method to prepare monodispersed silica NPs. The NPs were characterised using dynamic light scattering, UV spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The quantum efficiency of the dye inside the NPs, as a function of dye loading, was also determined. The fluorescent NPs were measured to be approximately 165 times brighter than the free dye, at an optimal loading of 2% (w/w). These experimental results were in good agreement with model predictions.

The change in nanoparticle fluorescence versus increased dye loading modelled using homo-Förster resonance energy transfer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haugland RP (2005) The handbook—a guide to fluorescent probes and labelling technologies. Molecular Probes, Eugene
Burns A, Ow H, Wiesner U (2006) Chem Soc Rev 35:1028–1042
Wang F, Tan W, Zhang Y, Fan X, Wang M (2006) Nanotechnology 17:R1–R13
Medintz I, Uyeda H, Goldman E, Mattoussi H (2005) Nature Mater 4:435–446
Chan WCW, Nie SM (1998) Science 285:2016–2018
Stöber W, Fink A, Bohn E (1968) J Colloid Interface Sci 26:62–69
Ow H, Larson D, Srivastava M, Baird B, Webb W, Wiesner U (2005) Nano Lett 5:113–117
Osseo-Asare K, Arriagada FJ (1990) Colloids Surf 50:321–339
Santra S, Zhang P, Wang K, Tapec R, Tan W (2001) Anal Chem 73:4988–4993
Lian W, Litherland SA, Badrane H, Tan W, Wu D, Baker HV, Gulig PA, Lim DV, Jin S (2004) Anal Biochem 334:135–144
Hoon KS, Jeyakumar M, Katzenellenbogen JA (2007) J Am Chem Soc 129:13254–13264
Wang L, Tan W (2006) Nano Lett 6:84–88
Wang L, Zhao W, O’Donoghue MB, Tan W (2007) Bioconj Chem 18:297–301
Deng T, Li J-S, Jiang J-H, Shen G-L, Yu R-Q (2006) Adv Funct Mater 16:2147–2155
Mank AJG, Yeung ES (1995) J. Chromatogr A 708:309–321
Novotny L, Hecht B (2007) Principles of nano-optics. Cambridge University Press, UK
Lakowicz JR (1999) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy. Kluwer Academic Press, New York
Yao G, Wang L, Wu Y, Smith J, Xu J, Zhao W, Lee E, Tan W (2006) Anal Bioanal Chem 385:518–524
Bagwe RP, Hilliard LR, Tan W (2006) Langmuir 22:4357–4362
Zhao X, Bagwe RP, Tan W (2004) Adv Mater 16:173–176
West W, Pearce S (1965) J Phys Chem 69:1894–1903
Williams ATR, Winfield SA, Miller JN (1983) Analyst 108:1067–1071
Larsons DR, Ow H, Vishwasrao HD, Heikal AA, Wiesner U, Webb WW (2008) Chem Mater 20:2677–2684
Acknowledgment
This material is based upon work supported by the Science Foundation Ireland under Grant No. 05/CE3/B754.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nooney, R.I., McCahey, C.M.N., Stranik, O. et al. Experimental and theoretical studies of the optimisation of fluorescence from near-infrared dye-doped silica nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem 393, 1143–1149 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2418-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2418-9