Abstract
The electrochemical behavior of paracetamol in 0.1 M acetate buffer solution (pH 4.6) was investigated at a traditional carbon paste electrode (TCPE) and a carbon ionic liquid electrode (CILE) fabricated by replacing nonconductive organic binders with a conductive hydrophobic room temperature ionic liquid, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate (BmimPF6). The results showed that the CILE exhibited better reversibility for the electrochemical redox of paracetamol. The oxidation potential of paracetamol at the CILE is +0.462 V, which is approximately 232 mV lower than that at the TCPE; the oxidation peak current response is nine times higher than that at the TCPE. The differential pulse voltammetric determination of paracetamol at the CILE was established based on this behavior. After optimizing several important parameters controlling the performance of paracetamol at the CILE, the oxidation peak current versus paracetamol concentration at the CILE showed linearity in the range from 1.0 μM to 2.0 mM (R 2 = 0.9992) with a detection limit of 0.3 μM (S/N = 3). The method has been applied to the determination of paracetamol in tablets and urine samples and the average recovery of paracetamol was 98.5% and 99.3%, respectively. The proposed CILE showed good sensitivity and reproducible response without influence of interferents commonly existing in pharmaceutical and urine samples.

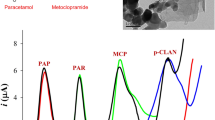
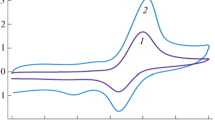
CV curves of paracetamol illustrate the enhanced electrochemical behavior of paracetamol at the CILE (b), which forms the basis for the differential pulse voltammetric determination of paracetamol





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang S, Xie F, Hu R (2007) Sens Actuators B 123:495–500
Bosch ME, Sánchez AJR, Rojas FS, Ojeda CB (2006) J Pharm Biomed Anal 42:291–321
Boopathi M, Won MS, Shim YB (2004) Anal Chim Acta 512:191–197
Carvalho RM, Freire RS, Rath S, Kubota LT (2004) J Pharm Biomed Anal 34:871–878
Trojanowicz M (2000) Flow injection analysis: instrumentation and applications. World Scientific, Singapore, p 481
Filik H, Tavman A (2007) J Anal Chem 62:530–535
Zarei AR, Afkhami A, Sarlak N (2005) J AOAC Int 88:1695–1701
Satinsky D, Neto I, Solich P, Sklenarova H, Conceicao M, Montenegro BSM (2004) J Sep Sci 27:529–536
Yang B, Mo J, Yang X, Wang L (2000) J Instrum Anal 19:13–15
Hilton MJ, Thomas KV (2003) J Chromatogr A 1015:129–141
Burgot G, Auffret F, Burgot JL (1997) Anal Chim Acta 343:125–141
Zen JM, Ting YS (1997) Anal Chim Acta 342:175–180
Gorton L (1995) Electroanalysis 7:23–25
Campanella L, Tomassetti M (1992) Electrochem 8:229–238
Maciej G, Andrzej L, Izabela S (2006) Electrochim Acta 51:5567–5580
Rika H, Takayuki H, Tetsuya T, Yasuhiko I (2000) J Fluorine Chem 105:221–227
Nishi N, Imakura S, Kakiuchi T (2006) Anal Chem 78:2726
Lang CM, Kim K, Guerra L, Kohl PA (2005) J Phys Chem B 109:19454–19462
Brooks CA, Doherty AP (2004) Electrochem Commun 6:867–871
Zheng J, Zhang Y, Yang P (2007) Talanta 73:920–925
Chen H, Wang Y, Liu Y, Wang Y, Qi L, Dong S (2007) Electrochem Commun 9:469–474
Shan D, Wang S, Xue H, Cosnier S (2007) Electrochem Commun 9:529–534
Heitzman H, Young BA, Rausch DJ, Rickert P, Stepinski DC, Dietz ML (2006) Talanta 69:527–531
Maleki N, Safavi A, Tajabadi F (2006) Anal Chem 78:3820–3826
Liu H, He P, Li Z, Sun C, Shi L, Liu Y, Zhu G, Li J (2005) Electrochem Commun 7:1357–1363
Reis APD, Tarley CRT, Maniasso N, Kubota LT (2005) Talanta 67:829–835
Laviron E (1979) J Electroanal Chem 101:19–28
Goyal RN, Singh SP (2006) Electrochim Acta 51:3008–3012
Fatibello-Filho O, Lupetti KO, Vieira IC (2001) Talanta 55:685–692
Duan L, Xie F, Zhou F, Wang S (2007) Anal Lett 40:2653–2663
Sun D, Zhang H (2007) Microchim Acta 158:131–136
Li M, Jing L (2007) Electrochim Acta 17:3250–3257
Silva MLS, Garcia MBQ, Lima JLFC, Barrado E (2006) Anal Chim Acta 573–574:383–390
Tungkananuruk K, Tungkananuruk N, Burns DT (2005) KMITL Sci Tech J 5:547–551
Özcan L, Şahin Y (2007) Sens Actuators B 127:362–369
Li L, Cheng H, Chen Q, Kong H, Wu J (2006) J Instrum Anal 25:38–40
Goyal RN, Gupta VK (2005) Electrochem Commun 7:803–807
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20675062) and the Research Foundation for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (No. 20060697013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ShangGuan, X., Zhang, H. & Zheng, J. Electrochemical behavior and differential pulse voltammetric determination of paracetamol at a carbon ionic liquid electrode. Anal Bioanal Chem 391, 1049–1055 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2096-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2096-7