Abstract
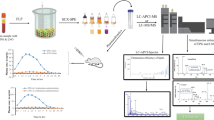
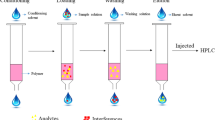
An advanced quantification method was developed with solid-phase extraction (SPE) and mass spectrometry (MS) determination for nafamostat, an unstable and highly polar drug, in human plasma. For unstable drugs with an ester group, the main analytical challenge is how to avoid the ester hydrolysis, and strong acid or alkaline conditions should be excluded during sample preparation. Considering that, we developed a relatively mild method with SPE for sample preparation without strong acid and alkaline treatment, which was optimized with different pHs and salt concentrations in phosphate-buffered saline treatment. The results indicated that pH 5 gave the most efficient extraction and 0.1 M salt concentration enhanced the extraction the most, with a minor effect on MS monitoring. The extraction method effectively avoided drug hydrolysis and achieved good drug enrichment over 82.2%. The linear range of quantification was 1.25–160 ng mL−1. The stability of the drug in sample treatment was fully validated according to the sample processing procedure, including the stability in fresh blood, mobile phase, plasma and acidic methanol, and the results indicated that the drug remained stable during the whole sample preparation. Compared with a previous isotope-labeling method, more accurate and specific quantification of plasma concentration was achieved with liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization MS determination. With use of our method, nafamostat mesilate pharmacokinetics in 30 Chinese healthy volunteers was investigated with three doses via intravenous-drip infusion. The pharmacokinetic parameters were also estimated and compared with those of Japanese volunteers (slightly lower plasma concentration and longer terminal elimination half-life for Chinese volunteers). The difference in the pharmacokinetics may be ascribed to the quantification method, because previous isotope labeling may have overestimated the parent drug.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dobosz M, Sledzinski Z, Juszkiewicz P, Babicki A, Stanek A, Wajda Z, Basinski A (1991) Hepatogastroenterology 38:139–142
Horiuchi H, Suzuki T, Taniguchi M, Magata S, Jin MB, Ishikawa H, Ogata K, Shimamura T, Furukawa H, Todo S (2001) Transplant Proc 33:848
Kimura T, Fuchimoto S, Iwagaki H, Orita K (1993) Nippon Geka Gakkai Zasshi 94:66–70
Kotani K, Ichiba S, Andou M, Sano Y, Date H, Tedoriya T, Goto K, Shimizu N (2002) J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 124:626–627
Miyaso H, Morimoto Y, Ozaki M, Haga S, Shinoura S, Choda Y, Murata H, Katsuno G, Huda K, Takahashi H, Tanaka N, Iwagaki H (2006) Dig Dis Sci 51:2007–2012
Ohtake Y, Hirasawa H, Sugai T, Oda S, Shiga H, Matsuda K, Kitamura N (1991) Contrib Nephrol 93:215–217
Tsukagoshi S (2001) Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 28:1237–1243
Yamashita Y, Ishiguro Y, Sano D, Kimura M, Fujita K, Yoshida T, Horiuchi C, Taguchi T, Matsuda H, Mikami Y, Tsukuda M (2007) Auris Nasus Larynx 34:487–491
Yamaori S, Fujiyama N, Kushihara M, Funahashi T, Kimura T, Yamamoto I, Sone T, Isobe M, Ohshima T, Matsumura K, Oda M, Watanabe K (2006) Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 21:147–155
Yang H, Henkin J, Kim KH, Greer J (1990) J Med Chem 33:2956–2961
Aoyama T, Okutome T, Nakayama T, Yaegashi T, Matsui R, Nunomura S, Kurumi M, Sakurai Y, Fujii S (1985) Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 33:1458–1471
Abe T, Kinoshita T, Matsuda J, Ogushi T, Kawasugi K, Yoshimura Y, Otromo M (1984) Jpn Pharmacol Ther 12:4941–4964
Aoyama T, Sasaki H, Shibuya M, Suzuki Y (1985) Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 33:2142–2144
Yamaori S, Ukena E, Fujiyama N, Funahashi T, Kimura T, Yamamoto I, Ohshima T, Matsumura K, Oda M, Watanabe K (2007) Xenobiotica 37:260–270
Acknowledgment
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of the People’s Republic of China (nos. 30572228, 30630076).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Yg., Zhang, M., Yu, D. et al. A method for quantifying the unstable and highly polar drug nafamostat mesilate in human plasma with optimized solid-phase extraction and ESI-MS detection: more accurate evaluation for pharmacokinetic study. Anal Bioanal Chem 391, 1063–1071 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2054-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2054-4