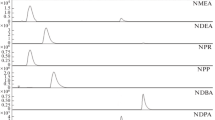
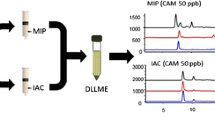
Abstract
Heterocyclic aromatic amines are formed in protein and amino acid-rich foods at temperatures above 150 °C. Of more than twenty heterocyclic aromatic amines identified ten have been shown to have carcinogenic potential. As nutritional hazards, their reliable determination in prepared food, their uptake and elimination in living organisms, including humans, and assessment of associated risks are important food-safety issues. The concentration in foods is normally in the low ng g−1 range, which poses a challenge to the analytical chemist. Because of the complex nature of food matrixes, clean-up and enrichment of the extracts are also complex, usually involving both cation-exchange (propylsulfonic acid silica gel, PRS) and reversed-phase purification. The application of novel solid-phase extraction cartridges with a wettable apolar phase combined with cation-exchange characteristics simplified this process—both the polar and apolar heterocyclic aromatic amines were recovered in one fraction. Copper phthalocyanine trisulfonate bonded to cotton (“blue cotton”) or rayon, and molecular imprinted polymers have also been successfully used for one-step sample clean-up. For analysis of the heterocyclic aromatic amines, liquid chromatography with base-deactivated reversed-phase columns has been used, and, recently, semi-micro and capillary columns have been introduced. The photometric, fluorimetric, or electrochemical detectors used previously have been replaced by mass spectrometers. Increased specificity and sub-ppb sensitivities have been achieved by the use of the selected-reaction-monitoring mode of detection of advanced MS instrumentation, for example the triple quadrupole and Q-TOF instrument combination. Gas chromatography, also with mass-selective detection, has been used for specific applications; the extra derivatization step needed for volatilization has been balanced by the higher chromatographic resolution.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander J, Reistad R, Hegstad S, Frandsen H, Ingebrigsten K, Paulsen JE, Becher G (2002) Food Chem Toxicol 40:113–1137
Alexander J, Wallin H (1991) Metabolic fate of heterocyclic amines in cooked foods. In: Hayatsu H (ed) Mutagens in food: detection and prevention. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 143–156
Arvidsson P, vanBoekel MAJS, Skog K, Jägerstad M (1997) J Food Sci 62:911–916
Augustsson K, Skog K, Jägerstad M, Steineck G (1997) Carcinogenesis 18:1931–1935
Barceló-Barrachina E, Moyano E, Puignou L, Galceran MT (2004) J Chromatogr B 802:45–59
Bermudo E, Busquets R, Barcelo-Barrachina E, Puignou L, Santos FJ, Galceran MT (2004) J Chromatogr B 802:61–68
Bohatsch G (2002) Thesis, Graz University of Technology
Busquets R, Bordas M, Toribio F, Puignou L, Galceran MT (2004) J Chromatogr B 802:79–86
deMeester C (1998) Z Lebensm Unters Forsch A 207:441–447
DuPont RL, Baumgartner WA (1995) Forensic Sci Int 70:63–76
Frandsen H (2007) Food Chem Toxicol 45:863–870
Frandsen H, Frederiksen H, Alexander J (2002) Food Chem Toxicol 40:1125–1130
Frederiksen H, Frandsen H (2004) Food Chem Toxicol 42:879–885
Galceran MT, Pais P, Puignou L (1996) J Chromatogr A 719:203–212
Galceran MT, Puignou L (2006) Latest developments in the analysis of heterocyclic amines in cooked foods. In: Skog K, Alexander J (eds) Acrylamide and other hazardous compounds in heat-treated foods. Woodhead, Cambridge, 68–116
Gerbl U, Cichna M, Zsivkovits M, Knasmüller S, Sontag G (2004) J Chromatogr B 802:107–114
Grivas S, Nyhammar T (1985) Mutat Res 142:5–8
Gross GA, Grüter A, Heyland S (1992) Food Chem Toxic 30:491–498
Guy PA, Gremaud E, Richoz J, Turesky RJ (2000) J Chromatogr A 883:89–102
Hashimoto H, Hanaoka T, Kobayashi M, Tsugane S (2004) J Chromatogr B 803:209–213
Hayatsu H (1992) J Chromatogr 597:37–56
Hayatsu H, Oka T, Wakata A, Ohara Y, Hayatsu T, Kobayashi H, Arimoto S (1983) Mutat Res 119:233–238
Herraiz T (2002) Food Add Cont 19:748–754
IARC (1993) Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans: some naturally occurring substances: food items and constituents, heterocyclic amines and mycotoxins. IARC 56:165–242
Jägerstad M, Skog K, Arvidsson P, Solyakov A (1998) Z Lebensm Unters Forsch A 207:419–427
Jautz U, Morlock G (2006) J Chromatogr A 1128:244–250
Kataoka H, Hayatsu T, Hietsch G, Steinkellner H, Nishioka S, Narimatsu S, Knasmüller S, Hayatsu H (2000) Mutat Res 466:27–35
Kataoka H, Kijima K (1997) J Chromatogr A 767:187–194
Keating GA, Bogen KT (2004) Food Chem Toxicol 39:29–43
Knize MG, Dolbeare FA, Carroll KL, Moore DH, Felton JS (1994) Food Chem Toxicol 32:595–603
Knize MG, Salmon CP, Pais P, Felton JS (1999) Adv Exp Med Biol 459:179–193
Krach C, Sontag G (2000) Anal Chim Acta 417:77–83
Luftmann H (2004) Anal Bioanal Chem 378:964–968
Martín-Calero A, Ayala JH, González V, Afonso AM (2007) Anal Chim Acta 582:259–266
Mayes AG, Mosbach K (1997) Trends Anal Chem 16:321–332
Murkovic M (2004) J Chromatogr B 802:3–10
Murkovic M, Friedrich M, Pfannhauser W (1997) Z Lebensm Unters Forsch A 205:347–350
Murkovic M, Steinberger D, Pfannhauser W (1998) Z Lebensm Unters Forsch A 207:477–480
Nagao M, Honda M, Seino Y, Yahagi T, Sugimura T (1977) Cancer Lett 2:221–226
Nagao M, Honda M, Seino Y, Yahagi T, Sugimura T (1977a) Cancer Lett 2:335–339
Pfau W, Skog K (2004) J Chromatogr B 802:115–126
Reistad R, Nyholm SH, Haug LS, Becher G, Alexander J (1999) Biomarkers 4:263–271
Ristic A, Cichna M, Sontag G (2004) J Chromatogr B 802:87–94
Rohrmann S, Linseisen J, Becker N, Norat T, Sinha R, Skeie G, Lund E, Martinez C, Barricarte A, Mattisson I, Berglund G, Welch A, Davey G, Overvad K, Tjonneland A, Clavelchapelon F, Kesse E, Lotze G, Klipsteingrobusch K, Vasilopoulou E, Polychronopoulos E, Pala V, Celentano E, Buenodemesquita HB, Peeters PHM, Riboli E, Slimani N (2002) Eur J Clin Nutr 56:1216–1230
Santos FJ, Barcelo E, Toribio F, Puignou L, Galceran MT, Persson E, Skog K, Messner C, Murkovic M, Nabinger U, Ristic A (2004) J Chromatogr B 802:69–78
Sinha R, Knize MG, Salmon CP, Brown ED, Rhodes D, Felton JS, Levander OA, Rothman N (1998) Heterocyclic amine content of pork products cooked by different methods and to varying degrees of doneness. Food Chem Toxicol 36:289–297
Skog K (2004) J Chromatogr B 802:39–44
Sugimura T (1988) Trends Pharmacol Sci 9:205–209
Sugimura T (1995) History, present and future, of heterocyclic amines, cooked food mutagens. In: Adamson R H, Gustafsson A, Ito N, Nagao M, Sugimura T, Wakabyashi K, Yamazoe Y, Proceedings of the 23rd International Symposium of the Princess Takamatsu Cancer Research Fund, Tokyo, Princeton Scientific, pp 214–231
Sugimura T (1997) Mutat Res 376:211–219
Sugimura T, Nagao M, Kawachi T, Honda M, Yahagi T, Seino Y, Sato S, Matsukura M, Matsushima T, Shirai A, Sawamura M, Matsumoto M (1977) Mutagens-carcinogens in foods with special reference to highly mutagenic pyrolytic products in broiled foods. In: Hiatt HH, Watson JD, Winsten JA (eds) Origin of human cancer. Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbour, pp 1561–1577
Strickland PT, Qian Z, Friesen MD, Rothman N, Sinha R (2001) Biomarkers 6:313–325
Takahashi M, Wakabayashi K, Nagao M, Yamamoto M, Masui T, Goto T, Kinae N, Tomita I, Sugimura T (1985) Carcinogenesis 6:1195–1199
Toribio F, Busquets R, Puignou L, Galceran MT (2007) Food Chem Toxicol 45:667–675
Toribio F, Moyano E, Puignou L, Galceran MT (2002) J Chromatogr A 948:267–281
Turesky RJ, Taylor J, Schnackenberg L, Freeman JP, Holland RD (2005) J Agric Food Chem 53:3248–3258
Turteltaub KW, Felton JS, Gledhill BL, Vogel JS, Southon JR, Caffee MW, Finkel RC, Nelson DE, Proctor ID, Davis JC (1990) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:5288–5292
Turteltaub KW, Dingley KH, Curtis KD, Malfatti MA, Turesky RJ, Colin Garner R, Felton JS, Lang NP (1999) Cancer Letters 143:149–155
Viberg P, Nilsson S, Skog K (2004) Anal Bioanal Chem 378:1729–1734
Viberg P, Wahlund KG, Skog K (2006) J Chromatogr A 1133:347–532
Wakabayashi K, Kim I-S, Kurosaka R, Yamaizumi Z, Ushiyama H, Takahashi M, Koyota S, Fecuda A, Nukaya H, Goto S, Sugimura T, Nagao M (1995) Identification of new mutagenic heterocyclic amines and quantification of known heterocyclic amines. In: Adamson PH, Gustavsson JA, Ito N, Nagao M, Sugimura T, Wakabayashi K, Yamazoe Y (eds) Heterocyclic amines in cooked foods: possible human carcinogens. Princeton Scientific Publishing, Princeton, pp 39–49
Wakabayashi K, Totsuka Y, Fukutome K, Oguri A, Ushiyama H, Sugimura T (1997) Mutat Res 376:253–259
Widmark E (1939) Nature 143:984
Zimmerli B, Rhyn P, Zoller O, Schlatter J (2001) Food Add Contam 18:533–551
Zöchling S, Murkovic M (2002) Food Chem 79:125–134
Zöchling S, Murkovic M, Pfannhauser W (2002) J Biochem Biophys Methods 53:37–44
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murkovic, M. Analysis of heterocyclic aromatic amines. Anal Bioanal Chem 389, 139–146 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-007-1306-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-007-1306-z