Abstract
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and odors in cattle rumen gas have been characterized by in-vivo headspace sampling by solid-phase microextraction (SPME) and analysis by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry–olfactometry (GC–MS–O). A novel device enabling headspace SPME (HS-SPME) sampling through a cannula was designed, refined, and used to collect rumen gas samples from steers. A Carboxen–polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) fiber (85 μm) was used for SPME sampling. Fifty VOCs from ten chemical groups were identified in the rumen headspace. The VOCs identified had a wide range of molecular weight (MW) (34 to 184), boiling point (−63.3 to 292 °C), vapor pressure (1.05 × 10−5 to 1.17 × 102 Pa), and water solubility (0.66 to 1 × 106 mg L−1). Twenty-two of the compounds have a published odor detection thresholds (ODT) of less than 1 ppm. More than half of the compounds identified are reactive and have an estimated atmospheric lifetime of <24 h. The amounts of VFAs, sulfide compounds, phenolic compounds, and skatole, and the odor intensity of VFAs and sulfide compounds in the rumen gas were all higher after feeding than before feeding. These results indicate that rumen gases can be an important potential source of aerial emissions of reactive VOCs and odor. In-vivo sampling by SPME then GC–MS–O analysis can be a useful tool for qualitative characterization of rumen gases, digestion, and its relationship to odor and VOC formation.

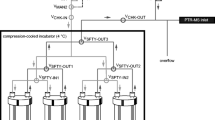
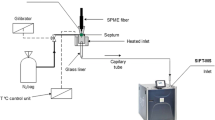
Modified cannula for rumen gas sampling with SPME







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Church DC (ed) (1988) The ruminant animal. Prentice–Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Calabro S, Lopez S, Piccolo V, Dijkstra J, Dhanoa MS, France J (2005) Anim Feed Sci Technol 123–124:51–65
Dirksen GU, Smith MC (1987) Bovine Pract 22:108–116
Garrett EF, Pereira MN, Nordlund KV, Armentano LE, Goodger WJ, Oetzel GR (1999) J Dairy Sci 82:1170–1178
Hungate RE (1996) The rumen and its microbes. Academic Press, New York
Erlich GG, Goerlitz DF, Bourell JH, Eisen GV, Godsy EM (1981) Appl Environ Microbiol 42:878–885
Brotz PG, Schaefer DM (1987) J Microbiol Methods 6:139–144
Ziolecki A, Kwiatkowska E (1973) J Chromatogr 80:250–254
Teunissen MJ, Marras SAE, Op den Camp HJM, Vogels GD (1989) J Microbiol Methods 10:247–254
Faichney GJ (1967) J Chromatogr 27:482–484
Williams GD, Rippon P, Chen P, Camp BJ (1979) Anal Biochem 99:324–331
Phillips KD, Tearle PV, Willis AT (1976) J Clin Pathol 29:22–27
Brooks JB, Moore WEC (1969) Can J Microbiol 15:143–147
Salanitro JP, Muirhead PA (1975) Appl Microbiol 29:374–381
Dewhurst RJ, Evans RT, Mottram TT, Spanel P, Smith D (2001) J Dairy Sci 84:1438–1444
Spinhirne JP, Koziel JA, Chirase NK (2003) Trans ASAE 46:585–588
Schneider IC, Ames ML, Rasmussen MA, Reilly PJ (2002) J Agric Food Chem 50:2267–2273
Koziel JA, Spinhirne JP, Lloyd J, Parker D, Wright D, Kuhrt F (2005) J Air Waste Manage Assoc 55:1147–1157
Keener KM, Zhang J, Bottcher RW, Munilla RD (2002) Trans ASAE 45:1579–1584
Huebner MA, Hoff SJ, Zelle BC, Gralapp AK (2005) Paper 05-A-1067-AWMA in the Proceedings of the AWMA Annual Conference and Exhibition, Minneapolis
Koziel JA, Noah J, and Pawliszyn J (2001) Environ Sci Technol 35:1481–1486
Pawliszyn J (1999) (eds) Applications of Solid Phase Microextraction, The Royal Society of Chemistry, Hertfordshire, UK
Koziel JA, Pawliszyn J (2001) J Air Waste Manage Assoc 51:173–184
Gorecki T, In: Pawliszyn J (eds) (1999) Applications of Solid Phase Microextraction, Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge
Koziel JA, Jia M, Pawliszyn J (2000) Anal Chem 72:5178–5186
Spinhirne JP, Koziel JA, Chirase N (2004) J Chromatogr A 1025:63–69
Cai L, Koziel JA, Lo YC, Hoff SJ (2006) J Chromatogr A 1102:60–72
Wright D, Nielsen L, Eaton D, Kuhrt F, Koziel JA, Spinhirne JP, Parker DB (2005) J Agric Food Chem 53:8663–8672
Koziel JA, Cai L, Wright D, Hoff S (2006) J Chromatogr Sci 44:451–457
Haberhauer-Troyer C, Rosenberg E, Grasserbauer M (1999) J Chromatogr A48:305–315
Pan L, Adams M, Pawliszyn J (1995) Anal Chem 67:4396–4402
Augusto F, Koziel JA, Pawliszyn J (2001) Anal Chem 73:481–486
Devos M, Patte F, Roualt J, Laffort P, Van Gemert LJ (eds) (1990)Standardized Human Olfactory Thresholds, IRL Press at Oxford Press, NY, New York
Sunesson AL, Gullberg J, Blomquist G (2001) J Environ Monit 3:210–216
Fukui Y, Doskey PV (2000) Atmos Environ 34:2947–2956
Rabaud NE, Ebeler SE, Ashbaugh LL, Flocchini RG (2003) Atmos Environ 37:933–940
Flavornet. http://www.flavornet.org/flavornet.html accessed on June 22, 2006
Air Pollution Engineering Manual, Davis WT (eds) (2000) Wiley, New York
Barnes RF, Nelson CJ, Collins M, Moore KJ (eds) (2003) Forages, 6th edn. Blackwell, Ames, Iowa
Zhu J (1999) Trans ASAE 42:175–182
Wiles M, Elwell D, Keener H, Amburgey J, Borger D, Willett L (2000) Compost Sci Util 9:27–37
Allen MS (1997) J Dairy Sci 80:1447–1462
Mottram TT, Ditcham WJF, Bolam H, Short L, Cammell S, Beever DE, Hobbs PJ (2000) Silsoe Research Institute, Bedfordshire, UK
Williams J, Wang N, Cicerone RJ, Yagi K, Kurihara M, Terada F (1999) Glob Biogeochem Cycl 13:485–491
Bates TS, Charlson RJ, Gammon RH (1987) Nature 329:319–321
Charlson RJ, Lovelock JE, Andrea MO, Warren SG (1987) Nature 326:655–661
Acknowledgements
This project was sponsored in part by Iowa State University and the Iowa Beef Center. The assistance of Rod Berryman, Kelly Nissen, Jeff Thorsen, Kevin Twedt and Dave Fisher of the ISU Beef Nutrition Center is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, L., Koziel, J.A., Davis, J. et al. Characterization of volatile organic compounds and odors by in-vivo sampling of beef cattle rumen gas, by solid-phase microextraction, and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry–olfactometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 386, 1791–1802 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0799-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0799-1