Abstract
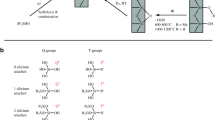
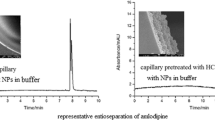
The applicability of three-layer coatings consisting of three different polymers (A+-B−-C+ coating) prepared by a successive multiple ionic-polymer layer (SMIL) coating technique to the immobilization of polypeptides and/or proteins onto the inner surface of the capillaries was investigated to provide a high-performance separation medium for proteins and enantiomers in capillary electrophoresis (CE). To obtain a stable protein-coated capillary, high molecular mass poly(ethyleneimine) (PEI) was employed as the first layer in the A+-B−-C+ coating, and then a cationic protein was immobilized as the third layer. Comparisons of analytical performances between the A+-B−-C+ coating and the conventional SMIL-coated (A+-B−-A+ coating) capillary were conducted. The CE separation of cationic proteins was successfully achieved with the prepared capillaries. In addition, the polypeptide- and protein-coated capillaries were applied to the chiral separation of a binaphthyl compound. It should be noted that the chiral separation efficiency was strongly dependent on the second anionic polymer layer of the coating. Effects of the interaction between oppositely charged ionic polymer layers on the separation efficiency are discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Landers JP (ed) (1997) Handbook of capillary electrophoresis, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Rodoriguez I, Li SFY (1999) Anal Chim Acta 383:1–26
Chiu RW, Jimenez JC, Monnig CA (1995) Anal Chim Acta 307:193–201
Cordova E, Gao J, Whitesides JM (1997) Anal Chem 69:1370–1379
Okamoto Y, Kitagawa F, Otsuka K (2006) Electrophoresis 27:1031–1040
Erim FB, Cifuentus A, Poppe H, Kraak JC (1995) J Chromatogr A 708:356–361
Chankvetadze B, Schulte G, Blaschke G (1997) J Pharm Biomed Anal 15:1577–1584
Katayama H, Ishihama Y, Asakawa N (1998) Anal Chem 70:2254–2260
Katayama H, Ishihama Y, Asakawa N (1998) Anal Chem 70:5272–5277
Katayama H, Ishihama Y, Asakawa N (2000) J Chromatogr A 875:315–322
Kamande MW, Zhu X, Kapnissi-Christodoulou C, Warner IM (2004) Anal Chem 75:6681–6692
Zhu X, Kamande MW, Thiam S, Mwongela SM, Warner IM (2004) Electrophoresis 25:562–568
Haginaka J (2000) J Chromatogr A 875:235–254
Tanaka Y, Terabe S (2001) J Biochem Biophys Methods 48:103–116
Graul TW, Schlenoff JB (1999) Anal Chem 71:4007–4013
Ramamurthy N, Baliga N, Wahr JA, Schaller U, Yang VC, Meyerhoff ME (1998) Clin Chem 44:606–613
Sequaris JM, Babmann F, Hild A, Narres HD, Schwuger MJ (1999) Colloid Surf A 159:503–512
Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software V8.14 for Solaris (1994–2005 ACD/Labs)
Warrant RW, Kim S-H (1978) Nature 271:130–135
Weinberger S, Berman C, Minsky A (1988) J Am Chem Soc 110:8231–8232
Reich Z, Schramm O, Brumfeld V, Minsky A (1996) J Am Chem Soc 118:6345–6349
Acknowledgements
K.O. is grateful for the Grant in Aid for Scientific Research (No. 15350041) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. This work was supported in part by the Grant in Aid for Regional Rebirth Consortium R&D program, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, Japan. This work was also supported in part by the Grant in Aid for 21st Century Program, COE for a United Approach for New Materials of Science, from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kitagawa, F., Kamiya, M., Okamoto, Y. et al. Electrophoretic analysis of proteins and enantiomers using capillaries modified by a successive multiple ionic-polymer layer (SMIL) coating technique. Anal Bioanal Chem 386, 594–601 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0438-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0438-x