Abstract
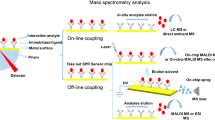
This paper describes the combination of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry with label free bio-interaction analysis based on reflectometric interference spectroscopy (RIfS). The potential of this concerted approach is demonstrated by measuring the binding properties of different vancomycin-type glycopeptide antibiotic mixtures. Although RIfS is sensitive and does not require use of a label, it cannot determine which components of a mixture have bound to the surface after incubation. Fortunately, each bound species has a unique mass that can, afterwards, be determined by mass spectrometry. Thus, the screening capability of RIfS is combined with the identification capability of mass spectrometry.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schmitt H-M, Brecht A, Piehler J, Gauglitz G (1997) Biosens Bioelectron 12:219–233
Brecht A, Lang G, Gauglitz G (1993) J Anal Chem 346:615–617
Brecht A, Gauglitz G, Kraus G, Nahm W (1993) Sens Actuator 11B:21–27
Löfas S, Malmqvist M, Rönnberg I, Stenberg E, Liedberg B, Lundström I (1991) Sens Actuators B 5:79–84
Myska DG (1997) Curr Opin Biotechnol 7:11–19
Malmqvist M, Karlsson R (1997) Curr Opin Chem Biol 3:378–383
Tünnemann R, Mehlmann M, Süßmuth R D, Bühler B, Pelzer S, Wohlleben W, Fiedler H-P, Wiesmüller K-H, Gauglitz G, Jung G (2001) Anal Chem 73:4313–4318
Mehlmann M (2003) Einsatz optischer Biosensoren für die Protein- und Fermentationsanalyse. Dissertation, Eberhard-Karls-Universität Tübingen, Germany
Mann M, Talbo G (1996) Curr Opin Biotechnol 7:11–19
Krone JR, Nelson RW, Dogruel D, Williams P, Granzow R (1997) Anal Biochem 244:124–132
Nelson RW, Jarvik JW, Taillon BE, Tubbs KA (1999) Anal Chem 71:2858–2865
Nelson RW, Nedlekov D, Tubbs KA (2000) Electrophoresis 21:1155–1163
Yao C, Crandall LW (1994) In: Nagarajan R (ed) Glycopeptide antibiotics. R. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, p 1
Barna JCJ, Williams DH (1984) Ann Rev Microbiol 38:339–357
Piehler J, Brecht A, Geckeler KE, Gauglitz G (1996) Biosens Bioelectron 11:579–590
Brecht A, Gauglitz G, Nahm W (1992) Interferometric measurements used in chemical and biochemical sensors. Analusis 20(3):135–140
Gauglitz G, Nahm W (1991) Fresenius Z Anal Chem 341:279–283
Krauss G (1993) Reflektometrisch-interferometrische Bestimmung organischer Verbindungen. Dissertation, Eberhard-Karls-Universität Tübingen, Germany
Brecht A, Gauglitz G, Polster J (1993) Biosens Bioelectron 8:387–392
Schmitt HM, Brecht A, Piehler J, Gauglitz G (1997) Biosens Bioelectron 12:809–816
Piehler J, Brecht A, Valiokas R, Liedberg B, Gauglitz G (2000) Biosens Bioelectron 15(9–10):473–481
Hänel C (2003) Parameteroptimierung für zwei Verfahren zur markierungsfreien Analyse biomolekularer Wechselwirkungen. Dissertation. Eberhard-Karls-Universität Tübingen, Germany
Jensen O, Podtelejnikov A, Mann M (1996) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 10:1371–1378
Nastume T, Nakayama H, Jansson Ö, Isobe T, Takio K, Mikoshiba K (2000) Anal Chem 72:4193–4198
Sönksen CP, Nordhoff E, Jansson Ö, Malmqvist M, Roepstorff P (1998) Anal Chem 70:2731–2736
Krone JR, Nelson RW, Dogruel D, Williams P, Granzow R (1997) Anal Biochem 244:124–132
Acknowledgments
Martin Mehlmann was supported by the DFG-Graduate colleague “Quantitative Analysis and Characterisation of Pharmaceutically and Biochemically relevant Substances” at the University of Tübingen and by the Fonds der Chemischen Industrie. Desvancosamin-vancomycin was a kind gift from Dr Evi Stegmann, AG Wohlleben, University of Tübingen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dedicated to the memory of Wilhelm Fresenius
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehlmann, M., Garvin, A.M., Steinwand, M. et al. Reflectometric interference spectroscopy combined with MALDI−TOF mass spectrometry to determine quantitative and qualitative binding of mixtures of vancomycin derivatives. Anal Bioanal Chem 382, 1942–1948 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-005-3329-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-005-3329-7