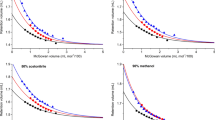
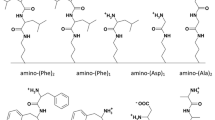
Abstract
Basic phenomena in reversed-phase liquid chromatography have been quantitatively analyzed using a computational chemical calculation. Pyridine interacted with an ionized silica surface under neutral conditions. Alkyl-chain length affected the contact surface area with an analyte. Steric hindrance was demonstrated using a model graphitic carbon phase and unsaturated alkenes. Quantitative structure–retention relationships in reversed-phase liquid chromatography were demonstrated for phenolic compounds and acidic and basic drugs. The correlations between predicted and measured retention factors were satisfactory. Dissociation constants were derived from the atom partial charge and used to predict retention factors of partially ionized compounds.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanai T (ed) (1999) HPLC A practical guide. Royal Chemical Society, Cambridge
Hanai T (1995) Encyclopedia of analytical science. Academic Press, London, pp 2558–2567
Hanai T (1996) In: Hatano H, Hanai T (eds) Advances in liquid chromatography. World Scientifics, Singapore, pp 307–327
Hanai T in Brown PR, Grushka E (eds) (2000) Advances in chromatography, vol 40. pp 315–357
Berendsen GE, Galan LD (1980) J Chromatogr 196:21–37
Hanai T (2004) J Chromatogr A 1027:279–287
Hanai T, Miyazaki R, Koseki A, Kinoshita T (2004) J Chromatogr Sci 42:354–360
Hanai T (2004) Presented at 27th international symposium in capillary chromatography, Riva del Garda, 2004
McGraw KJ, Hill GF, Stradi R, Parker RS (2001) Physiol Biochem Zool 74:843–852
McGraw KJ, Hill GF, Stradi R, Parker RS (2002) Comp Biochem Physiol B 131:261–269
Hanai T (2003) J Chromatogr A 989:183–196
Hanai T (2004) J Chromatogr A 1030:13–16
Hanai T, Mizutani Chi, Homma H (2003) J Liq Chromatogr Rel Technol 26:2031–2039
Hanai T (2005) J Chromatogr A (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanai, T. Chromatography in silico, basic concept in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Anal Bioanal Chem 382, 708–717 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-005-3069-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-005-3069-8