Abstract
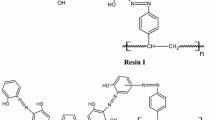
A new grafted polymer has been developed by the chemical modification of Amberlite XAD-16 (AXAD-16) polymeric matrix with [(2-dihydroxyarsinoylphenylamino)methyl]phosphonic acid (AXAD-16-AsP). The modified polymer was characterized by a combination of 13C CPMAS and 31P solid-state NMR, Fourier transform-NIR-FIR-Raman spectroscopy, CHNPS elemental analysis, and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The distribution studies for the extraction of U(VI), Th(IV), and La(III) from acidic solutions were performed using an AXAD-16-AsP-packed chromatographic column. The influences of various physiochemical parameters on analyte recovery were optimized by both static and dynamic methods. Accordingly, even under high acidities (>4 M), good distribution ratio (D) values (102–104) were achieved for all the analytes. Metal ion desorption was effective using 1 mol L−1 (NH4)2CO3. From kinetic studies, a time duration of <15 min was sufficient for complete metal ion saturation of the resin phase. The maximum metal sorption capacities were found to be 0.25, 0.13, and 1.49 mmol g−1 for U(VI); 0.47, 0.39, and 1.40 mmol g−1 for Th(IV); and 1.44, 1.48, and 1.12 mmol g−1 for La(III), in the presence of 2 mol L−1 HNO3, 2 mol L−1 HCl, and under pH conditions, respectively. The analyte selectivity of the grafted polymer was tested in terms of interfering species tolerance studies. The system showed an enrichment factor of 365, 300, and 270 for U(VI), Th(IV), and La(III), and the limit of analyte detection was in the range of 18–23 ng mL−1. The practical applicability of the polymer was tested with synthetic nuclear spent fuel and seawater mixtures, natural water, and geological samples. The RSD of the total analytical procedure was within 4.9%, thus confirming the reliability of the developed method.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geckeler EK (2001) Advanced functional molecules and polymers, 1st edn. Gordon and Breach, Singapore
Kantipuly C, Katrogadda S, Chow A, Gesser HD (1990) Talanta 37:491–517
Torre M, Marina ML (1994) CRC Crit Rev Anal Chem 24:327–361
Prabhakaran D, Subramanian MS (2003) Talanta 59:1227–1236
Condamines N, Musikas C (1992) Solvent Extr Ion Exch 10:69–100
Cuillerdier C, Musikas C (1995) Sep Sci Tech 30:2075–2099
Hennion MC (1999) J Chromatogr A 856:3–54
Kantipuly JC, Westland DA (1988) Talanta 35:1–13
Savvin SB, Mikhailova AV (1996) J Anal Chem 51(1):42–49.
Myasoedova GV, Savvin SB (1987) CRC Crit Rev Anal Chem 17:1–63.
Fritz JS (1999) Analytical solid phase extraction, 1st edn. Wiley-VCH, New York
Rao PRV, Patil SK (1978) J Radioanal Chem 42:399–410
Snell FD (1978) Photometric and fluorometric methods of analysis metals. Wiley, New York
Oscar AN, Bernard WW, Michael A (1958) Anal Chem 30:1182–1185
Maji S, Sundarajan K, Hemamalini G, Viswanathan KS (2001) Fluorimetric estimation of uranium: applications in nuclear technology, IGC 228. Indra Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research, India
Whitefield H, Jagnee D (1956) Marine electrochemistry: a practical introduction. Wiley-Interscience, Northern Ireland
Komoroski RA (1986) High resolution NMR spectroscopy of synthetic polymers in bulk, 1st edn. VCH, Deerfield Beach, Florida
Verkade JG, Quin LD (1987) Phosphorous-31 NMR spectroscopy in stereochemical analysis, 1st edn. VCH, Deerfield Beach, Florida
Prabhakaran D, Subramanian MS (2003) Anal Lett 36:2277–2289
Jain VK, Handa A, Sait SS, Shrivastav P, Agrawal YK (2001) Anal Chim Acta 429:237–246
Merdivan M, Zahir Duz M, Hamamci C (2001) Talanta 55:639–645
Pathak R, Rao GN (2000) Anal Chim Acta 335:283–290
Pakalns P (1980) Anal Chim Acta 120:289–296
Ueda K, Sato Y, Yoshimura O, Yamamoto Y (1988) Analyst 113:773–777
Prabhakaran D, Subramanian MS (2003) Talanta 61:423–430
Prabhakaran D, Subramanian MS (2003) React Funct Polym 57:147–155
Dev K, Pathak R, Rao GN (1999) Talanta 48:579–584
Kumar M, Rathore DPS, Singh AK (2000) Analyst 125:1221–1226
Prabhakaran D, Subramanian MS (2004) Sep Sci Tech 39:941–957
Maheswari AM, Subramanian MS (2003) Anal Lett 36:2875–2892
Chiarizia R, Horwitz EP, Alexandratos SD (1993) Solvent Extr Ion Exch 11:211–237
Horwitz EP, Chiarizia R, Diamond H, Gatrone RC, Alexandratos SD, Trochimczuk AQ, Crick DW (1993) Solvent Extr Ion Exch 11:943–966
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prabhakaran, D., Subramanian, M.S. Selective extraction of U(VI), Th(IV), and La(III) from acidic matrix solutions and environmental samples using chemically modified Amberlite XAD-16 resin. Anal Bioanal Chem 379, 519–525 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-004-2600-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-004-2600-7