Abstract
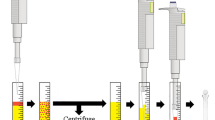
A method for the determination of aldrin, dieldrin, DDT, DDE, and DDD contamination in animal fats (beef tallow, lard, and chicken fat) without using toxic reagents is developed, that uses high-performance liquid chromatography after the sample has been prepared by matrix solid-phase dispersion (MSPD) with acidic alumina oxide. A reversed-phase C1-silica column with a mobile phase of 50% (v/v) ethanol solution (in water) and a photo-diode array detector were used for the determination. Average recoveries of the target compounds (0.2–5.0 μg g−1) ranged from 84–98%, with coefficients of variation of <5%. The limits of quantitation were ≤0.16 μg g−1 for AD, ≤0.10 μg g−1 for DD, ≤0.06 μg g−1 for DDT, ≤0.07 μg g−1 for DDE, and ≤0.05 μg g−1 for DDD. No toxic reagents were used at all.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
US Environmental Protection Agency (1997) Special report on environmental endocrine disruption. US EPA, Washington, DC
International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) (1987) Overall evaluations of carcinogenicity. IARC monographs on the evaluation of the carcinogenic risk of chemicals to humans, Suppl. 7. IARC, Lyon, France
Malisch R, Bourgeois B, Lippold R (1992) Deut Lebensm-Rundsch 88:205–216
Anastas PT, Warner JC (eds)(1998) Green chemistry – theory and practice. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK
Dost K, Jones DC, Davidson G (2000) Analyst 125:1243–1247
Barker SV (1989) J Chromatogr 475:353–361
Barker SV (2000) J Chromatogr A 880:63–68
Barker SV (2000) J Chromatogr A 885:115–127
Grice ID, Salzmann I, Stiff I, Griffiths LR (1999) J Liq Chromatogr R T 22:2337–2344
Furusawa N (2001) J Chromatgr Sci 39:183–187
Merck KGaA (2000) Catalogue 2000/2001. Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd. (2002) Chemicals, 32nd end. Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., Osaka, Japan
Bentabol A, Jodral M (1995) Pestic Sci 44:177–182
Schenck FJ, Calderon L, Saudarg DE (1996) J AOAC Int 79:1454–1458
Doong RJ, Lee C (1999) Analyst 124:1287–1289
Nerin C, Tornes AR, Domeno C, Cacho J (1995) Fresen J Anal Chem 352:364–371
AOAC (1990) Official methods of analysis (sec 970.520). AOAC, Gaithersburg, MA
Codex Alimentarius Commission (1993) Joint FAO/WHO food standards program: Residues of veterinary drugs in food, vol 3. Codex Alimentarius Commission (FAO/WHO), Rome, Italy
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furusawa, N. A toxic reagent-free method for normal-phase matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and reversed-phase liquid chromatographic determination of aldrin, dieldrin, and DDTs in animal fats. Anal Bioanal Chem 378, 2004–2007 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-004-2548-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-004-2548-7