Abstract.
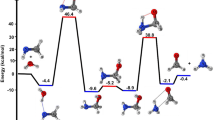
Ab initio molecular dynamics simulations at the Hartree-Fock/6-31G level of theory are performed on methyl chloride hydrolysis with explicit consideration of one solute and two solvent water molecules at a temperature of 298 K. The reaction involves the formation of a reactant complex and the energy surface to the transition state is found to be simple. Two types of trajectories toward the product are observed. In the first type, the system reaches an intermediate complex (complex-P1) region after two nearly concerted proton transfers involving the attacking water molecule and the solvent water molecules. These trajectories resemble the intrinsic reaction coordinate trajectory. The thermal motion of the atoms leads the system to another intermediate complex (complex-P2) region. A second type of trajectory is found in which the system reaches the complex-P2 region directly after the proton transfers. In both of these forward trajectories, back proton transfers lead the system to a final complex-F region which resembles protonated methanol.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 July 1998 / Accepted: 2 September 1998 / Published online: 15 February 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aida, M., Yamataka, H. & Dupuis, M. Ab initio MD simulations of a prototype of methyl chloride hydrolysis with explicit consideration of three water molecules: a comparison of MD trajectories with the IRC path. Theor Chem Acc 102, 262–271 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002140050497
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002140050497