Abstract
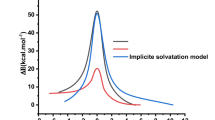
The current work investigates the lactamization reaction of neuropsychotropic medicine phenibut to higher toxicity phenibut-lactam. The reaction is considered as an intramolecular cyclization which finally leads to generation of phenibut-lactam component. Herein, we considered three different structural forms for the chemically intact phenibut which consist of two stable R1, R2, and a relatively distorted isomer R*. The initial stage in this reaction is the transformation of two stable isomers into the unstable form, R*. The calculations showed that there is a transition state (TS) close to the unstable geometry, R*. This transition state possesses 31.30 kcal/mol more energy compared to the isomer R* (5.98 kcal/mol). By studying the thermodynamic stability of the lactam structure (− 13.55 kcal/mol), we can clearly conclude that pheni-l component has higher thermal stability compared to its related phenibut. Also, from the investigation of this reaction in various pH, it was found that the rate of reaction reduces under both basic and acidic conditions.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
All analyses shown in the text were done using the the B3LYP-D3 level except mentioned otherwise.
References
Lapin I (2001) Phenibut (β-Phenyl-GABA): a tranquilizer and nootropic drug. CNS Drug Rev 7:471–481
Khaunina R (1964) Tranquilizing effects of beta-phenyl-gamma-aminobutyric acid (FENIGAM). Biulleten’eksperimental’noi Biol Med 57:54
Khaunina R, Lapin I (1989) Use of fenibut in psychiatry and neurology and its place among other psychotropic drugs (review of the literature). Zhurnal nevropatologii i psikhiatrii imeni SS Korsakova (Moscow, Russia: 1952), 89: 142.
Sytinsky I, Soldatenkov A, Lajtha A (1978) Neurochemical basis of the therapeutic effect of γ-aminobutyric acid and its derivatives. Prog Neurobiol 10:89–133
Perfilova V, Tiurenkov I, Berestovitskaia V, Vasil’eva O (2006) Cardioprotective effect of GABA derivatives in acute alcohol intoxication. Eksperimental’naia i klinicheskaia farmakologiia 69:23–27
Tyurenkov I, Perfilova V, Popova T, Ivanova L, Prokofiev I, Gulyaeva O, Stepa L (2013) Changes in oxidant and antioxidant status of females with experimental gestosis under the effect of GABA derivatives. Bull Exp Biol Med 2013:155
Dambrova M, Zvejniece L, Liepinsh E, Cirule H, Zharkova O, Veinberg G, Kalvinsh I (2008) Comparative pharmacological activity of optical isomers of phenibut. Eur J Pharmacol 583:128–134
Zvejniece L, Vavers E, Svalbe B, Veinberg G, Rizhanova K, Liepins V, Kalvinsh I, Dambrova M (2015) R-phenibut binds to the α2–δ subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels and exerts gabapentin-like anti-nociceptive effects. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 137:23–29
Bowery NG (2006) GABAB receptor: a site of therapeutic benefit. Curr Opin Pharmacol 6:37–43
Ziablitseva E, Pavlova I (2007) Effect of GABA receptor agonist phenibut on behavior and respiration of rabbits in the negative emotional situation. Zhurnal vysshei nervnoi deiatelnosti imeni IP Pavlova 57:479–488
Owen DR, Wood DM, Archer JR, Dargan PI (2016) Phenibut (4-amino-3-phenyl-butyric acid): availability, prevalence of use, desired effects and acute toxicity. Drug Alcohol Rev 35:591–596
Calandre EP, Rico-Villademoros F, Slim M (2016) Alpha2delta ligands, gabapentin, pregabalin and mirogabalin: a review of their clinical pharmacology and therapeutic use. Expert Rev Neurother 16:1263–1277
Eroglu C, Allen NJ, Susman MW, O’Rourke NA, Park CY, Özkan E, Chakraborty C, Mulinyawe SB, Annis DS, Huberman AD (2009) Gabapentin receptor α2δ-1 is a neuronal thrombospondin receptor responsible for excitatory CNS synaptogenesis. Cell 139:380–392
Zong Z, Desai SD, Kaushal AM, Barich DH, Huang HS, Munson EJ, Suryanarayanan R, Kirsch LE (2011) The stabilizing effect of moisture on the solid-state degradation of gabapentin. AAPS PharmSciTech 12:924
Zour E, Lodhi SA, Nesbitt RU, Silbering SB, Chaturvedi PR (1992) Stability studies of gabapentin in aqueous solutions. Pharm Res 9:595–600
Hadidi S, Shiri F, Norouzibazaz M (2020) Mechanistic study of fenoprofen photoisomerization to pure (S)-fenoprofen: a DFT study. Struct Chem 31:115–122
Hadidi S, Shiri F, Norouzibazaz M (2019) Conversion mechanism and isomeric preferences of the cis and trans isomers of anti-cancer medicine carmustine. A double hybrid DFT calculation. Chem Phys 522:39–43
Hadidi S, Shiri F, Norouzibazaz M (2019) A theoretical survey of the ability of nanocarbon layers to deliver anti-cancer drug temozolomide to the target cancer cells. Curr Chem Lett 8:53–62
Parr RG (1980) Density functional theory of atoms and molecules. In: Horizons of quantum chemistry. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 5–15
Burke K (2012) Perspective on density functional theory. J Chem Phys 136:150901
Montgomery JA Jr, Frisch MJ, Ochterski JW, Petersson GA (1999) A complete basis set model chemistry. VI. Use of density functional geometries and frequencies. J Chem Phys 110:2822–2827
Montgomery JA Jr, Frisch MJ, Ochterski JW, Petersson GA (2000) A complete basis set model chemistry. VII. Use of the minimum population localization method. J Chem Phys 112:6532–6542
Elstner M, Hobza P, Frauenheim T, Suhai S, Kaxiras E (2001) Hydrogen bonding and stacking interactions of nucleic acid base pairs: a density-functional-theory based treatment. J Chem Phys 114:5149–5155
Grimme S, Antony J, Ehrlich S, Krieg H (2010) A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J Chem Phys 132:154104
Grimme S (2006) Semiempirical hybrid density functional with perturbative second-order correlation. J Chem Phys 124:034108
Zahedi E, Shaabani S, Shiroudi A (2017) Following the molecular mechanism of decarbonylation of unsaturated cyclic ketones using bonding evolution theory coupled with NCI analysis. J Phys Chem A 121:8504–8517
Li X, Frisch MJ (2006) Energy-represented direct inversion in the iterative subspace within a hybrid geometry optimization method. J Chem Theory Comput 2:835–839
Fukui K (1981) The path of chemical reactions-the IRC approach. Acc Chem Res 14:363–368
Hratchian H, Schlegel H (2005) Theory and applications of computational chemistry: the first 40 years, Dykstra, CE, pp. 195-249.
Marenich AV, Cramer CJ, Truhlar DG (2009) Universal solvation model based on solute electron density and on a continuum model of the solvent defined by the bulk dielectric constant and atomic surface tensions. J Phys Chem B 113:6378–6396
Barone V, Cossi M (1998) Quantum calculation of molecular energies and energy gradients in solution by a conductor solvent model. J Phys Chem A 102:1995–2001
Cossi M, Rega N, Scalmani G, Barone V (2003) Energies, structures, and electronic properties of molecules in solution with the C-PCM solvation model. J Comput Chem 24:669–681
Lu T, Chen F (2012) Atomic dipole moment corrected Hirshfeld population method. J Theor Comput Chem 11:163–183
Neese F (2009) Orca, An Ab Initio, DFT and semiempirical electronic structure package, p. 3.
Shiri F, Norouzibazaz M, Yari A, Taherpour AA (2018) A DFT study of both the hydrolytic degradation and protonation of semustine in variation conditions of pH and interaction of drug with DNA nucleobases. Struct Chem 29:1465–1474
Hadidi S, Shiri F, Norouzibazaz M (2019) A DFT study of the degradation mechanism of anticancer drug carmustine in an aqueous medium. Struct Chem 30:1315–1321
Verma AM, Kishore N (2018) Kinetics of decomposition reactions of acetic acid using DFT approach. Open Chem Eng J 2018:12
Jong UG, Yu CJ, Ri GC, McMahon AP, Harrison NM, Barnes PR, Walsh A (2018) Influence of water intercalation and hydration on chemical decomposition and ion transport in methylammonium lead halide perovskites. J Mate Chem A 6:1067–1074
Brea O, Daver H, Rebek J Jr, Himo F (2019) Mechanism (s) of thermal decomposition of N-Nitrosoamides: a density functional theory study. Tetrahedron 75:929–935
Chen CS, Shieh WR, Lu PH, Harriman S, Chen CY (1991) Metabolic stereoisomeric inversion of ibuprofen in mammals. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Protein Struct Mol Enzymol 1078:411–417
Zong Z, Qiu J, Tinmanee R, Kirsch LE (2012) Kinetic model for solid-state degradation of gabapentin. J Pharm Sci 101:2123–2133
Huang PQ, Huang YH, Geng H, Ye JL (2016) Metal-free C–H alkyliminylation and acylation of alkenes with secondary amides. Sci Rep 6:1–10
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Medical Biology Research Center, Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences, Kermanshah, Iran, and the Research and Computational Lab of Theoretical Chemistry and Nano Structures of Razi University Kermanshah-Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hadidi, S., Shiri, F. & Norouzibazaz, M. A computational study on phenibut lactamization mechanism and the pH effects on the process. Theor Chem Acc 139, 100 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00214-020-02617-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00214-020-02617-9