Abstract
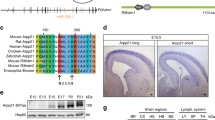
In this study, we investigate whether miRNAs located within “host” protein-coding genes may regulate the expression of their host genes. We find that 43 of 174 miRNAs encoded within RefSeq genes are predicted to target their host genes. Statistical analysis of this phenomenon suggests that gene auto-regulation via miRNAs may be under positive selective pressure. Our analysis also indicates that several of the 43 miRNAs have a much lower expectation of targeting their host genes by chance than others. Among these examples, we identify miR-128b:ARPP-21 (cyclic AMP-regulated phosphoprotein, 21 kD) as a case in which both the miRNA and the target site are also evolutionarily conserved. We provide experimental support for this miRNA:target interaction via reporter silencing assays, and present evidence that this isoform-specific gene auto-regulation has been preserved in vertebrate species in order to prevent detrimental consequences of ARPP-21 over-expression in brain.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Griffiths-Jones S, Grocock RJ, van Dongen S, Bateman A, Enright AJ (2006) miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D140–D144
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T (2001) Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science 294:853–858
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG, Bartel DP (2001) An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 294:858–862
Lee RC, Ambros V (2001) An extensive class of small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 294:862–864
Mourelatos Z, Dostie J, Paushkin S, Sharma A, Charroux B, Abel L, Rappsilber J, Mann M, Dreyfuss G (2002) miRNPs: a novel class of ribonucleoproteins containing numerous microRNAs. Genes Dev 16:720–728
Kloosterman WP, Plasterk RH (2006) The diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease. Dev Cell 11:441–450
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120:15–20
Paukku K, Silvennoinen O (2004) STATs as critical mediators of signal transduction and transcription: lessons learned from STAT5. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 15:435–455
Haberland M, Arnold MA, McAnally J, Phan D, Kim Y, Olson EN (2007) Regulation of HDAC9 gene expression by MEF2 establishes a negative-feedback loop in the transcriptional circuitry of muscle differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 27:518–525
Schefe JH, Menk M, Reinemund J, Effertz K, Hobbs RM, Pandolfi PP, Ruiz P, Unger T, Funke-Kaiser H (2006) A novel signal transduction cascade involving direct physical interaction of the renin/prorenin receptor with the transcription factor promyelocytic zinc finger protein. Circ Res 99:1355–1366
Tsang J, Zhu J, van Oudenaarden A (2007) MicroRNA-mediated feedback and feedforward loops are recurrent network motifs in mammals. Mol Cell 26:753–767
Baskerville S, Bartel DP (2005) Microarray profiling of microRNAs reveals frequent coexpression with neighboring miRNAs and host genes. RNA 11:241–247
Du G, Yonekubo J, Zeng Y, Osisami M, Frohman MA (2006) Design of expression vectors for RNA interference based on miRNAs and RNA splicing. FEBS J 273:5421–5427
Lin SL, Miller JD, Ying SY (2006) Intronic MicroRNA (miRNA). J Biomed Biotechnol 2006:26818
Lin SL, Ying SY (2006) Gene silencing in vitro and in vivo using intronic microRNAs. Methods Mol Biol 342:295–312
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB (2003) Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 115:787–798
Kiriakidou M, Nelson PT, Kouranov A, Fitziev P, Bouyioukos C, Mourelatos Z, Hatzigeorgiou A (2004) A combined computational-experimental approach predicts human microRNA targets. Genes Dev 18:1165–1178
Barad O, Meiri E, Avniel A, Aharonov R, Barzilai A, Bentwich I, Einav U, Gilad S, Hurban P, Karov Y, Lobenhofer EK, Sharon E, Shiboleth YM, Shtutman M, Bentwich Z, Einat P (2004) MicroRNA expression detected by oligonucleotide microarrays: system establishment and expression profiling in human tissues. Genome Res 14:2486–2494
Liu CG, Calin GA, Meloon B, Gamliel N, Sevignani C, Ferracin M, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Zupo S, Dono M, Alder H, Bullrich F, Negrini M, Croce CM (2004) An oligonucleotide microchip for genome-wide microRNA profiling in human and mouse tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9740–9744
Su AI, Wiltshire T, Batalov S, Lapp H, Ching KA, Block D, Zhang J, Soden R, Hayakawa M, Kreiman G, Cooke MP, Walker JR, Hogenesch JB (2004) A gene atlas of the mouse and human protein-encoding transcriptomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:6062–6067
Brene S, Lindefors N, Ehrlich M, Taubes T, Horiuchi A, Kopp J, Hall H, Sedvall G, Greengard P, Persson H (1994) Expression of mRNAs encoding ARPP-16/19, ARPP-21, and DARPP-32 in human brain tissue. J Neurosci 14:985–998
Ivkovic S, Ehrlich ME (1999) Expression of the striatal DARPP-32/ARPP-21 phenotype in GABAergic neurons requires neurotrophins in vivo and in vitro. J Neurosci 19:5409–5419
Caporaso GL, Bibb JA, Snyder GL, Valle C, Rakhilin S, Fienberg AA, Hemmings HC, Nairn AC, Greengard P (2000) Drugs of abuse modulate the phosphorylation of ARPP-21, a cyclic AMP-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in the basal ganglia. Neuropharmacology 39:1637–1644
Hipfel R, Hanes J, Von Der Kammer H, Pohlner J (2006) Camp-regulated phosphoprotein for diagnostic and therapeutic use in neurodegenerative diseases. Patent No. 20060024305
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Sempere LF, Freemantle S, Pitha-Rowe I, Moss E, Dmitrovsky E, Ambros V (2004) Expression profiling of mammalian microRNAs uncovers a subset of brain-expressed microRNAs with possible roles in murine and human neuronal differentiation. Genome Biol 5:R13
Shingara J, Keiger K, Shelton J, Laosinchai-Wolf W, Powers P, Conrad R, Brown D, Labourier E (2005) An optimized isolation and labeling platform for accurate microRNA expression profiling. RNA 11:1461–1470
Megraw M, Sethupathy P, Corda B, Hatzigeorgiou AG (2007) miRGen: a database for the study of animal microRNA genomic organization and function. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D149–D155
Kawahara Y, Zinshteyn B, Sethupathy P, Iizasa H, Hatzigeorgiou AG, Nishikura K (2007) Redirection of silencing targets by adenosine-to-inosine editing of miRNAs. Science 315:1137–1140
Brennecke J, Stark A, Russell RB, Cohen SM (2005) Principles of microRNA-target recognition. PLoS Biol 3:e85
Krek A, Grun D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg L, Epstein EJ, MacMenamin P, da Piedade I, Gunsalus KC, Stoffel M, Rajewsky N (2005) Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet 37:495–500
Acknowledgments
A.G.H., M.M., and P.S. were supported by an NSF Career Award (DBI-0238295). P.S. was also supported by a predoctoral NIH training grant (5T32GM008216). S.T.J. was supported by a University of Pennsylvania Research Foundation Grant. Q.H. and K.G. were supported by the Commonwealth Universal Research Enhancement Program, Pennsylvania Department of Health, and Wistar startup fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Dedicated to Professor Sandor Suhai on the occasion of his 65th birthday and published as part of the Suhai Festschrift Issue.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Megraw, M., Sethupathy, P., Gumireddy, K. et al. Isoform specific gene auto-regulation via miRNAs: a case study on miR-128b and ARPP-21. Theor Chem Acc 125, 593–598 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00214-009-0647-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00214-009-0647-4