Abstract.
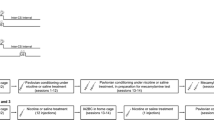
Rationale: Many recent theoretical approaches to drug-taking behavior feature a role for Pavlovian conditioning. Despite growing evidence for that role, the particular contributions of Pavlovian conditioning to self-administration are not clear. For example, few studies have addressed the effects of Pavlovian conditioning on the acquisition of self-administration. Objectives: The purpose of this study was to test the effect of Pavlovian conditioning with an environmental conditioned stimulus and an ethanol unconditioned stimulus on the acquisition of self-administration reinforced by ethanol. Methods: Rats were either given ethanol by gastric gavage in a distinctive context or in their home cage. All animals were then trained to bar press on a variable interval schedule for a sweetened ethanol solution in the distinctive context. Results: Animals that had received ethanol associated with the training context maintained a higher level of bar press behavior for ethanol as the reinforcing solution. This effect developed only after the first session and resulted from differences in response rates, but did not affect the rate of reinforcement. Conclusions: This study demonstrates that an environmental context signaling the effects of ethanol maintains a higher operant response rate when ethanol is used subsequently as a reinforcer. This finding replicates previous reports of Pavlovian conditioning effects on ethanol consumption. The specific pattern of results suggests that conditioned tolerance modifies the reinforcing impact of ethanol. Context conditioning with ethanol reduces the aversive impact of initial ethanol consumption and maintains the reinforcing value of the ethanol solution.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krank, M.D., O'Neill, S. Environmental context conditioning with ethanol reduces the aversive effects of ethanol in the acquisition of self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology 159, 258–265 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130100903
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130100903