Abstract
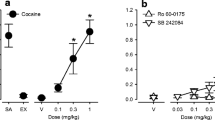
Rats were trained on a fixed ratio 10, food-reinforced schedule to recognize a discriminative stimulus (DS) elicited by the selective serotonin (5-HT) reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), citalopram (2.5 mg/kg, IP). The preferential, high efficacy agonist at 5-HT2C receptors, Ro60-0175, dose-dependently generalized to citalopram with an ED50 of 0.3 mg/kg, IP. Further, the selective 5-HT2C receptor antagonist, SB242,084, dose-dependently (ED50=0.1 mg/kg, IP) blocked the citalopram DS. These data suggest that 5-HT2C receptors are involved in the DS properties of the SSRI, citalopram, in rats. They do not, however, exclude a potential role of other 5-HT receptor types.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 15 October 1998 / Final version: 10 December 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Millan, M., Girardon, S. & Dekeyne, A. 5-HT2C receptors are involved in the discriminative stimulus effects of citalopram in rats. Psychopharmacology 142, 432–434 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050910
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050910