Abstract.
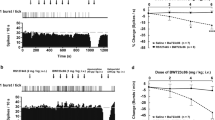
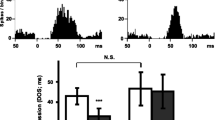
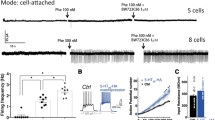
Rationale: Pindolol has been reported to shorten the onset of antidepressant action of selective serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) as well as to increase their efficacy. It has been postulated that pindolol enhances the antidepressant effect of SSRIs by blocking somatodendritic 5-HT1A autoreceptors, thus antagonizing the SSRI-induced feedback inhibition of midbrain 5-HT cell firing. A recent study, however, found that pindolol suppresses the firing rate of central 5-HT cells, suggesting that the compound possesses agonistic activity at 5-HT1A autoreceptors. Objectives: The purpose of the present study was to investigate if acute administration of (–)pindolol antagonizes the decrease in firing rate of dorsal raphe 5-HT cells produced by acute treatment with the SSRI citalopram. Methods: Extracellular recordings of single 5-HT neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus in anaesthetized rats. Results: Administration of 0.25 or 3.0 mg/kg (IV) (–)pindolol alone decreased the firing rate of a majority of the 5-HT cells studied, an effect that was reversed by the 5-HT1A receptor antagonist WAY100635 (0.1 mg/kg, IV). Neither 0.25 nor 3.0 mg/kg (–)pindolol reversed the citalopram (0.1–0.2 mg/kg, IV)-induced suppression of 5-HT cell activity, but produced a further decrease in firing rate. In contrast, WAY100635 (0.1 mg/kg) completely reversed this effect of citalopram. Yet, pretreatment with 3.0, but not 0.25 mg/kg (–)pindolol significantly attenuated the acute inhibitory effect of citalopram on serotonergic cell firing. Conclusions: The present findings support the previous notion that (–)pindolol possesses prominent agonistic activity at somatodendritic 5-HT1A autoreceptors, but also indicate that it may possess a weak antagonistic action at these receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arborelius, L., Linnér, L., Wallsten, C. et al. Partial 5-HT1A receptor agonist properties of (–)pindolol in combination with citalopram on serotonergic dorsal raphe cell firing in vivo. Psychopharmacology 151, 77–84 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130000470
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130000470