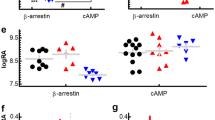
Abstract
Rationale
Dopamine D1 receptor agonists have been shown to improve working memory, but often have a non-monotonic (inverted-U) dose–response curve. One hypothesis is that this may reflect dose-dependent differential engagement of D1 signaling pathways, a mechanism termed functional selectivity or signaling bias.
Objectives and methods
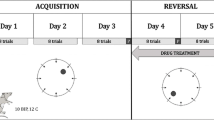
To test this hypothesis, we compared two D1 ligands with different signaling biases in a rodent T-maze alternation task. Both tested ligands (2-methyldihydrexidine and CY208243) have high intrinsic activity at cAMP signaling, but the former also has markedly higher intrinsic activity at D1-mediated recruitment of β-arrestin. The spatial working memory was assessed via the alternation behavior in the T-maze where the alternate choice rate quantified the quality of the memory and the duration prior to making a choice represented the decision latency.
Results
Both D1 drugs changed the alternate rate and the choice latency in a dose-dependent manner, albeit with important differences. 2-Methyldihydrexidine was somewhat less potent but caused a more homogeneous improvement than CY208243 in spatial working memory. The maximum changes in the alternate rate and the choice latency tended to occur at different doses for both drugs.
Conclusions
These data suggest that D1 signaling bias in these two pathways (cAMP vs β-arrestin) has complex effects on cognitive processes as assessed by T-maze alternation. Understanding these mechanisms should allow the identification or discovery of D1 agonists that can provide superior cognitive enhancement.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The raw data supporting the conclusion of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
References
Abbott B, Starr BS, Starr MS (1991) CY 208–243 behaves as a typical D-1 agonist in the reserpine-treated mouse. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 38:259–263
Andersen PH, Jansen JA (1990) Dopamine receptor agonists: selectivity and dopamine D1 receptor efficacy. Eur J Pharmacol 188:335–347
Arnsten AF, Cai JX, Murphy BL, Goldman-Rakic PS (1994) Dopamine D1 receptor mechanisms in the cognitive performance of young adult and aged monkeys. Psychopharmacology 116:143–151
Arnsten AF, Girgis RR, Gray DL, Mailman RB (2017) Novel dopamine therapeutics for cognitive deficits in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiat 81:67–77
Atkinson RC, Shiffrin RM (1971) The control of short-term memory. Sci Am 225:82–90
Barrett J, Livesey PJ (1985) Low level lead effects on activity under varying stress conditions in the developing rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 22:107–118
Beaulieu JM, Gainetdinov RR (2011) The physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 63:182–217
Cai JX, Arnsten AF (1997) Dose-dependent effects of the dopamine D1 receptor agonists A77636 or SKF81297 on spatial working memory in aged monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283:183–189
Dudchenko PA (2001) How do animals actually solve the T maze? Behav Neurosci 115:850–860
Dudchenko PA (2004) An overview of the tasks used to test working memory in rodents. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 28:699–709
Goldman-Rakic PS (1995) Cellular basis of working memory. Neuron 14:477–485
Huang C, Wu J, Liao R, Zhang W (2012) SKF83959, an agonist of phosphatidylinositol-linked D(1)-like receptors, promotes ERK1/2 activation and cell migration in cultured rat astrocytes. PLoS ONE 7:e49954
Huang X, Lewis MM, Van Scoy LJ, De Jesus S, Eslinger PJ, Arnold AC, Miller AJ, Fernandez-Mendoza J, Snyder B, Harrington W, Kong L, Wang X, Sun D, Delnomdedieu M, Duvvuri S, Mahoney SE, Gray DL, Mailman RB (2020) The D1/D5 dopamine partial agonist PF-06412562 in advanced-stage parkinson’s disease: a feasibility study. J Parkinsons Dis 10:1515–1527
Jiang T, Yu JT, Tan MS, Zhu XC, Tan L (2013) beta-Arrestins as potential therapeutic targets for Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 48:812–818
Karalunas SL, Huang-Pollock CL, Nigg JT (2012) Decomposing attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)-related effects in response speed and variability. Neuropsychology 26:684–694
Kenakin T (2012) The potential for selective pharmacological therapies through biased receptor signaling. Bmc Pharmacol Toxico 13:3
Klyubin I, Betts V, Welzel AT, Blennow K, Zetterberg H, Wallin A, Lemere CA, Cullen WK, Peng Y, Wisniewski T, Selkoe DJ, Anwyl R, Walsh DM, Rowan MJ (2008) Amyloid beta protein dimer-containing human CSF disrupts synaptic plasticity: prevention by systemic passive immunization. J Neurosci 28:4231–4237
Knoerzer TA, Watts VJ, Nichols DE, Mailman RB (1995) Synthesis and biological evaluation of a series of substituted benzo[a]phenanthridines as agonists at D1 and D2 dopamine receptors. J Med Chem 38:3062–3070
Leonard SK, Anderson CM, Lachowicz JE, Schulz DW, Kilts CD, Mailman RB (2003) Amygdaloid D1 receptors are not linked to stimulation of adenylate cyclase. Synapse (New York, NY) 50:320–333
Lewis MM, Van Scoy LJ, Mailman RB, De Jesus S, Hakun J, Kong L, Yang Y, Snyder B, Duvvuri S, Gray DL, Huang X (2022) Dopamine D1 agonist effects in late-stage Parkinson’s disease. medRxiv: 2022.04.30.22270885
Markstein R, Seiler MP, Jaton A, Briner U (1992) Structure activity relationship and therapeutic uses of dopaminergic ergots. Neurochem Int 20(Suppl):211S-214S
Miyamoto K, Osada T, Setsuie R, Takeda M, Tamura K, Adachi Y, Miyashita Y (2017) Causal neural network of metamemory for retrospection in primates. Science 355:188–193
Morellini F (2013) Spatial memory tasks in rodents: what do they model? Cell Tissue Res 354:273–286
Mu Q, Johnson K, Morgan PS, Grenesko EL, Molnar CE, Anderson B, Nahas Z, Kozel FA, Kose S, Knable M, Fernandes P, Nichols DE, Mailman RB, George MS (2007) A single 20 mg dose of the full D1 dopamine agonist dihydrexidine (DAR-0100) increases prefrontal perfusion in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 94:332–341
Mulder MJ, Bos D, Weusten JMH, van Belle J, van Dijk SC, Simen P, van Engeland H, Durston S (2010) Basic impairments in regulating the speed-accuracy tradeoff predict symptoms of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiat 68:1114–1119
Murphy BL, Arnsten AF, Jentsch JD, Roth RH (1996) Dopamine and spatial working memory in rats and monkeys: pharmacological reversal of stress-induced impairment. J Neurosci 16:7768–7775
Murray AM, Waddington JL (1990) New putative selective agonists at the D-1 dopamine receptor: behavioural and neurochemical comparison of CY 208–243 with SK&F 101384 and SK&F 103243. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 35:105–110
Paul CM, Magda G, Abel S (2009) Spatial memory: theoretical basis and comparative review on experimental methods in rodents. Behav Brain Res 203:151–164
Peck RW (2016) The right dose for every patient: a key step for precision medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov 15:145–146
Rosell DR, Zaluda LC, McClure MM, Perez-Rodriguez MM, Strike KS, Barch DM, Harvey PD, Girgis RR, Hazlett EA, Mailman RB, Abi-Dargham A, Lieberman JA, Siever LJ (2015) Effects of the D1 dopamine receptor agonist dihydrexidine (DAR-0100A) on working memory in schizotypal personality disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 40:446–453
Rutishauser U (2021) Metamemory: Rats know the strength of their memory. Curr Biol: CB 31:R1432-r1434
Schneider JS, Sun ZQ, Roeltgen DP (1994) Effects of dihydrexidine, a full dopamine D-1 receptor agonist, on delayed response performance in chronic low dose MPTP-treated monkeys. Brain Res 663:140–144
Tamm L, Narad ME, Antonini TN, O’Brien KM, Hawk LW Jr, Epstein JN (2012) Reaction time variability in ADHD: a review. Neurotherapeutics 9:500–508
Thathiah A, Horre K, Snellinx A, Vandewyer E, Huang Y, Ciesielska M, De Kloe G, Munck S, De Strooper B (2013) beta-arrestin 2 regulates Abeta generation and gamma-secretase activity in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Med 19:43–49
Urban JD, Clarke WP, von Zastrow M, Nichols DE, Kobilka B, Weinstein H, Javitch JA, Roth BL, Christopoulos A, Sexton PM, Miller KJ, Spedding M, Mailman RB (2007) Functional selectivity and classical concepts of quantitative pharmacology. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:1–13
Vallesi A, D’Agati E, Pasini A, Pitzianti M, Curatolo P (2013) Impairment in flexible regulation of speed and accuracy in children with ADHD. J Int Neuropsychol Soc: JINS 19:1016–1020
Van der Poel AM (1973) Registration of choice direction in a T-maze in rats under the influence of N-methyl-4-piperidyl cyclopentyl methylethynyl glycolate (PCMG), a centrally acting cholinolytic. Psychopharmacologia 31:271–290
Van der Poel AM (1974) The effect of some cholinolytic drugs on a number of behavioural parameters measured in the T-maze alternation test: dose-response relationships. Psychopharmacologia 37:45–58
Vijayraghavan S, Wang M, Birnbaum SG, Williams GV, Arnsten AF (2007) Inverted-U dopamine D1 receptor actions on prefrontal neurons engaged in working memory. Nat Neurosci 10:376–384
Wang M, Datta D, Enwright J, Galvin V, Yang ST, Paspalas C, Kozak R, Gray DL, Lewis DA, Arnsten AFT (2019) A novel dopamine D1 receptor agonist excites delay-dependent working memory-related neuronal firing in primate dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Neuropharmacology 150:46–58
Yang Y (2021) Functional selectivity of dopamine D1 receptor signaling: retrospect and prospect. Int J Mol Sci 22:11914
Yang Y, Mailman RB (2018) Strategic neuronal encoding in medial prefrontal cortex of spatial working memory in the T-maze. Behav Brain Res 343:50–60
Yang Y, Lee SM, Imamura F, Gowda K, Amin S, Mailman RB (2021) D1 dopamine receptors intrinsic activity and functional selectivity affect working memory in prefrontal cortex. Mol Psychiatry 26:645–655
Yang Y, Kocher SD, Lewis MM, Mailman RB (2022a) Dose-dependent regulation on prefrontal neuronal working memory by dopamine D1 agonists: evidence of receptor functional selectivity-related mechanisms. Front Neurosci 16:898051
Yang Y, Lewis MM, Huang X, Dokholyan NV, Mailman RB (2022b) Dopamine D(1) receptor-mediated beta-arrestin signaling: Insight from pharmacology, biology, behavior, and neurophysiology. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 148:106235
Yang Y, Lewis MM, Kong L, Mailman RB (2022c) A dopamine D(1) agonist versus methylphenidate in modulating prefrontal cortical working memory. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 382:88–99
Zahrt J, Taylor JR, Mathew RG, Arnsten AF (1997) Supranormal stimulation of D1 dopamine receptors in the rodent prefrontal cortex impairs spatial working memory performance. J Neurosci 17:8528–8535
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Xuemei Huang for her insight into these results and supportive comments during the study, and Susan Kocher and Natalia Loktionova for their invaluable technique support.
This work was supported by the Brain & Behavior Research Foundation Young Investigator Award (19469), Children’s Miracle Network Research Grant (2022–2023) and Trainee Grant (2023-2024), the National Institutes of Health (R01 NS105471, RF1 AG071675), and the Penn State Translational Brain Research Center.
Portions of this work were presented at the International Behavioral Neuroscience Society Annual Meeting in June 2023 (Niagara Falls, Ontario, Canada)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
RBM is a consultant for Cerevel Therapeutics and also is an inventor of D1-related technology. His conflicts of interest have been disclosed and are managed by the Pennsylvania State University. JW has a research contract with Supernus Pharmaceuticals and is a consultant for Ironshore Pharmaceuticals and Adlon Pharmaceuticals.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cimino, J.X., Zhou, M., Waxmonsky, J. et al. Characterization of behavioral changes in T-maze alternation from dopamine D1 agonists with different receptor coupling mechanisms. Psychopharmacology 240, 2187–2199 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-023-06440-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-023-06440-5