Abstract
Background
Diabetic encephalopathy is manifested by cognitive dysfunction. Salidroside, a nature compound isolated from Rhodiola rosea L, has the effects of anti-inflammatory and antioxidant, hypoglycemic and lipid-lowering, improving insulin resistance, inhibiting cell apoptosis, and protecting neurons. However, the mechanism by which salidroside alleviates neuronal degeneration and improves learning and memory impairment in diabetic mice remains unclear.
Objective
To investigate the effects and mechanisms of salidroside on hippocampal neurons in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice.
Materials and methods
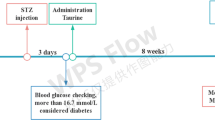
C57BL/6 mice were randomly divided into 4 groups to receive either sham (control group (CON)), diabetes mellitus (diabetes group (DM)), diabetes mellitus + salidroside (salidroside group (DM + SAL)), and diabetes mellitus + salidroside + phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor LY294002 (diabetes mellitus + salidroside + LY294002 group (DM + SAL + LY294002)). After 12 weeks of diabetes onset, the cognitive behaviors were tested using Morris water maze. The number of hippocampal neurons was detected by Nissl staining. The expressions of PI3K, p-PI3K, Akt, p-Akt, GSK-3β, p-GSK-3β, cleaved caspase-3, caspase-3, Bax, Bcl-2, MAP2, and SYN in the hippocampus were detected by Western blot. Moreover, the expression of MAP2 and SYN in the hippocampus was further confirmed by immunofluorescence staining.
Results
Salidroside increased the time of diabetic mice in the platform quadrant and reduced the escape latency of diabetic mice. Salidroside also increased the expression of p-PI3K, p-Akt, p-GSK-3β, MAP2, SYN, Bcl-2, while suppressed the expression of cleaved caspase-3, caspase3, and Bax in the DM + SAL group compared with the DM group (P < 0.05). The Nissl staining showed that the number of hippocampus neurons in the DM + SAL group was increased with the intact, compact, and regular arrangement, compared with the DM groups (P < 0.05). Interestingly, the protective effects of salidroside on diabetic cognitive dysfunction, hippocampal morphological alterations, and protein expressions were abolished by inhibition of PI3K with LY294002.
Conclusions
Salidroside exerts neuroprotective properties in diabetic cognitive dysfunction partly via activating the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal R, Tyagi E, Shukla R, Nath C (2011) Insulin receptor signaling in rat hippocampus: a study in STZ (ICV) induced memory deficit model. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 21:261–273
Biessels GJ, Despa F (2018) Cognitive decline and dementia in diabetes mellitus: mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat Rev Endocrinol 14:591–604
Cai L, Li W, Wang G, Guo L, Jiang Y, Kang YJ (2002) Hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis in mouse myocardium: mitochondrial cytochrome C-mediated caspase-3 activation pathway. Diabetes 51:1938–1948
Ebadi SA, Darvish P, Fard AJ, Lima BS, Ahangar OG (2018) Hypoglycemia and cognitive function in diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab Syndr 12:893–896
Endo H, Nito C, Kamada H, Nishi T, Chan PH (2006) Activation of the Akt/GSK3beta signaling pathway mediates survival of vulnerable hippocampal neurons after transient global cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26(12):1479–89
Fu H, Xu H, Chen H, Li Y, Li W, Zhu Q, Zhang Q, Yuan H, Liu F, Wang Q, Miao M, Shi X (2014) Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3 ameliorates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury via an energy-dependent mitochondrial mechanism. J Hepatol 61:816–824
Grech-Baran M, Syklowska-Baranek K, Pietrosiuk A (2015) Biotechnological approaches to enhance salidroside, rosin and its derivatives production in selected Rhodiola spp. in vitro cultures. Phytochem Rev 14:657–674
Han X, Min M, Wang J, Bao Z, Fan H, Li X, Adelusi TI, Zhou X, Yin X (2018) Quantitative profiling of neurotransmitter abnormalities in brain, cerebrospinal fluid, and serum of experimental diabetic encephalopathy male rat. J Neurosci Res 96:138–150
Hao X, Yuan J, Dong H (2019) Salidroside prevents diabetes-induced cognitive impairment via regulating the Rho pathway. Mol Med Rep 19:678–684
Haybaeck J, Llenos IC, Dulay RJ, Bettermann K, Miller CL, Walchli T, Frei K, Virgintino D, Rizzi M, Weis S (2012) Expression of nogo-a is decreased with increasing gestational age in the human fetal brain. Dev Neurosci 34:402–416
Jafari M, Ghadami E, Dadkhah T, Akhavan-Niaki H (2019) PI3k/AKT signaling pathway: Erythropoiesis and beyond. J Cell Physiol 234:2373–2385
Kamal A, Biessels GJ, Gispen WH, Ramakers GM (2006) Synaptic transmission changes in the pyramidal cells of the hippocampus in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus in rats. Brain Res 1073–1074:276–280
Karlsson TE, Smedfors G, Brodin AT, Aberg E, Mattsson A, Hogbeck I, Wellfelt K, Josephson A, Brene S, Olson L (2016) NgR1: a tunable sensor regulating memory formation, synaptic, and dendritic plasticity. Cereb Cortex 26:1804–1817
Kaytor M, Orr HT (2002) The GSK3β signaling cascade and neurodegenerative disease. 12: 275–278
Ketschek A, Gallo G (2010) Nerve growth factor induces axonal filopodia through localized microdomains of phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity that drive the formation of cytoskeletal precursors to filopodia. J Neurosci 30:12185–12197
Kuhad A, Chopra K (2007) Curcumin attenuates diabetic encephalopathy in rats: behavioral and biochemical evidences. Eur J Pharmacol 576:34–42
Lauretti E, Dincer O, Praticò D (2020) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1867:118664
Li HY, Wang XC, Xu YM, Luo NC, Luo S, Hao XY, Cheng SY, Fang JS, Wang Q, Zhang SJ, Chen YB (2018) Berberine improves diabetic encephalopathy through the SIRT1/ER stress pathway in db/db mice. Rejuvenation Res 21:200–209
Lim CS, Walikonis RS (2008) Hepatocyte growth factor and c-Met promote dendritic maturation during hippocampal neuron differentiation via the Akt pathway. Cell Signal 20:825–835
Liu S, Zheng M, Li Y, He L, Chen T (2020) The protective effect of Geniposide on diabetic cognitive impairment through BTK/TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway. Psychopharmacology 237:465–477
Lu J, Wu DM, Zheng YL, Hu B, Zhang ZF (2010) Purple sweet potato color alleviates D-galactose-induced brain aging in old mice by promoting survival of neurons via PI3K pathway and inhibiting cytochrome C-mediated apoptosis. Brain Pathol 20:598–612
Marder TJ, Flores VL, Bolo NR, Hoogenboom WS, Simonson DC, Jacobson AM, Foote SE, Shenton ME, Sperling RA, Musen G (2014) Task-induced brain activity patterns in type 2 diabetes: a potential biomarker for cognitive decline. Diabetes 63:3112–3119
Minaz N, Razdan R, Hammock BD, Goswami SK (2018) An inhibitor of soluble epoxide hydrolase ameliorates diabetes-induced learning and memory impairment in rats. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 136:84–89
Petrova M, Prokopenko S, Pronina E, Mozheyko E (2010) Diabetes type 2, hypertension and cognitive dysfunction in middle age women. J Neurol Sci 299:39–41
Rajab E, Abdeen Z, Hassan Z, Alsaffar Y, Mandeel M, Al Shawaaf F, Al-Ansari S, Kamal A (2014) Cognitive performance and convulsion risk after experimentally-induced febrile-seizures in rat. Int J Dev Neurosci 34:19–23
Samarghandian S, Azimi-Nezhad M, Samini F (2014) Ameliorative effect of saffron aqueous extract on hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and oxidative stress on diabetic encephalopathy in streptozotocin-induced experimental diabetes mellitus. Biomed Res Int 2014:920857
Shonesy BC, Thiruchelvam K, Parameshwaran K, Rahman EA, Karuppagounder SS, Huggins KW, Pinkert CA, Amin R, Dhanasekaran M, Suppiramaniam V (2012) Central insulin resistance and synaptic dysfunction in intracerebroventricular-streptozotocin injected rodents. Neurobiol Aging 33(430):e5-18
Sima AA (2010) Encephalopathies: the emerging diabetic complications. Acta Diabetol 47:279–293
Song L, Zhuang P, Lin M, Kang M, Liu H, Zhang Y, Yang Z, Chen Y, Zhang Y (2017) Urine metabonomics reveals early biomarkers in diabetic cognitive dysfunction. J Proteome Res 16:3180–3189
Shu Y, Zhang H, Kang T, Zhang JJ, Yang Y, Liu H, Zhang L (2013) PI3K/Akt signal pathway involved in the cognitive impairment caused by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. PLoS One 8(12):e81901
Tian H, Ding N, Guo M, Wang S, Wang Z, Liu H, Yang J, Li Y, Ren J, Jiang J, Li Z (2019) Analysis of learning and memory ability in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model using the Morris water maze. J Vis Exp
Tumminia A, Vinciguerra F, Parisi M, Frittitta L (2018) Type 2 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer’s disease: role of insulin signalling and therapeutic implications. Int J Mol Sci 19
Wang B, Jin X, Kuang X, Tian S (2017) Chronic administration of parecoxib exerts anxiolytic-like and memory enhancing effects and modulates synaptophysin expression in mice. BMC Anesthesiol 17:152
Wang S, He B, Hang W, Wu N, Xia L, Wang X, Zhang Q, Zhou X, Feng Z, Chen Q, Chen J (2018) Berberine alleviates Tau hyperphosphorylation and axonopathy-associated with diabetic encephalopathy via restoring PI3K/Akt/GSK3beta pathway. J Alzheimers Dis 65:1385–1400
Wu Y, Wang Y, Wu Y, Li T, Wang W (2020) Salidroside shows anticonvulsant and neuroprotective effects by activating the Nrf2-ARE pathway in a pentylenetetrazol-kindling epileptic model. Brain Res Bull 164:14–20
Xie Z, Lu H, Yang S, Zeng Y, Li W, Wang L, Luo G, Fang F, Zeng T, Cheng W (2020) Salidroside attenuates cognitive dysfunction in senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 (SAMP8) mice and modulates inflammation of the gut-brain axis. Front Pharmacol 11:568423
Xu ZP, Gan GS, Liu YM, Xiao JS, Liu HX, Mei B, Zhang JJ (2018) Adiponectin attenuates streptozotocin-induced Tau hyperphosphorylation and cognitive deficits by rescuing PI3K/Akt/GSK-3beta pathway. Neurochem Res 43:316–323
Xu N, Huang F, Jian C, Qin L, Lu F, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Zhang Q (2019) Neuroprotective effect of salidroside against central nervous system inflammation-induced cognitive deficits: a pivotal role of sirtuin 1-dependent Nrf-2/HO-1/NF-kappaB pathway. Phytother Res 33:1438–1447
Yu S, Liu M, Gu X, Ding F (2008) Neuroprotective effects of salidroside in the PC12 cell model exposed to hypoglycemia and serum limitation. Cell Mol Neurobiol 28:1067–1078
Zhang B, Li Q, Chu X, Sun S, Chen S (2016a) DrosophilaSalidroside reduces tau hyperphosphorylation via up-regulating GSK-3β phosphorylation in a tau transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Transl Neurodegen 5:21
Zhang B, Wang Y, Li H, Xiong R, Zhao Z, Chu X, Li Q, Sun S, Chen S (2016b) Neuroprotective effects of salidroside through PI3K/Akt pathway activation in Alzheimer’s disease models. Drug Des Dev Ther 10:1335–1343
Zhang W, He H, Song H, Zhao J, Li T, Wu L, Zhang X, Chen J (2016c) Neuroprotective effects of salidroside in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: involvement of the PI3K/Akt/GSK3beta pathway. Parkinsons Dis 2016:9450137
Zhang J, Chen C, Hua S, Liao H, Wang M, Xiong Y, Cao F (2017) An updated meta-analysis of cohort studies: diabetes and risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 124:41–47
Zhang Y, Huang NQ, Yan F, Jin H, Zhou SY, Shi JS, Jin F (2018) Diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer’s disease: GSK-3β as a potential link. Behav Brain Res 339:57–65
Zhang W, Zhao L, Zhang J, Li P, Lv Z (2021) Metformin improves cognitive impairment in diabetic mice induced by a combination of streptozotocin and isoflurane anesthesia. Bioengineered 12:10982–10993
Zhao S, Fu J, Liu X, Wang T, Zhang J, Zhao Y (2012) Activation of Akt/GSK-3beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway is involved in survival of neurons after traumatic brain injury in rats. Neurol Res 34:400
Zhong Z, Han J, Zhang J, Xiao Q, Hu J, Chen L (2018) Pharmacological activities, mechanisms of action, and safety of salidroside in the central nervous system. Drug Des Devel Ther 12:1479–1489
Zhuang W, Yue L, Dang X, Chen F, Gong Y, Lin X, Luo Y (2019) Rosenroot (Rhodiola): potential applications in aging-related diseases. Aging Dis 10:134–146
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge and appreciate our teachers and classmates for their valuable efforts and comments on this paper.
Funding
This study was supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2017M612870) and Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (No. 2019-ZD-0807).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Compliance with ethical standards
All experiments were performed according to the NIH guidelines and approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Department of Jinzhou Medical University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, XH., Zuo, ZF., Meng, L. et al. Neuroprotective effect of salidroside on hippocampal neurons in diabetic mice via PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway. Psychopharmacology 240, 1865–1876 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-023-06373-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-023-06373-z