Abstract
Rationale
Disorders caused by total sleep deprivation can be modulated by the administration of growth hormone, which could affect the expression of microRNA-9 and dopamine D2 receptor expressions followed by improvement in the hippocampal synaptic potential, spatial cognition, and inflammation in rats.
Objectives
The present study aimed to elucidate the putative effects of exogenous growth hormone (GH) against total sleep deprivation (TSD)-induced learning and memory dysfunctions and possible involved mechanisms.
Methods
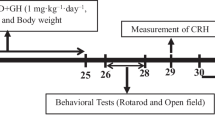
To induce TSD, rats were housed in homemade special cages equipped with stainless steel wire conductors to induce general and inconsistent TSD. They received a mild repetitive electric shock to their paws every 10 min for 21 days. GH (1 mg/kg, sc) was administered to adult young male rats once daily for 21-day-duration induction of TSD. Spatial learning and memory performance, inflammatory status, microRNA-9 (miR-9) expression, dopamine D2 receptor (DRD2) protein level, and hippocampal histological changes were assayed at scheduled times after TSD.
Results
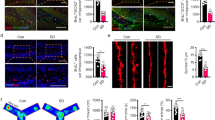
The results indicated that TSD impaired spatial cognition, increased TNF-α, decreased level of miR-9, and increased DRD2 levels. Treatment with exogenous GH improved spatial cognition, decreased TNF-α, increased level of miR-9, and decreased DRD2 levels after TSD.
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that GH may play a key role in the modulation of learning and memory disorders as well as the ameliorating abnormal DRD2-related functional disorders associated with miR-9 in TSD.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abraham WC, Jones OD, Glanzman DL (2019) Is plasticity of synapses the mechanism of long-term memory storage? NPJ Sci Learn 4:1–10
Alhaider IA, Aleisa AM, Tran TT, Alkadhi KA (2011) Sleep deprivation prevents stimulation-induced increases of levels of P-CREB and BDNF: protection by caffeine. Mol Cell Neurosci 46:742–751
Andiran N, Yordam N (2007) TNF-α levels in children with growth hormone deficiency and the effect of long-term growth hormone replacement therapy. Growth Horm IGF Res 17:149–153
Barf R, Van Dijk G, Scheurink A, Hoffmann K, Novati A, Hulshof H, Fuchs E, Meerlo P (2012) Metabolic consequences of chronic sleep restriction in rats: changes in body weight regulation and energy expenditure. Physiol Behav 107:322–328
Borbély AA, Daan S, Wirz-Justice A, Deboer T (2016) The two-process model of sleep regulation: a reappraisal. J Sleep Res 25:131–143
Bozzola M, De Amici M, Zecca M, Schimpff RM, Rapaport R (1998) Modulating effect of human growth hormone on tumour necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β. Eur J Endocrinol 138:640–643
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brandenberger G, Gronfier C, Chapotot F, Simon C, Piquard F (2000) Effect of sleep deprivation on overall 24 h growth-hormone secretion. The Lancet 356:1408
Campbell I, Guinan M, Horowitz J (2002) Sleep deprivation impairs long-term potentiation in rat hippocampal slices. J Neurophysiol 88:1073–1076
Cespuglio R, Gomez M, Faradji H, Jouvet M (1982) Alterations in the sleep-waking cycle induced by cooling of the locus coeruleus area. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 54:570–578
Chennaoui M, Gomez-Merino D, Drogou C, Geoffroy H, Dispersyn G, Langrume C, Ciret S, Gallopin T, Sauvet F (2015) Effects of exercise on brain and peripheral inflammatory biomarkers induced by total sleep deprivation in rats. J Inflamm 12:1–10
Chow JC, Ling PR, Qu Z, Laviola L, Ciccarone A, Bistrian BR, Smith RJ (1996) Growth hormone stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of JAK2 and STAT5, but not insulin receptor substrate-1 or SHC proteins in liver and skeletal muscle of normal rats in vivo. Endocrinology 137:2880–2886
Davis CJ, Harding JW, Wright JW (2003) REM sleep deprivation-induced deficits in the latency-to-peak induction and maintenance of long-term potentiation within the CA1 region of the hippocampus. Brain Res 973:293–297
Deepak D, Daousi C, Javadpour M, Clark D, Perry Y, Pinkney J, Macfarlane I (2010) The influence of growth hormone replacement on peripheral inflammatory and cardiovascular risk markers in adults with severe growth hormone deficiency. Growth Horm IGF Res 20:220–225
Diekelmann S, Born J (2010) The memory function of sleep. Nat Rev Neurosci 11:114–126
Dienes Z (2014) Using Bayes to get the most out of non-significant results. Front Psychol 5:781
Djuranovic S, Nahvi A, Green R (2012) miRNA-mediated gene silencing by translational repression followed by mRNA deadenylation and decay. Science 336:237–240
Everson CA, Crowley WR (2004) Reductions in circulating anabolic hormones induced by sustained sleep deprivation in rats. Am J Physiol-Endocrinol Metab 286:E1060–E1070
Fan J, Char D, Bagby GJ, Gelato MC, Lang CH (1995) Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding proteins by tumor necrosis factor. Am J Physiol-Regul, Integr Comp Physiol 269:R1204–R1212
Fifel K, Meijer JH, Deboer T (2018) Long-term effects of sleep deprivation on neuronal activity in four hypothalamic areas. Neurobiol Dis 109:54–63
Gaine ME, Chatterjee S, Abel T (2018) Sleep deprivation and the epigenome. Front Neural Circ 12:14
Hascup KN, Lynn MK, Fitzgerald PJ, Randall S, Kopchick JJ, Boger HA, Bartke A, Hascup ER (2017) Enhanced cognition and hypoglutamatergic signaling in a growth hormone receptor knockout mouse model of successful aging. J Gerontol Series A: Biomed Sci Med Sci 72:329–337
He B, Peng H, Zhao Y, Zhou H, Zhao Z (2011) Modafinil treatment prevents REM sleep deprivation-induced brain function impairment by increasing MMP-9 expression. Brain Res 1426:38–42
He X, Yan T, Chen R, Ran D (2012) Acute effects of electro-acupuncture (EA) on hippocampal long term potentiation (LTP) of perforant path-dentate gyrus granule cells synapse related to memory. Acupunct Electro-Ther Res 37:89–101
Jaworek J, Leja-Szpak A, Dembiński A, Tomaszewska R, Szklarczyk J, Kot M, Nawrot-Porąbka K, Bonior J, Warzecha Z, Pawlik WW (2009) Involvement of sensory nerves in the protective effect of growth hormone on acute pancreatitis. Growth Horm IGF Res 19:517–522
Jørgensen JO, Møller L, Krag M, Billestrup N, Christiansen JS (2007) Effects of growth hormone on glucose and fat metabolism in human subjects. Endocrinol Metab Clin 36:75–87
Kim EY, Mahmoud GS, Grover LM (2005) REM sleep deprivation inhibits LTP in vivo in area CA1 of rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 388:163–167
Kim E, Grover LM, Bertolotti D, Green TL (2010) Growth hormone rescues hippocampal synaptic function after sleep deprivation. Am J Physiol-Regul, Integr Comp Physiol 298:R1588–R1596
Kimura F, Tsai C (1984) Ultradian rhythm of growth hormone secretion and sleep in the adult male rat. J Physiol 353:305–315
Koban M, Swinson KL (2005) Chronic REM-sleep deprivation of rats elevates metabolic rate and increases UCP1 gene expression in brown adipose tissue. Am J Physiol-Endocrinol Metab 289:E68–E74
Lang CH, Fan J, Wojnar MM, Vary TC, Cooney R (1998) Role of central IL-1 in regulating peripheral IGF-I during endotoxemia and sepsis. Am J Physiol-Regul, Integr Comp Physiol 274:R956–R962
Lelbach A, Scharf J-G, Ramadori G (2001) Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I and of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1,-3 and-4 in cocultures of rat hepatocytes and Kupffer cells by interleukin-6. J Hepatol 35:558–567
Liu S-C, Hu W-Y, Zhang W-Y, Yang L, Li Y, Xiao Z-C, Zhang M, He Z-Y (2019) Paeoniflorin attenuates impairment of spatial learning and hippocampal long-term potentiation in mice subjected to chronic unpredictable mild stress. Psychopharmacology 236:2823–2834
Lu H-J (2021) β-adrenergic receptor activity in the hippocampal dentate gyrus participates in spatial learning and memory impairment in sleep-deprived rats. Exp Neurobiol 30:144
Luyster FS, Strollo PJ, Zee PC, Walsh JK (2012) Sleep: a health imperative. Sleep 35:727–734
Lyu X, Wang G, Pi Z, Wu L (2020) Acute sleep deprivation leads to growth hormone (GH) resistance in rats. Gen Comp Endocrinol 296:113545
Manchanda S, Singh H, Kaur T, Kaur G (2018) Low-grade neuroinflammation due to chronic sleep deprivation results in anxiety and learning and memory impairments. Mol Cell Biochem 449:63–72
Mavanji V, Teske JA, Billington CJ, Kotz CM (2013) Partial sleep deprivation by environmental noise increases food intake and body weight in obesity-resistant rats. Obesity 21:1396–1405
McDermott CM, LaHoste GJ, Chen C, Musto A, Bazan NG, Magee JC (2003) Sleep deprivation causes behavioral, synaptic, and membrane excitability alterations in hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 23:9687–9695
McDermott CM, Hardy MN, Bazan NG, Magee JC (2006) Sleep deprivation-induced alterations in excitatory synaptic transmission in the CA1 region of the rat hippocampus. J Physiol 570:553–565
Møller N, Copeland KC, Nair KS (2007) Growth hormone effects on protein metabolism. Endocrinol Metab Clin 36:89–100
Monti JM, Monti D (2007) The involvement of dopamine in the modulation of sleep and waking. Sleep Med Rev 11:113–133
Moreira KM, Ferreira TL, Hipolide DC, Fornari RV, Tufik S, Oliveira MGM (2010) Modafinil prevents inhibitory avoidance memory deficit induced by sleep deprivation in rats. Sleep 33:990–993
Motivala SJ, Irwin MR (2007) Sleep and immunity: cytokine pathways linking sleep and health outcomes. Curr Dir Psychol Sci 16:21–25
Mr I (2006) Wang M. Campomayor CO. Collado-Hidalgo A. Cole S. Sleep deprivation and activation of morning levels of cellular and genomic markers of inflammation. Arch Intern Med 166:1756–1762
Musah S, DeJarnett N, Hoyle GW (2012) Tumor necrosis factor-α mediates interactions between macrophages and epithelial cells underlying proinflammatory gene expression induced by particulate matter. Toxicology 299:125–132
Naidoo N, Giang W, Galante RJ, Pack AI (2005) Sleep deprivation induces the unfolded protein response in mouse cerebral cortex. J Neurochem 92:1150–1157
Nunes G Jr, Tufik S, Nobrega JN (1994) Autoradiographic analysis of D1 and D2 dopaminergic receptors in rat brain after paradoxical sleep deprivation. Brain Res Bull 34:453–456
Nyberg F, Hallberg M (2013) Growth hormone and cognitive function. Nat Rev Endocrinol 9:357–365
Obál F, Fang J, Taishi P, Kacsóh B, Gardi J, Krueger JM (2001) Deficiency of growth hormone-releasing hormone signaling is associated with sleep alterations in the dwarf rat. J Neurosci 21:2912–2918
Park S-E, Dantzer R, Kelley KW, McCusker RH (2011) Central administration of insulin-like growth factor-I decreases depressive-like behavior and brain cytokine expression in mice. J Neuroinflammation 8:1–14
Piérard C, Liscia P, Philippin J-N, Mons N, Lafon T, Chauveau F, Van Beers P, Drouet I, Serra A, Jouanin J-C (2007) Modafinil restores memory performance and neural activity impaired by sleep deprivation in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 88:55–63
Qu W-M, Xu X-H, Yan M-M, Wang Y-Q, Urade Y, Huang Z-L (2010) Essential role of dopamine D2 receptor in the maintenance of wakefulness, but not in homeostatic regulation of sleep, in mice. J Neurosci 30:4382–4389
Redwine L, Hauger RL, Gillin JC, Irwin M (2000) Effects of sleep and sleep deprivation on interleukin-6, growth hormone, cortisol, and melatonin levels in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:3597–3603
Rosenfeld R (2001) Growth hormone deficiency in children. In: De Groot LJ, Jameson JL (eds) Endocrinology WB Saunders, pp 503–519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-008-0105-7
Safahani M, Amani R, Aligholi H, Sarkaki A, Badavi M, Moghaddam AZ, Haghighizadeh M (2011) Effect of different doses of soy isoflavones on spatial learning and memory in ovariectomized rats. Basic Clin Neurosci 2:12
Saleh Ahangar M (2014) Prevalence of sleep disorders among medical students of Babol University of Medical Sciences, Iran, 2013. J Babol Univ Med Sci 16:69–74
Saygin M, Ozguner M, Onder O, Doguc D, Ilhan I, Peker Y (2017) The impact of sleep deprivation on hippocampal-mediated learning and memory in rats. Bratislavske lekarske listy 118:408–416
Sesmilo G, Biller BM, Llevadot J, Hayden D, Hanson G, Rifai N, Klibanski A (2000) Effects of growth hormone administration on inflammatory and other cardiovascular risk markers in men with growth hormone deficiency: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. Ann Intern Med 133:111–122
Siegel JM (2004) The neurotransmitters of sleep. J Clin Psychiatry 65:4–7
Tartar JL, Ward CP, McKenna JT, Thakkar M, Arrigoni E, McCarley RW, Brown RE, Strecker RE (2006) Hippocampal synaptic plasticity and spatial learning are impaired in a rat model of sleep fragmentation. Eur J Neurosci 23:2739–2748
van Enkhuizen J, Acheson D, Risbrough V, Drummond S, Geyer MA, Young JW (2014) Sleep deprivation impairs performance in the 5-choice continuous performance test: similarities between humans and mice. Behav Brain Res 261:40–48
Vickers NJ (2017) Animal communication: when i’m calling you, will you answer too? Curr Biol 27:R713–R715
Volk DW, Lewis DA (2010) Prefrontal cortical circuits in schizophrenia. Behav Neurobiol Schizophr Treat :485–508. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/7854_2010_44
Wang P, Li N, Li J-S, Li W-Q (2002) The role of endotoxin, TNF-α, and IL-6 in inducing the state of growth hormone insensitivity. World J Gastroenterol 8:531
Wen R, Chen X, Huang D, Chen M, Liu Y (2015) Sleep deprivation increased Dopamine D2 receptor expression through downregulation of miR-9 2015 7th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education (ITME). IEEE, pp 239–242. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7429137
Wisor JP, Nishino S, Sora I, Uhl GH, Mignot E, Edgar DM (2001) Dopaminergic role in stimulant-induced wakefulness. J Neurosci 21:1787–1794
Wu X, Li D, Liu J, Diao L, Ling S, Li Y, Gao J, Fan Q, Sun W, Li Q (2017) Dammarane sapogenins ameliorates neurocognitive functional impairment induced by simulated long-duration spaceflight. Front Pharmacol 8:315
Yi C, Cao Y, Mao S, Liu H, Ji L, Xu S, Zhang M, Huang Y (2009) Recombinant human growth hormone improves survival and protects against acute lung injury in murine Staphylococcus aureus sepsis. Inflamm Res 58:855–862
Yoo AS, Staahl BT, Chen L, Crabtree GR (2009) MicroRNA-mediated switching of chromatin-remodelling complexes in neural development. Nature 460:642–646
Yuva-Aydemir Y, Simkin A, Gascon E, Gao F-B (2011) MicroRNA-9: functional evolution of a conserved small regulatory RNA. RNA Biol 8:557–564
Zagaar MA, Dao AT, Alhaider IA, Alkadhi KA (2018) Correction to: prevention by regular exercise of acute sleep deprivation-induced impairment of late phase LTP and related signaling molecules in the dentate gyrus. Mol Neurobiol 55:902–902
Zisapel N (2007) Sleep and sleep disturbances: biological basis and clinical implications. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:1174–1186
Acknowledgements
This article was extracted from Mrs. Parisa Arvin’s Ph.D. thesis (APRC-0005) and its complementary research project (APRC-01-07) in combination. These research works were approved and carried out at Medical Basic Sciences Research Institute, Persian Gulf Physiology Research Center, and were financially supported by the Vice Chancellor of Research, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Parisa Arvin: conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, resources, writing of the original draft, and project administration; Samireh Ghafouri: validation and resources; Kowsar Bavarsad: resources and data curation; Somayeh Hajipour: validation and writing of the original draft; Seyed Esmaeil Khoshnam: writing, review, and editing; Esrafil Mansouri: resources and data curation; Alireza Sarkaki: conceptualization, methodology, writing, review, editing, and project administration; Yaghoob Farbood: writing, review, editing, and supervision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The ethics governing the use and conduct of experiments on animals were strictly observed, and all procedures used in this study were done according to National Institute of Health (NIH) and were approved by the Local Ethics Committee of Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences (AJUMS) (Ethic codes: IR.AJUMS.REC.1400.163, IR.AJUMS.ABHC.REC.1401-041).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The corresponding author has the permission from the authors to publish the details of the study work.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Arvin, P., Ghafouri, S., Bavarsad, K. et al. Exogenous growth hormone administration during total sleep deprivation changed the microRNA-9 and dopamine D2 receptor expressions followed by improvement in the hippocampal synaptic potential, spatial cognition, and inflammation in rats. Psychopharmacology 240, 1299–1312 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-023-06369-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-023-06369-9