Abstract
Rationale
Animal models of compulsive drug use that continues despite negative consequences can be used to investigate the neural mechanisms of addiction. However, models of punished or aversion-resistant opioid self-administration are notably lacking.
Objectives
We sought to develop an aversion-resistant, oral fentanyl self-administration paradigm.
Methods
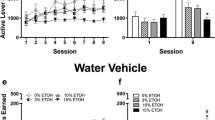
In Experiment 1, C57BL/6J male and female, adult mice consumed fentanyl (10 μg/mL) in a two-bottle drinking in the dark task and escalating concentrations of quinine were added to the bottles. In Experiment 2, mice were trained to administer oral fentanyl (10 μg/mL) in an operant response task. Quinine was next added to the fentanyl solution in escalating concentrations. In Experiment 3, mice were trained to respond for oral fentanyl or fentanyl adulterated with 500 μM quinine on every session. In Experiment 4, mice were trained to respond for a 1% sucrose solution before introduction of quinine.
Results
Quinine reduced two-bottle choice consumption in males but not in females. Both sexes demonstrated the ability to detect the selected concentrations of quinine in fentanyl. In the operant chamber, mice responded robustly for oral fentanyl but introduction of quinine at any stage of training was insufficient to reduce responding. In contrast, quinine reduced responding for sucrose at concentrations above 250 μM.
Conclusions
Mice will respond for and consume oral fentanyl in both a two-bottle choice and an operant response task. Quinine is detectable in fentanyl but mice will continue to respond for and consume fentanyl with quinine in both paradigms. These data support the use of these models in behavioral studies of compulsive-like opioid use.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belknap JK, Crabbe JC, Riggan J, O’Toole LA (1993) Voluntary consumption of morphine in 15 inbred mouse strains. Psychopharmacology 112:352–358
Blegen MB, Daniel da Silva ES, Bock R, Morisot N, Ron D, Alvarez VA (2018) Alcohol operant self-administration: investigating how alcohol seeking behaviors predicts drinking in mice using two operant approaches. Alcohol 67:23–36
Carlson KR (1989) Taste vs. CNS effects in voluntary oral opiate intake: studies with a novel device and technique. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 34:419–423
Chen BT, Yau H-J, Hatch C, Kusumoto-Yoshida I, Cho SL, Hopf FW, Bonci A (2013) Rescuing cocaine-induced prefrontal cortex hypoactivity prevents compulsive cocaine seeking. Nature 496:359–362
Cicero TJ, Aylward SC, Meyer ER (2003) Gender differences in the intravenous self-administration of mu opiate agonists. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 74:541–549
Darevsky D, Gill TM, Vitale KR, Hu B, Wegner SA, Hopf FW (2019) Drinking despite adversity: behavioral evidence for a head down and push strategy of conflict-resistant alcohol drinking in rats. Addict Biol 24:426–437
Deroche-Gamonet V, Belin D, Piazza PV (2004) Evidence for addiction-like behavior in the rat. Science 305:1014–1017
Eastwood EC, Phillips TJ (2014) Opioid sensitivity in mice selectively bred to consume or not consume methamphetamine. Addict Biol 19:370–379
Enga RM, Jackson A, Damaj MI, Beardsley PM (2016) Oxycodone physical dependence and its oral self-administration in C57BL/6J mice. Eur J Pharmacol 789:75–80
Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (2005) Neural systems of reinforcement for drug addiction: from actions to habits to compulsion. Nat Neurosci 8:1481–1489
Finlay JM, Jakubovic A, Phillips AG, Fibiger HC (1988) Fentanyl-induced conditional place preference: lack of associated conditional neurochemical events. Psychopharmacology 96:534–540
Forgie ML, Beyerstein BL, Alexander BK (1988) Contributions of taste factors and gender to opioid preference in C57BL and DBA mice. Psychopharmacology 95:237–244
Fujii K, Koshidaka Y, Adachi M, Takao K (2019) Effects of chronic fentanyl administration on behavioral characteristics of mice. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep 39:17–35
Fulenwider HD, Nennig SE, Price ME, Hafeez H, Schank JR (2019) Sex differences in aversion-resistant ethanol intake in mice. Alcohol Alcohol 54:345–352
Grim TW, Schmid CL, LaPrairie RB, Park J-H, Lin L, Cameron MD, Bohn LM (2017) Preference, dependence, and pharmacokinetic outcomes in an opioid two bottle choice paradigm. FASEB J 31:1059.1–1059.1
Grim TW, Park SJ, Schmid CL, Laprairie RB, Cameron M, Bohn LM (2018) The effect of quinine in two bottle choice procedures in C57BL6 mice: opioid preference, somatic withdrawal, and pharmacokinetic outcomes. Drug Alcohol Depend 191:195–202
Halladay LR, Kocharian A, Holmes A (2017) Mouse strain differences in punished ethanol self-administration. Alcohol 58:83–92
Halladay LR, Kocharian A, Piantadosi PT, Authement ME, Lieberman AG, Spitz NA, Coden K, Glover LR, Costa VD, Alvarez VA, Holmes A (2020) Prefrontal regulation of punished ethanol self-administration. Biol Psychiatry 87:967–978
Holtz NA, Carroll ME (2015) Cocaine self-administration punished by intravenous histamine in adolescent and adult rats. Behav Pharmacol 26:393–397
Holtz NA, Anker JJ, Regier PS, Claxton A, Carroll ME (2013) Cocaine self-administration punished by i.v. histamine in rat models of high and low drug abuse vulnerability: effects of saccharin preference, impulsivity, and sex. Physiol Behav 122:32–38
Hopf FW, Chang S-J, Sparta DR, Bowers MS, Bonci A (2010) Motivation for alcohol becomes resistant to quinine adulteration after 3 to 4 months of intermittent alcohol self-administration. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 34:1565–1573
Kenny PJ (2007) Brain reward systems and compulsive drug use. Trends Pharmacol Sci 28:135–141
Klein LC (2001) Effects of adolescent nicotine exposure on opioid consumption and neuroendocrine responses in adult male and female rats. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 9:251–261
Klein LC, Popke EJ, Grunberg NE (1997) Sex differences in effects of predictable and unpredictable footshock on fentanyl self-administration in rats. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 5:99–106
Kolodny A, Courtwright DT, Hwang CS, Kreiner P, Eadie JL, Clark TW, Alexander GC (2015) The prescription opioid and heroin crisis: a public health approach to an epidemic of addiction. Annu Rev Public Health 36:559–574
Lei K, Wegner SA, Yu J-H, Simms JA, Hopf FW (2016) A single alcohol drinking session is sufficient to enable subsequent aversion-resistant consumption in mice. Alcohol 55:9–16
Lesscher HMB, van Kerkhof LWM, Vanderschuren LJMJ (2010) Inflexible and indifferent alcohol drinking in male mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 34:1219–1225
Lewis SR, Ahmed S, Dym C, Khaimova E, Kest B, Bodnar RJ (2005) Inbred mouse strain survey of sucrose intake. Physiol Behav 85:546–556
Limpens JHW, Damsteegt R, Broekhoven MH, Voorn P, Vanderschuren LJMJ (2015) Pharmacological inactivation of the prelimbic cortex emulates compulsive reward seeking in rats. Brain Res 1628:210–218
Lüscher C, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2020) The transition to compulsion in addiction. Nat Rev Neurosci 21:247–263
Miller DK, Nation JR (1997) Chronic cadmium exposure attenuates the conditioned reinforcing properties of morphine and fentanyl. Brain Res 776:162–169
Minami K, Hasegawa M, Ito H, Nakamura A, Tomii T, Matsumoto M, Orita S, Matsushima S, Miyoshi T, Masuno K, Torii M, Koike K, Shimada S, Kanemasa T, Kihara T, Narita M, Suzuki T, Kato A (2009) Morphine, oxycodone, and fentanyl exhibit different analgesic profiles in mouse pain models. J Pharmacol Sci 111:60–72
Mucha RF, Herz A (1985) Motivational properties of kappa and mu opioid receptor agonists studied with place and taste preference conditioning. Psychopharmacology 86:274–280
Panlilio LV, Thorndike EB, Schindler CW (2003) Reinstatement of punishment-suppressed opioid self-administration in rats: an alternative model of relapse to drug abuse. Psychopharmacology 168:229–235
Panlilio LV, Thorndike EB, Schindler CW (2005) Lorazepam reinstates punishment-suppressed remifentanil self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology 179:374–382
Peacock A, Leung J, Larney S, Colledge S, Hickman M, Rehm J, Giovino GA, West R, Hall W, Griffiths P, Ali R, Gowing L, Marsden J, Ferrari AJ, Grebely J, Farrell M, Degenhardt L (2018) Global statistics on alcohol, tobacco and illicit drug use: 2017 status report. Addiction 113:1905–1926
Peck JA, Galaj E, Eshak S, Newman KL, Ranaldi R (2015) Environmental enrichment induces early heroin abstinence in an animal conflict model. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 138:20–25
Pelloux Y, Murray JE, Everitt BJ (2013) Differential roles of the prefrontal cortical subregions and basolateral amygdala in compulsive cocaine seeking and relapse after voluntary abstinence in rats. Eur J Neurosci 38:3018–3026
Pelz WE, Whitney G, Smith JC (1973) Genetic influences on saccharin preference of mice. Physiol Behav 10:263–265
Phillips AG, McGovern DJ, Lee S, Ro K, Huynh DT, Elvig SK, Fegan KN, Root DH (2019) Oral prescription opioid-seeking behavior in male and female mice. Addict Biol 25:e12828
Radke AK, Nakazawa K, Holmes A (2015) Cortical GluN2B deletion attenuates punished suppression of food reward-seeking. Psychopharmacology 232:3753–3761
Radke AK, Jury NJ, Kocharian A, Marcinkiewcz CA, Lowery-Gionta EG, Pleil KE, McElligott ZA, McKlveen JM, Kash TL, Holmes A (2017) Chronic EtOH effects on putative measures of compulsive behavior in mice. Addict Biol 22:423–434
Radke AK, Held IT, Sneddon EA, Riddle CA, Quinn JJ (2019) Additive influences of acute early life stress and sex on vulnerability for aversion-resistant alcohol drinking. Addict Biol 25:e12829
Rawls SM, Benamar K (2011) Effects of opioids, cannabinoids, and vanilloids on body temperature. Front Biosci 3:822–845
Rawls SM, Adler MW, Gaughan JP, Baron A, Geller EB, Cowan A (2003) NMDA receptors modulate morphine-induced hyperthermia. Brain Res 984:76–83
Savić Vujović KR, Vučković S, Srebro D, Ivanović M, Došen-Mićović L, Vučetić Č, Džoljić E, Prostran M (2013) A comparison of the antinociceptive and temperature responses to morphine and fentanyl derivatives in rats. Arch Pharm Res 36:501–508
Scholl L, Seth P, Kariisa M, Wilson N, Baldwin G (2018) Drug and opioid-involved overdose deaths - United States, 2013-2017. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 67:1419–1427
Seif T, Chang S-J, Simms JA, Gibb SL, Dadgar J, Chen BT, Harvey BK, Ron D, Messing RO, Bonci A, Hopf FW (2013) Cortical activation of accumbens hyperpolarization-active NMDARs mediates aversion-resistant alcohol intake. Nat Neurosci 16:1094–1100
Shaham Y, Alvares K, Nespor SM, Grunberg NE (1992) Effect of stress on oral morphine and fentanyl self-administration in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 41:615–619
Shaham Y, Klein LC, Alvares K, Grunberg NE (1993) Effect of stress on oral fentanyl consumption in rats in an operant self-administration paradigm. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 46:315–322
Siciliano CA, Noamany H, Chang C-J, Brown AR, Chen X, Leible D, Lee JJ, Wang J, Vernon AN, Vander Weele CM, Kimchi EY, Heiman M, Tye KM (2019) A cortical-brainstem circuit predicts and governs compulsive alcohol drinking. Science 366:1008–1012
Skupio U, Sikora M, Korostynski M, Wawrzczak-Bargiela A, Piechota M, Ficek J, Przewlocki R (2017) Behavioral and transcriptional patterns of protracted opioid self-administration in mice. Addict Biol 22:1802–1816
Smith SG, Davis WM (1974) Punishment of amphetamine and morphine self-administration behavior. Psychol Rec 24:477–480
Sneddon EA, White RD, Radke AK (2019) Sex differences in binge-like and aversion-resistant alcohol drinking in C57BL/6J mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 43:243–249
Sneddon EA, Ramsey OR, Thomas A, Radke AK (2020) Increased responding for alcohol and resistance to aversion in female mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 44:1400–1409
Sustkova-Fiserova M, Puskina N (2019) Ghrelin receptor antagonism of fentanyl-induced conditioned place preference, intravenous self-administration, and dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens in rats. Addict Biol 25:e12845. https://doi.org/10.1111/adb.12845
Thiele TE, Crabbe JC, Boehm SL 2nd (2014) “Drinking in the dark” (DID): a simple mouse model of binge-like alcohol intake. Curr Protoc Neurosci 68:9.49.1–9.4912
Thornton SR, Lohmann AB, Nicholson RA, Smith FL (2000) Fentanyl self-administration in juvenile rats that were tolerant and dependent to fentanyl as infants. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 65:563–570
Varshneya NB, Walentiny DM, Moisa LT, Walker TD, Akinfiresoye LR, Beardsley PM (2019) Opioid-like antinociceptive and locomotor effects of emerging fentanyl-related substances. Neuropharmacology 151:171–179
Veilleux JC, Colvin PJ, Anderson J, York C, Heinz AJ (2010) A review of opioid dependence treatment: pharmacological and psychosocial interventions to treat opioid addiction. Clin Psychol Rev 30:155–166
Vendruscolo LF, Barbier E, Schlosburg JE, Misra KK, Whitfield TW Jr, Logrip ML, Rivier C, Repunte-Canonigo V, Zorrilla EP, Sanna PP, Heilig M, Koob GF (2012) Corticosteroid-dependent plasticity mediates compulsive alcohol drinking in rats. J Neurosci 32:7563–7571
Wade CL, Schuster DJ, Domingo KM, Kitto KF, Fairbanks CA (2008) Supraspinally-administered agmatine attenuates the development of oral fentanyl self-administration. Eur J Pharmacol 587:135–140
Waxman AR, Arout C, Caldwell M, Dahan A, Kest B (2009) Acute and chronic fentanyl administration causes hyperalgesia independently of opioid receptor activity in mice. Neurosci Lett 462:68–72
Wolffgramm J (1991) An ethopharmacological approach to the development of drug addiction. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 15:515–519
Xie Q, Buck LA, Bryant KG, Barker JM (2019) Sex differences in ethanol reward seeking under conflict in mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 43:1556–1566
Zanni G, Featherstone BS, DeSalle MJ, Deutsch HM, Barr GA, Eisch AJ (2019) Development and validation of a novel oral oxycodone self-administration protocol for female and male rats. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/690735
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Marissa Muench and Kristen Schuh for technical assistance. Research is supported by the College of Arts and Sciences, Department of Psychology, Committee on Faculty Research, and the Office of Research and Innovation at Miami University. The authors declare no competing interests in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monroe, S.C., Radke, A.K. Aversion-resistant fentanyl self-administration in mice. Psychopharmacology 238, 699–710 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05722-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05722-6